Article contents
A suspension of conducting particles in a magnetic field – the particle stress
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 September 2020
Abstract
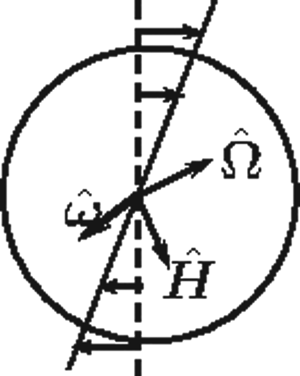
When a suspension of conducting particles is subjected to a shear flow, there is particle rotation due to the fluid vorticity. A conductor rotating in a uniform magnetic field experiences a torque due to eddy currents both parallel and perpendicular to the direction of rotation. Eddy currents induce a magnetic moment in a conducting particle, which disturbs the magnetic field around the particle. The effect of the Maxwell stress due to the magnetic field disturbance on the rheology of a dilute suspension is calculated in a manner similar to the Einstein viscosity for a suspension of rigid particles. The expression for the stress tensor contains three symmetric stress coefficients, and two normal stress coefficients, in addition to the three antisymmetric stress coefficients calculated in Kumaran (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 871, 2019, pp. 139–185). The stress coefficients depend on the relative orientation of the vorticity and magnetic field and two dimensionless parameters,  $\beta$, the product of the vorticity and current relaxation time, and
$\beta$, the product of the vorticity and current relaxation time, and  $\Sigma$, the ratio of the magnetic and hydrodynamic torques. In the ‘linear’ approximation, where only terms linear in the particle magnetic moment are retained, the particle stress depends on two dimensionless functions. For the physically important limit
$\Sigma$, the ratio of the magnetic and hydrodynamic torques. In the ‘linear’ approximation, where only terms linear in the particle magnetic moment are retained, the particle stress depends on two dimensionless functions. For the physically important limit  $\beta \ll 1$, as well as the limit
$\beta \ll 1$, as well as the limit  $\beta \gg 1$ and
$\beta \gg 1$ and  $\Sigma \gg 1$, these two functions are independent of the vorticity, and depend only on the magnetic field and material properties.
$\Sigma \gg 1$, these two functions are independent of the vorticity, and depend only on the magnetic field and material properties.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2020. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by


