Article contents
Continuum approaches for modeling radiation-induced self-organization in materials: From the rate theory to the phase field approach
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 February 2018
Abstract
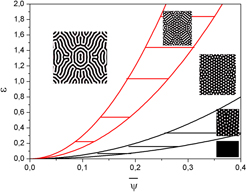
Microstructural patterns resulting from self-organization are responsible for phase transitions and property changes in many materials maintained far from the thermodynamic equilibrium. Understanding the origin and the selection of possible spatiotemporal patterns for dissipative systems, i.e., systems for which the energy is not conserved, is a major theme of research opening doors to many technological applications ranging from plasmonics to metamaterials. Almost forty years after Turing’s seminal paper on patterning, progress on modeling instabilities leading to pattern formation has been achieved. The first part of this work demonstrates that main field approaches succeeded in capturing the underlying physics responsible for the formation of radiation-induced spatiotemporal patterns experimentally observed. The second part of the text highlights the interest of the phase field method, a self-consistent mean field approach, to discuss the evolution of these patterns in a universal picture neglecting specific aspects of radiation-induced dynamics.
Information
- Type
- Reviews
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
Footnotes
This section of Journal of Materials Research is reserved for papers that are reviews of literature in a given area.
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by


