Article contents
Non-monotonic salt dependence of electro-osmotic flow in pH-regulated nanochannels
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 March 2025
Abstract
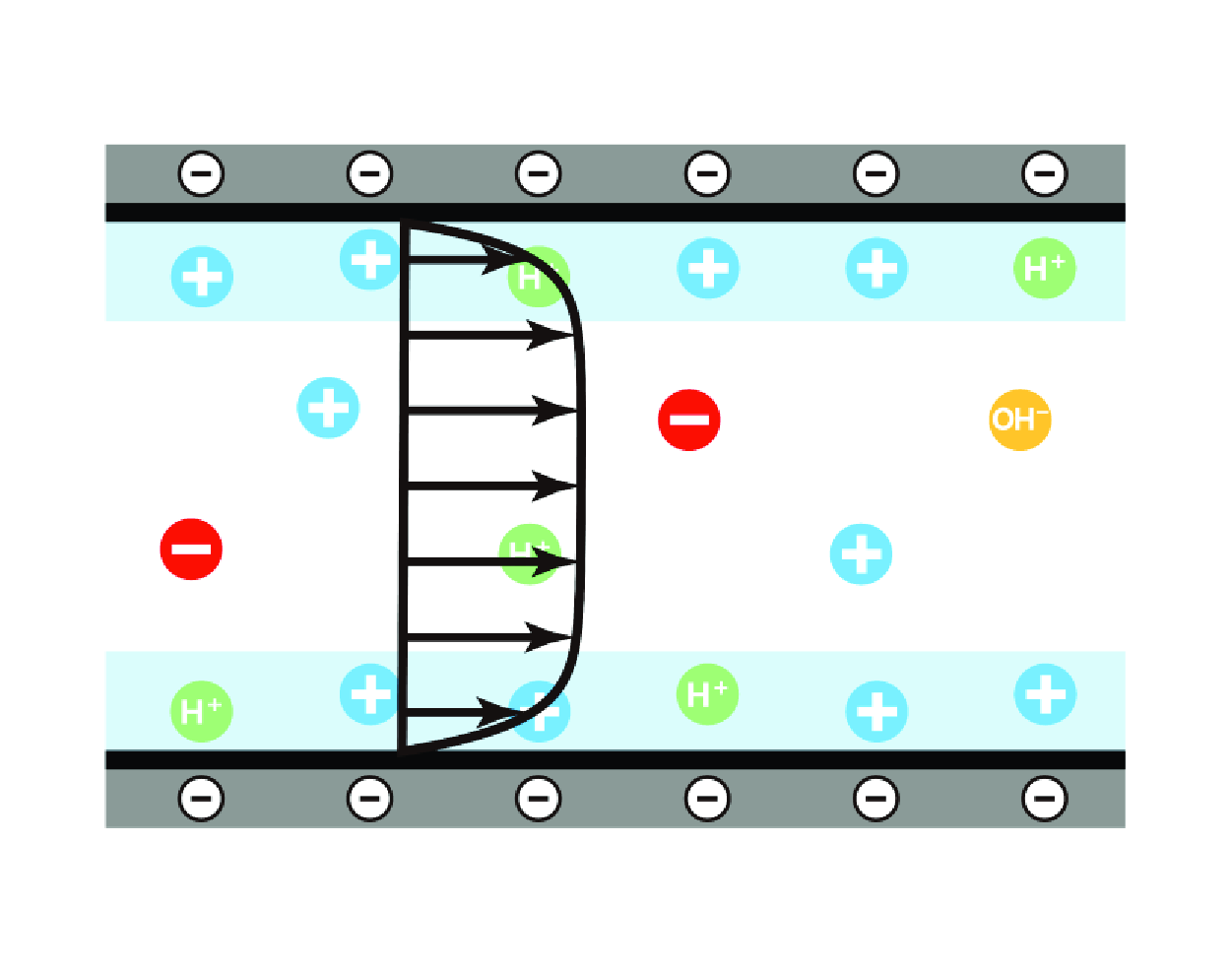
Electro-osmotic flow (EOF) in nanochannels exhibits a puzzling non-monotonic dependence on salt concentration, which contrasts with observations in microchannels and remains not fully understood. In this work, we address this phenomenon through a theoretical investigation of EOF in  $\mathrm{pH}$-regulated channels. New analytical approximations for electrostatic potential, EOF profile and electro-osmotic mobility beyond the Debye–Hückel limit are derived through asymptotic analysis. Our findings reveal that the surface electrostatic potential is independent of the channel size only when the half-channel size exceeds the Gouy–Chapman length. In contrast, surface ionization and net charge distribution play more crucial roles in EOF at the nanoscale, as they govern both the magnitude and the spatial distribution of the Coulomb driving force. As salt concentration increases, EOF velocity initially rises due to enhanced surface ionization, followed by a decline attributed to increased wall shear stress. This work provides key insights for EOF applications in nanofluidics and biomedical devices, and deepens the understanding of electrokinetic phenomena influenced by
$\mathrm{pH}$-regulated channels. New analytical approximations for electrostatic potential, EOF profile and electro-osmotic mobility beyond the Debye–Hückel limit are derived through asymptotic analysis. Our findings reveal that the surface electrostatic potential is independent of the channel size only when the half-channel size exceeds the Gouy–Chapman length. In contrast, surface ionization and net charge distribution play more crucial roles in EOF at the nanoscale, as they govern both the magnitude and the spatial distribution of the Coulomb driving force. As salt concentration increases, EOF velocity initially rises due to enhanced surface ionization, followed by a decline attributed to increased wall shear stress. This work provides key insights for EOF applications in nanofluidics and biomedical devices, and deepens the understanding of electrokinetic phenomena influenced by  $\mathrm{pH}$-regulation effects.
$\mathrm{pH}$-regulation effects.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Rapids
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 1
- Cited by


