Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Barrois, O.
Gillet, N.
and
Aubert, J.
2017.
Contributions to the geomagnetic secular variation from a reanalysis of core surface dynamics.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 211,
Issue. 1,
p.
50.
Maffei, S.
and
Jackson, A.
2017.
Kinematic validation of a quasi-geostrophic model for the fast dynamics in the Earth’s outer core.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 210,
Issue. 3,
p.
1772.
Jaupart, Etienne
and
Buffett, Bruce
2017.
Generation of MAC waves by convection in Earth's core.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 209,
Issue. 2,
p.
1326.
Currie, Laura K.
and
Browning, Matthew K.
2017.
The Magnitude of Viscous Dissipation in Strongly Stratified Two-dimensional Convection.
The Astrophysical Journal Letters,
Vol. 845,
Issue. 2,
p.
L17.
Aurnou, J. M.
and
King, E. M.
2017.
The cross-over to magnetostrophic convection in planetary dynamo systems.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 473,
Issue. 2199,
p.
20160731.
Starchenko, S. V.
2017.
Energy geodynamo parameters compatible with analytical, numerical, paleomagnetic models and observations.
Izvestiya, Physics of the Solid Earth,
Vol. 53,
Issue. 6,
p.
908.
Schaeffer, N.
Jault, D.
Nataf, H.-C.
and
Fournier, A.
2017.
Turbulent geodynamo simulations: a leap towards Earth’s core.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 211,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
More, Colin
and
Dumberry, Mathieu
2018.
Convectively driven decadal zonal accelerations in Earth’s fluid core.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 213,
Issue. 1,
p.
434.
Lesur, Vincent
Wardinski, Ingo
Baerenzung, Julien
and
Holschneider, Matthias
2018.
On the frequency spectra of the core magnetic field Gauss coefficients.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,
Vol. 276,
Issue. ,
p.
145.
Calkins, Michael A.
2018.
Quasi-geostrophic dynamo theory.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,
Vol. 276,
Issue. ,
p.
182.
Badro, James
Aubert, Julien
Hirose, Kei
Nomura, Ryuichi
Blanchard, Ingrid
Borensztajn, Stephan
and
Siebert, Julien
2018.
Magnesium Partitioning Between Earth's Mantle and Core and its Potential to Drive an Early Exsolution Geodynamo.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 24,
Ireland, Lewis G.
and
Browning, Matthew K.
2018.
The Radius and Entropy of a Magnetized, Rotating, Fully Convective Star: Analysis with Depth-dependent Mixing Length Theories.
The Astrophysical Journal,
Vol. 856,
Issue. 2,
p.
132.
Sreenivasan, Binod
and
Kar, Subhajit
2018.
Scale dependence of kinetic helicity and selection of the axial dipole in rapidly rotating dynamos.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 9,
Vidal, Jérémie
Cébron, David
Schaeffer, Nathanaël
and
Hollerbach, Rainer
2018.
Magnetic fields driven by tidal mixing in radiative stars.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,
Vol. 475,
Issue. 4,
p.
4579.
Petitdemange, Ludovic
2018.
Systematic parameter study of dynamo bifurcations in geodynamo simulations.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,
Vol. 277,
Issue. ,
p.
113.
Aubert, Julien
2018.
Geomagnetic acceleration and rapid hydromagnetic wave dynamics in advanced numerical simulations of the geodynamo.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 214,
Issue. 1,
p.
531.
Cao, Hao
Yadav, Rakesh K.
and
Aurnou, Jonathan M.
2018.
Geomagnetic polar minima do not arise from steady meridional circulation.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 115,
Issue. 44,
p.
11186.
Driscoll, Peter E.
and
Wilson, Cian
2018.
Paleomagnetic Biases Inferred From Numerical Dynamos and the Search for Geodynamo Evolution.
Frontiers in Earth Science,
Vol. 6,
Issue. ,
Afanasyev, Y. D.
2018.
High‐Latitude Westward Jets in the Earth's Outer Core Due to Small‐Scale Convection.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 15,
p.
7454.
Hardy, Colin M.
Livermore, Philip W.
Niesen, Jitse
Luo, Jiawen
and
Li, Kuan
2018.
Determination of the instantaneous geostrophic flow within the three-dimensional magnetostrophic regime.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 474,
Issue. 2218,
p.
20180412.
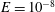 $E=10^{-8}$ . We obtain strong-field convective dynamos approaching the MAC balance and a Taylor state to an unprecedented degree of accuracy. The physical connection between classical models and asymptotic conditions is shown to be devoid of abrupt transitions, demonstrating the asymptotic relevance of classical numerical dynamo mechanisms. The fields of the system are confirmed to follow diffusivity-free, power-based scaling laws along the path.
$E=10^{-8}$ . We obtain strong-field convective dynamos approaching the MAC balance and a Taylor state to an unprecedented degree of accuracy. The physical connection between classical models and asymptotic conditions is shown to be devoid of abrupt transitions, demonstrating the asymptotic relevance of classical numerical dynamo mechanisms. The fields of the system are confirmed to follow diffusivity-free, power-based scaling laws along the path.

