No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 June 2025
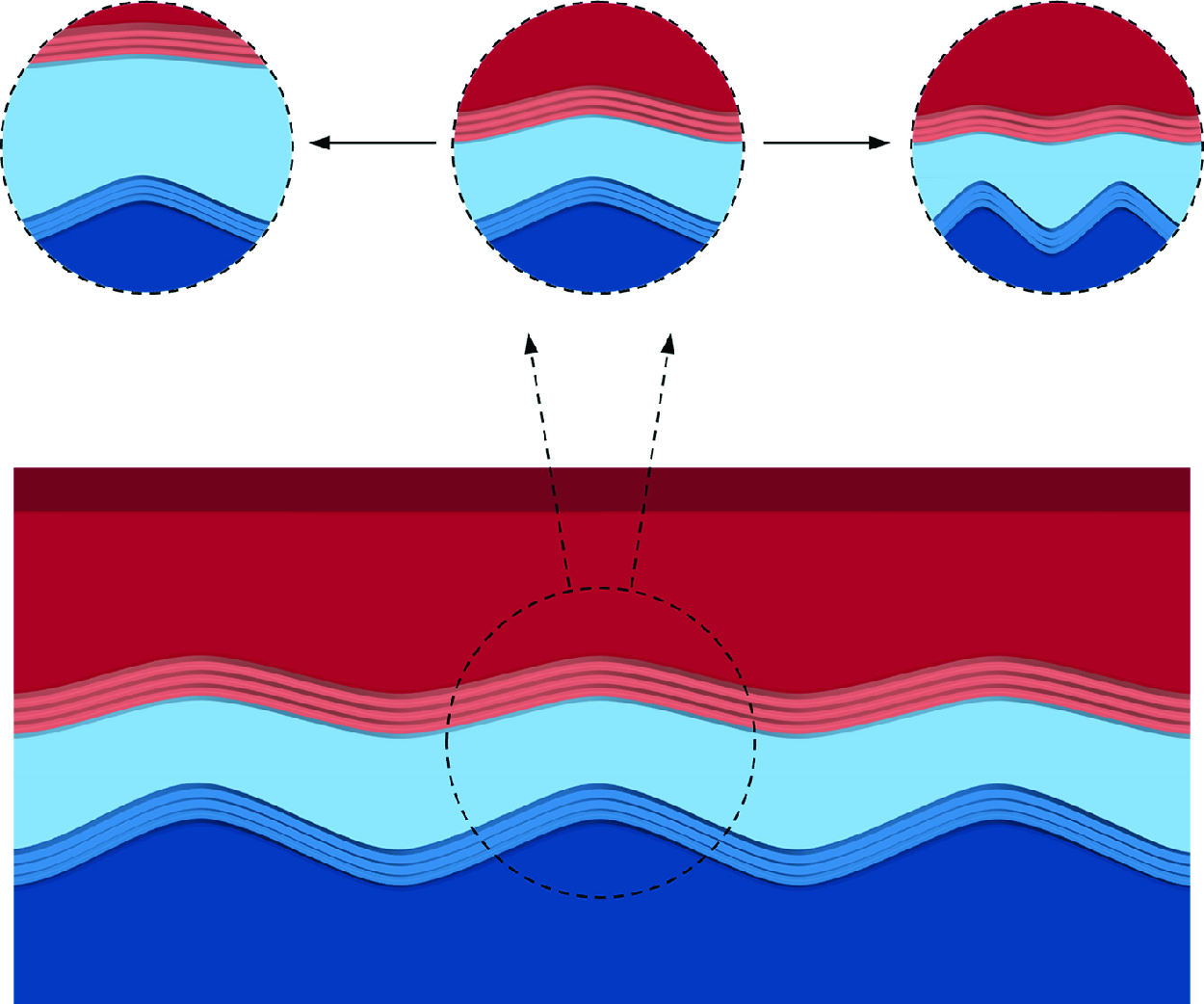
A linear stability model based on a phase-field method is established to study the formation of ripples on the ice surface. The pattern on horizontal ice surfaces, e.g. glaciers and frozen lakes, is found to be originating from a gravity-driven instability by studying ice–water–air flows with a range of water and ice thicknesses. Contrary to gravity, surface tension and viscosity act to suppress the instability. The results demonstrate that a larger value of either water thickness or ice thickness corresponds to a longer dominant wavelength of the pattern, and a favourable wavelength of 90 mm is predicted, in agreement with observations from nature. Furthermore, the profiles of the most unstable perturbations are found to be with two peaks at the ice–water and water–air interfaces whose ratio decreases exponentially with the water thickness and wavenumber.