Article contents
Lagrangian dynamics and heat transfer in porous-media convection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 April 2021
Abstract
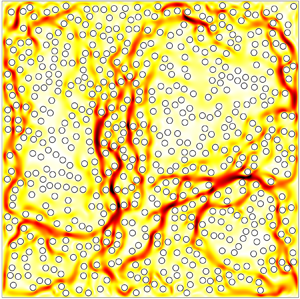
We report a numerical study of Rayleigh–Bénard convection through random porous media using pore-scale modelling, focusing on the Lagrangian dynamics of fluid particles and heat transfer for varied porosities  $\phi$. Due to the interaction between the porous medium and the coherent flow structures, the flow is found to be highly heterogeneous, consisting of convection channels with strong flow strength and stagnant regions with low velocities. The modifications of flow field due to porous structure have a significant influence on the dynamics of fluid particles. Evaluation of the particle displacement along the trajectory reveals the emergence of anomalous transport for long times as
$\phi$. Due to the interaction between the porous medium and the coherent flow structures, the flow is found to be highly heterogeneous, consisting of convection channels with strong flow strength and stagnant regions with low velocities. The modifications of flow field due to porous structure have a significant influence on the dynamics of fluid particles. Evaluation of the particle displacement along the trajectory reveals the emergence of anomalous transport for long times as  $\phi$ is decreased, which is associated with the long-time correlation of Lagrangian velocity of the fluid. As porosity is decreased, the cross-correlation between the vertical velocity and temperature fluctuation is enhanced, which reveals a mechanism to enhance the heat transfer in porous-media convection.
$\phi$ is decreased, which is associated with the long-time correlation of Lagrangian velocity of the fluid. As porosity is decreased, the cross-correlation between the vertical velocity and temperature fluctuation is enhanced, which reveals a mechanism to enhance the heat transfer in porous-media convection.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by


