Article contents
Stochastic Lagrangian dynamics of vorticity. Part 2. Application to near-wall channel-flow turbulence
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 August 2020
Abstract
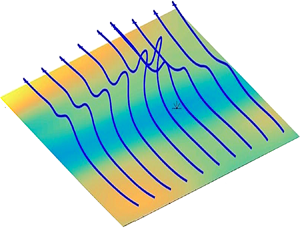
We use an online database of a turbulent channel-flow simulation at  $Re_\tau =1000$ (Graham et al. J. Turbul., vol. 17, issue 2, 2016, pp. 181–215) to determine the origin of vorticity in the near-wall buffer layer. Following an experimental study of Sheng et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 633, 2009, pp.17–60), we identify typical ‘ejection’ and ‘sweep’ events in the buffer layer by local minima/maxima of the wall stress. In contrast to their conjecture, however, we find that vortex lifting from the wall is not a discrete event requiring
$Re_\tau =1000$ (Graham et al. J. Turbul., vol. 17, issue 2, 2016, pp. 181–215) to determine the origin of vorticity in the near-wall buffer layer. Following an experimental study of Sheng et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 633, 2009, pp.17–60), we identify typical ‘ejection’ and ‘sweep’ events in the buffer layer by local minima/maxima of the wall stress. In contrast to their conjecture, however, we find that vortex lifting from the wall is not a discrete event requiring  $\sim$1 viscous time and
$\sim$1 viscous time and  $\sim$10 wall units, but is instead a distributed process over a space–time region at least
$\sim$10 wall units, but is instead a distributed process over a space–time region at least  $1\sim 2$ orders of magnitude larger in extent. To reach this conclusion, we exploit a rigorous mathematical theory of vorticity dynamics for Navier–Stokes solutions, in terms of stochastic Lagrangian flows and stochastic Cauchy invariants, conserved on average backward in time. This theory yields exact expressions for vorticity inside the flow domain in terms of vorticity at the wall, as transported by viscous diffusion and by nonlinear advection, stretching and rotation. We show that Lagrangian chaos observed in the buffer layer can be reconciled with saturated vorticity magnitude by ‘virtual reconnection’: although the Eulerian vorticity field in the viscous sublayer has a single sign of spanwise component, opposite signs of Lagrangian vorticity evolve by rotation and cancel by viscous destruction. Our analysis reveals many unifying features of classical fluids and quantum superfluids. We argue that ‘bundles’ of quantized vortices in superfluid turbulence will also exhibit stochastic Lagrangian dynamics and satisfy stochastic conservation laws resulting from particle relabelling symmetry.
$1\sim 2$ orders of magnitude larger in extent. To reach this conclusion, we exploit a rigorous mathematical theory of vorticity dynamics for Navier–Stokes solutions, in terms of stochastic Lagrangian flows and stochastic Cauchy invariants, conserved on average backward in time. This theory yields exact expressions for vorticity inside the flow domain in terms of vorticity at the wall, as transported by viscous diffusion and by nonlinear advection, stretching and rotation. We show that Lagrangian chaos observed in the buffer layer can be reconciled with saturated vorticity magnitude by ‘virtual reconnection’: although the Eulerian vorticity field in the viscous sublayer has a single sign of spanwise component, opposite signs of Lagrangian vorticity evolve by rotation and cancel by viscous destruction. Our analysis reveals many unifying features of classical fluids and quantum superfluids. We argue that ‘bundles’ of quantized vortices in superfluid turbulence will also exhibit stochastic Lagrangian dynamics and satisfy stochastic conservation laws resulting from particle relabelling symmetry.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2020. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 15
- Cited by

