Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Marchioli, Cristian
2017.
Particles in Wall-Bounded Turbulent Flows: Deposition, Re-Suspension and Agglomeration.
Vol. 571,
Issue. ,
p.
151.
Yang, Kun
Zhao, Lihao
and
Andersson, Helge I.
2017.
Preferential particle concentration in wall-bounded turbulence with zero skin friction.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 11,
Milici, B.
2018.
Modification of particle laden near-wall turbulence in a vertical channel bounded by rough walls.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 103,
Issue. ,
p.
151.
Yang, Kun
Zhao, Lihao
and
Andersson, Helge I.
2018.
Particle segregation in turbulent Couette–Poiseuille flow with vanishing wall shear.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 98,
Issue. ,
p.
45.
Yuan, Wenjun
Zhao, Lihao
Challabotla, Niranjan Reddy
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Deng, Jianqiang
2018.
On wall-normal motions of inertial spheroids in vertical turbulent channel flows.
Acta Mechanica,
Vol. 229,
Issue. 7,
p.
2947.
Sweet, James
Richter, David H.
and
Thain, Douglas
2018.
GPU acceleration of Eulerian–Lagrangian particle-laden turbulent flow simulations.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 99,
Issue. ,
p.
437.
Fong, Kee Onn
Amili, Omid
and
Coletti, Filippo
2019.
Velocity and spatial distribution of inertial particles in a turbulent channel flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 872,
Issue. ,
p.
367.
Jie, Yucheng
Xu, Chunxiao
Dawson, James R.
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Zhao, Lihao
2019.
Influence of the quiescent core on tracer spheroidal particle dynamics in turbulent channel flow.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 7,
p.
424.
Mortimer, L. F.
and
Fairweather, M.
2020.
Density ratio effects on the topology of coherent turbulent structures in two-way coupled particle-laden channel flows.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 10,
Mahananda, Minakshee
Hanmaiahgari, Prashanth Reddy
and
Balachandar, Ram
2020.
Advanced Numerical Methods in Foundation Engineering.
p.
133.
Johnson, Perry L.
Bassenne, Maxime
and
Moin, Parviz
2020.
Turbophoresis of small inertial particles: theoretical considerations and application to wall-modelled large-eddy simulations.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 883,
Issue. ,
Pan, Qingqing
Xiang, Hong
Wang, Ze
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Zhao, Lihao
2020.
Kinetic energy balance in turbulent particle-laden channel flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 7,
Berk, Tim
and
Coletti, Filippo
2020.
Transport of inertial particles in high-Reynolds-number turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 903,
Issue. ,
Chiarini, Alessandro
and
Quadrio, Maurizio
2021.
The light/dark cycle of microalgae in a thin-layer photobioreactor.
Journal of Applied Phycology,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 1,
p.
183.
Baker, Lucia J.
and
Coletti, Filippo
2021.
Particle–fluid–wall interaction of inertial spherical particles in a turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 908,
Issue. ,
Wang, Ping
Li, Jinchi
and
Zheng, Xiaojing
2021.
The effect of gravity on turbulence modulation in particle-laden horizontal open channel flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 8,
Wang, Ping
Wei, Qingqing
and
Zheng, Xiaojing
2021.
Differences of turbulence modulation by heavy particles on solid wall and erodible bed surface.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 11,
Michel, A.
and
Arcen, B.
2021.
Long time statistics of prolate spheroids dynamics in a turbulent channel flow.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 135,
Issue. ,
p.
103525.
Michel, A.
and
Arcen, B.
2021.
Reynolds number effect on the concentration and preferential orientation of inertial ellipsoids.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 11,
Jie, Yucheng
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Zhao, Lihao
2021.
Effects of the quiescent core in turbulent channel flow on transport and clustering of inertial particles.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 140,
Issue. ,
p.
103627.
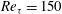 $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}\mathit{Re}_{\tau } = 150$ to
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}\mathit{Re}_{\tau } = 150$ to 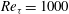 $\mathit{Re}_{\tau } = 1000$ . Lagrangian particle tracking is used to study the motion of six different particle sets, described by a Stokes number in the range
$\mathit{Re}_{\tau } = 1000$ . Lagrangian particle tracking is used to study the motion of six different particle sets, described by a Stokes number in the range 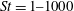 $\mathit{St} = 1\text {--}1000$ . At all Reynolds numbers a strong segregation in the near-wall region is observed for particles characterized by intermediate Stokes number, in the range
$\mathit{St} = 1\text {--}1000$ . At all Reynolds numbers a strong segregation in the near-wall region is observed for particles characterized by intermediate Stokes number, in the range 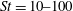 $\mathit{St} =10\text {--}100$ . The wall-normal concentration profiles of such particles collapse in inner scaling, thus suggesting the independence of the turbophoretic drift from the large-scale outer motions. This observation is also supported by the spatial organization of the suspended phase in the inner layer, which is found to be universal with the Reynolds number. The deposition rate coefficient increases with
$\mathit{St} =10\text {--}100$ . The wall-normal concentration profiles of such particles collapse in inner scaling, thus suggesting the independence of the turbophoretic drift from the large-scale outer motions. This observation is also supported by the spatial organization of the suspended phase in the inner layer, which is found to be universal with the Reynolds number. The deposition rate coefficient increases with 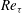 $\mathit{Re}_{\tau }$ for a given
$\mathit{Re}_{\tau }$ for a given 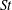 $\mathit{St}$ . Suitable inner and outer scalings are proposed to collapse the deposition curves across the available ranges of Reynolds and Stokes numbers for the different deposition regimes.
$\mathit{St}$ . Suitable inner and outer scalings are proposed to collapse the deposition curves across the available ranges of Reynolds and Stokes numbers for the different deposition regimes.
