Article contents
Three-dimensional numerical simulation of flow past a rotating step cylinder
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 May 2023
Abstract
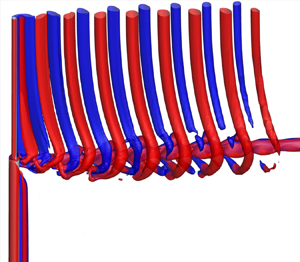
Flow past a rotating step cylinder is investigated through three-dimensional numerical simulations for a diameter ratio of 0.5 and a Reynolds number of 150. The step cylinder comprises two cylinders with different diameters arranged coaxially with a step between them. The rotation rate α is defined as the ratio of the rotation speed of the larger cylinder surface to the free-stream velocity. Vortex shedding happens for both cylinders at α = 0, 0.5 and 1, and is suppressed only for the larger cylinder at α = 2 and 3 and fully suppressed for both cylinders at α = 4. The vortex shedding suppression for the larger cylinder or for both cylinders has significant effects on the wake. The S-, N- and L-cells at α = 0 are in good agreement with those reported in previous studies and still exist at α = 1. The N-cell disappears at α = 0.5, and as a result, the L- and S-cells interact with each other directly at the step position. An additional cellular zone is found at α = 0.5 and 1 and this zone has multiple cells with vortex dislocation between them. At α = 2 and 3, there is a strong hub vortex in the streamwise direction behind the step and the vortices in the wake of the smaller cylinder form helical vortices after they roll around this hub vortex. The hub vortex is generated by the difference between the Magnus effect between the smaller and larger cylinders. At α = 4, the hub vortex still exists but the helical vortices disappear because vortex shedding is suppressed for both cylinders. At this rotation rate, the pressure on the cylinder surface oscillates with a frequency much higher than the vortex shedding frequency. The oscillation of the pressure is caused by the combination of periodic generation of ring vortices and their motion along the span of the larger cylinder.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 9
- Cited by


