Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Goudar, Manu V.
Breugem, W.-P.
and
Elsinga, G. E.
2016.
Auto-generation in wall turbulence by the interaction of weak eddies.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 3,
Schneiders, Jan F. G.
Scarano, Fulvio
and
Elsinga, Gerrit E.
2017.
Resolving vorticity and dissipation in a turbulent boundary layer by tomographic PTV and VIC+.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 4,
Wu, Xiaohua
Moin, Parviz
Wallace, James M.
Skarda, Jinhie
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
and
Hickey, Jean-Pierre
2017.
Transitional–turbulent spots and turbulent–turbulent spots in boundary layers.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 114,
Issue. 27,
Tan, Yan Ming
and
Longmire, Ellen K.
2017.
Recovery of vortex packet organization in perturbed turbulent boundary layers.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Lee, Jae Hwa
2017.
Large-scale motions in turbulent boundary layers subjected to adverse pressure gradients.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 810,
Issue. ,
p.
323.
Schneiders, Jan F G
and
Sciacchitano, Andrea
2017.
Track benchmarking method for uncertainty quantification of particle tracking velocimetry interpolations.
Measurement Science and Technology,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 6,
p.
065302.
Marusic, Ivan
Baars, Woutijn J.
and
Hutchins, Nicholas
2017.
Scaling of the streamwise turbulence intensity in the context of inner-outer interactions in wall turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Deng, Sichao
Pan, Chong
Wang, Jinjun
and
He, Guosheng
2018.
On the spatial organization of hairpin packets in a turbulent boundary layer at low-to-moderate Reynolds number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 844,
Issue. ,
p.
635.
Li, Shan
Jiang, Nan
Yang, Shaoqiong
Huang, Yongxiang
and
Wu, Yanhua
2018.
Coherent structures over riblets in turbulent boundary layer studied by combining time-resolved particle image velocimetry (TRPIV), proper orthogonal decomposition (POD), and finite-time Lyapunov exponent (FTLE).
Chinese Physics B,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 10,
p.
104701.
Fiscaletti, D.
de Kat, R.
and
Ganapathisubramani, B.
2018.
Spatial–spectral characteristics of momentum transport in a turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 836,
Issue. ,
p.
599.
Discetti, Stefano
and
Coletti, Filippo
2018.
Volumetric velocimetry for fluid flows.
Measurement Science and Technology,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 4,
p.
042001.
Kim, Hyoungsoo
and
Stone, Howard A.
2018.
Direct measurement of selective evaporation of binary mixture droplets by dissolving materials.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 850,
Issue. ,
p.
769.
Bernard, Peter S.
2019.
On the inherent bias of swirling strength in defining vortical structure.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 3,
Marusic, Ivan
and
Monty, Jason P.
2019.
Attached Eddy Model of Wall Turbulence.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 1,
p.
49.
Wang, Chengyue
Gao, Qi
Wang, Jinjun
Wang, Biao
and
Pan, Chong
2019.
Experimental study on dominant vortex structures in near-wall region of turbulent boundary layer based on tomographic particle image velocimetry.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 874,
Issue. ,
p.
426.
Jiang, Xianyang
2019.
Revisiting coherent structures in low-speed turbulent boundary layers.
Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,
Vol. 40,
Issue. 2,
p.
261.
Motoori, Yutaro
and
Goto, Susumu
2019.
Generation mechanism of a hierarchy of vortices in a turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 865,
Issue. ,
p.
1085.
Ling, Y.
Fuster, D.
Tryggvason, G.
and
Zaleski, S.
2019.
A two-phase mixing layer between parallel gas and liquid streams: multiphase turbulence statistics and influence of interfacial instability.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 859,
Issue. ,
p.
268.
Martins, Fabio J.W.A.
Foucaut, Jean-Marc
Stanislas, Michel
and
Azevedo, Luis Fernando A.
2019.
Characterization of near-wall structures in the log-region of a turbulent boundary layer by means of conditional statistics of tomographic PIV data.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
Vol. 105,
Issue. ,
p.
191.
Motoori, Yutaro
and
Goto, Susumu
2020.
Hairpin vortices in the largest scale of turbulent boundary layers.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 86,
Issue. ,
p.
108658.
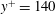 $y^{+}=140$ , where
$y^{+}=140$ , where 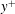 $y^{+}$ is the wall-normal distance in wall units. Instantaneous visualizations of the flow reveal near-wall low-speed streaks with associated quasi-streamwise vortices, retrograde inverted arch vortices, hairpin vortices and hairpin packets. The hairpin heads are observed as close to the wall as
$y^{+}$ is the wall-normal distance in wall units. Instantaneous visualizations of the flow reveal near-wall low-speed streaks with associated quasi-streamwise vortices, retrograde inverted arch vortices, hairpin vortices and hairpin packets. The hairpin heads are observed as close to the wall as 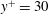 $y^{+}=30$ . Examples of hairpin packet evolution reveal the development of new hairpin vortices, which are created upstream and close to the wall in a manner consistent with the auto-generation model (Zhou et al., J. Fluid Mech., vol. 387, 1999, pp. 353–396). The development of the new hairpin appears to be initiated by an approaching sweep event, which perturbs the shear layer associated with the initial packet. The shear layer rolls up, thereby forming the new hairpin head. The head subsequently connects to existing streamwise vortices and develops into a hairpin. The time scale associated with the hairpin auto-generation is 20–30 wall units of time. This demonstrates that hairpins can be created over short distances within a developed turbulent boundary layer, implying that they are not simply remnants of the laminar-to-turbulent transition process far upstream.
$y^{+}=30$ . Examples of hairpin packet evolution reveal the development of new hairpin vortices, which are created upstream and close to the wall in a manner consistent with the auto-generation model (Zhou et al., J. Fluid Mech., vol. 387, 1999, pp. 353–396). The development of the new hairpin appears to be initiated by an approaching sweep event, which perturbs the shear layer associated with the initial packet. The shear layer rolls up, thereby forming the new hairpin head. The head subsequently connects to existing streamwise vortices and develops into a hairpin. The time scale associated with the hairpin auto-generation is 20–30 wall units of time. This demonstrates that hairpins can be created over short distances within a developed turbulent boundary layer, implying that they are not simply remnants of the laminar-to-turbulent transition process far upstream.

