Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Wook Shin, Seung
Ung Sim, Kyu
Pawar, S.M.
Moholkar, A.V.
Ok Jung, In
Ho Yun, Jae
Moon, Jong-Ha
Hyeok Kim, Jin
and
Yong Lee, Jeong
2010.
Effect of a ZnO buffer layer on the properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films grown on Al2O3 (0001) substrates at a low growth temperature of 250°C.
Journal of Crystal Growth,
Vol. 312,
Issue. 9,
p.
1551.
Shin, Seung Wook
Lee, Gyoung Hoon
Moholkar, A.V.
Moon, Jong-Ha
Heo, Gi-Seok
Kim, Tae-Won
Kim, Jin Hyeok
and
Lee, Jeong Yong
2011.
A study on the epitaxy nature and properties of 3wt% Ga-doped epitaxial ZnO thin film on Al2O3 (0001) substrates.
Journal of Crystal Growth,
Vol. 322,
Issue. 1,
p.
51.
Le, Hong Quang
and
Chua, Soo Jin
2011.
Gallium and indium co-doping of epitaxial zinc oxide thin films grown in water at 90 °C.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 12,
p.
125104.
Shin, Seung Wook
Kwon, Ye Bin
Moholkar, A.V.
Heo, Gi-Seok
Jung, In Ok
Moon, Jong-Ha
Kim, Jin Hyeok
and
Lee, Jeong Yong
2011.
Hydrothermally grown ZnO buffer layer for the growth of highly (4wt%) Ga-doped ZnO epitaxial thin films on MgAl2O4 (111) substrates.
Journal of Crystal Growth,
Vol. 322,
Issue. 1,
p.
45.
Kim, Ji-Hong
Roh, Ji-Hyung
Lee, Kyung-Ju
Moon, Sung-Joon
Kim, Jae-Won
Do, Kang-Min
Moon, Byung-Moo
and
Koo, Sang-Mo
2011.
Growth and electrical properties of nonpolar and polar Ga-doped ZnO thin films on LaAlO3 and SrTiO3 substrates.
Journal of Crystal Growth,
Vol. 334,
Issue. 1,
p.
72.
Shin, Seung Wook
Agawane, G.L.
Kim, In Young
Kwon, Ye Bin
Jung, In Ok
Gang, Myeng Gil
Moholkar, A.V.
Moon, Jong-Ha
Kim, Jin Hyeok
and
Lee, Jeong Yong
2012.
Low temperature epitaxial growth and characterization of Ga-doped ZnO thin films on Al2O3 (0001) substrates prepared with different buffer layers.
Applied Surface Science,
Vol. 258,
Issue. 12,
p.
5073.
AlKahlout, Amal
2013.
A wet chemical preparation of transparent conducting thin films of Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles.
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology,
Vol. 67,
Issue. 2,
p.
331.
김, 인영
김, 진혁
신, 승욱
김, 민성
윤, 재호
허, 기석
정, 채환
문, 종하
and
이, 정용
2013.
Effect of Sputtering Powers on Mg and Ga Co-Doped ZnO Thin Films with Transparent Conducting Characteristics.
Korean Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 3,
p.
155~160.
Shin, Seung Wook
Agawane, G.L.
Kim, In Young
Jo, Seung Hyun
Kim, Min Sung
Heo, Gi-Seok
Kim, Jin Hyeok
and
Lee, Jeong Yong
2013.
Development of transparent conductive Mg and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films: Effect of Mg concentration.
Surface and Coatings Technology,
Vol. 231,
Issue. ,
p.
364.
Shin, Seung Wook
Kim, In Young
Jeon, Ki Seok
Heo, Jae Yeong
Heo, Gi-Seok
Patil, P.S.
Kim, Jin Hyeok
and
Lee, Jeong Yong
2013.
Wide band gap characteristic of quaternary and flexible Mg and Ga co-doped ZnO transparent conductive thin films.
Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 3,
p.
262.
Liu, Yanli
Li, Yufang
Zeng, Haibo
and
Xu, Xijin
2013.
ZnO‐Based Transparent Conductive Thin Films: Doping, Performance, and Processing.
Journal of Nanomaterials,
Vol. 2013,
Issue. 1,
Shin, Seung Wook
Kim, In Young
Kishor, G.V.
Yoo, Yeong Yung
Kim, Young Baek
Heo, Jae Yeong
Heo, Gi-Seok
Patil, P.S.
Kim, Jin Hyeok
and
Lee, Jeong Yong
2014.
Development of flexible Mg and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films with wide band gap energy and transparent conductive characteristics.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds,
Vol. 585,
Issue. ,
p.
608.
Serrao, Felcy Jyothi
and
Dharmaprakash, S. M.
2016.
Sol ageing effect on the structural, optical and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films.
Materials Technology,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 8,
p.
443.
Song, Huaping
Makino, Hisao
Nomoto, Junichi
Yamamoto, Naoki
and
Yamamoto, Tetsuya
2018.
Improved moisture stability of thin Ga-doped ZnO films by indium codoping.
Applied Surface Science,
Vol. 457,
Issue. ,
p.
241.
Tareq, Shahad
Kirkil, Gokhan
and
Özuğur Uysal, Bengü
2023.
Superior Conductivity of Transparent ZnO/MoS2 Composite Films for Optoelectronic and Solar Cell Applications.
Gels,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 11,
p.
906.
Hossein-Babaei, Faramarz
and
Alizadeh, Armin
2024.
Contact resistances between ZnO and Ti, Al, Zn, and Bi: correlation with the density of states at Fermi energies.
Journal of Materials Chemistry C,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 18,
p.
6495.
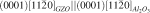 . The structural images from scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy showed that the GZO thin films on glass substrates had a rougher surface morphology than those on Al2O3 (0001) substrates. The electrical resistivity of 1000 nm-thick GZO thin films grown on glass and Al2O3 (0001) substrates was 3.04 × 10−4 Ωcm and 1.50 × 10−4 Ωcm, respectively. It was also found that the electrical resistivity difference between the films on the two substrates decreased from 9.48 × 10−4 Ωcm to 1.45 × 10−4 Ωcm with increasing the film thickness from 100 nm to 1000 nm.
. The structural images from scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy showed that the GZO thin films on glass substrates had a rougher surface morphology than those on Al2O3 (0001) substrates. The electrical resistivity of 1000 nm-thick GZO thin films grown on glass and Al2O3 (0001) substrates was 3.04 × 10−4 Ωcm and 1.50 × 10−4 Ωcm, respectively. It was also found that the electrical resistivity difference between the films on the two substrates decreased from 9.48 × 10−4 Ωcm to 1.45 × 10−4 Ωcm with increasing the film thickness from 100 nm to 1000 nm.