Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Švančara, P.
Pavelka, M.
and
La Mantia, M.
2020.
An experimental study of turbulent vortex rings in superfluid 4He.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 889,
Issue. ,
Galantucci, Luca
Baggaley, Andrew W.
Barenghi, Carlo F.
and
Krstulovic, Giorgio
2020.
A new self-consistent approach of quantum turbulence in superfluid helium.
The European Physical Journal Plus,
Vol. 135,
Issue. 7,
Polanco, Juan Ignacio
and
Krstulovic, Giorgio
2020.
Inhomogeneous distribution of particles in coflow and counterflow quantum turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 3,
Proment, Davide
and
Krstulovic, Giorgio
2020.
Matching theory to characterize sound emission during vortex reconnection in quantum fluids.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 10,
Outrata, O.
Pavelka, M.
Hron, J.
La Mantia, M.
Polanco, J.I.
and
Krstulovic, G.
2021.
On the determination of vortex ring vorticity using Lagrangian particles.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 924,
Issue. ,
Zhang, Qingqing
and
Xiao, Zuoli
2021.
On the time irreversibility of compressible turbulence reflected by particles of various inertias.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 3,
Švančara, P.
Duda, D.
Hrubcová, P.
Rotter, M.
Skrbek, L.
La Mantia, M.
Durozoy, E.
Diribarne, P.
Rousset, B.
Bourgoin, M.
and
Gibert, M.
2021.
Ubiquity of particle–vortex interactions in turbulent counterflow of superfluid helium.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 911,
Issue. ,
Polanco, Juan Ignacio
Müller, Nicolás P.
and
Krstulovic, Giorgio
2021.
Vortex clustering, polarisation and circulation intermittency in classical and quantum turbulence.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 1,
Švančara, P.
and
La Mantia, M.
2022.
Coherent propagation of vortex rings at extremely high Reynolds numbers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 953,
Issue. ,
Kiran, Kolluru Venkata
Gupta, Anupam
Verma, Akhilesh Kumar
and
Pandit, Rahul
2023.
Irreversibility in bacterial turbulence: Insights from the mean-bacterial-velocity model.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 2,
Bret, Clément
Chartier, Jérôme
Diribarne, Pantxo
Duplat, Jérôme
and
Rousset, Bernard
2023.
Controlled spherical deuterium droplets as Lagrangian tracers for cryogenic turbulence experiments.
Review of Scientific Instruments,
Vol. 94,
Issue. 10,
Shukla, Sanjay
Verma, Akhilesh Kumar
Shukla, Vishwanath
Bhatnagar, Akshay
and
Pandit, Rahul
2023.
Inertial particles in superfluid turbulence: Coflow and counterflow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 1,
Bret, Clément
Diribarne, Pantxo
Duplat, Jérôme
and
Rousset, Bernard
2025.
Kolmogorov cascade as the governing mechanism for intervortex spacing in quantum turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 9,
Blaha, Jiří
Xu, Ling
and
La Mantia, Marco
2025.
Newtonian-like behaviour of starting vortex flow in superfluid helium at high Reynolds numbers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 1015,
Issue. ,
Pandit, Rahul
and
Kiran, Kolluru Venkata
2025.
Particles and fields in minimal hydrodynamic models for active turbulence.
Europhysics Letters,
Vol. 150,
Issue. 1,
p.
13001.
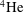 $^{4}\text{He}$ are strikingly different from those occurring in turbulent flows of viscous fluids. We argue that the result can be related to the role played by quantized vortices in this unique type of turbulence. The flow-induced motions of relatively small particles suspended in the liquid reveal that, for scales of the order of the mean distance between the vortices, the particles do not tend on average to decelerate faster than they accelerate, whereas, at larger scales, a classical-like asymmetry is recovered. It follows that, in the range of investigated parameters, flight-crash events are less apparent than in classical turbulence. We specifically link the outcome to the time symmetry of quantized vortex reconnections observed at scales comparable to the typical particle size.
$^{4}\text{He}$ are strikingly different from those occurring in turbulent flows of viscous fluids. We argue that the result can be related to the role played by quantized vortices in this unique type of turbulence. The flow-induced motions of relatively small particles suspended in the liquid reveal that, for scales of the order of the mean distance between the vortices, the particles do not tend on average to decelerate faster than they accelerate, whereas, at larger scales, a classical-like asymmetry is recovered. It follows that, in the range of investigated parameters, flight-crash events are less apparent than in classical turbulence. We specifically link the outcome to the time symmetry of quantized vortex reconnections observed at scales comparable to the typical particle size.
