Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Kou, Zuhao
and
Dejam, Morteza
2019.
Dispersion due to combined pressure-driven and electro-osmotic flows in a channel surrounded by a permeable porous medium.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 5,
p.
056603.
Ling, Bowen
and
Battiato, Ilenia
2020.
τ-SIMPLE Algorithm for the closure problem in homogenization of stokes flows.
Advances in Water Resources,
Vol. 144,
Issue. ,
p.
103712.
Liu, Shi Yue
Chen, Zhengyi
and
Sanaei, Pejman
2020.
Effects of Particles Diffusion on Membrane Filters Performance.
Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 3,
p.
121.
Malakian, Anna
Zhou, Zuo
Messick, Lucas
Spitzer, Tara N.
Ladner, David A.
and
Husson, Scott M.
2020.
Understanding the Role of Pattern Geometry on Nanofiltration Threshold Flux.
Membranes,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 12,
p.
445.
Fan, Shouhong
Aghajani, Masoud
Wang, Mengyuan
Martinez, Jaylene
and
Ding, Yifu
2020.
Patterning flat-sheet Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane using templated thermally induced phase separation.
Journal of Membrane Science,
Vol. 616,
Issue. ,
p.
118627.
Denizer, Didem
ElSherbiny, Ibrahim M. A.
Ulbricht, Mathias
and
Panglisch, Stefan
2021.
Studying Fluid Characteristics Atop Surface Patterned Membranes via Particle Image Velocimetry.
Chemie Ingenieur Technik,
Vol. 93,
Issue. 9,
p.
1401.
Ling, Bowen
Xie, Peng
Ladner, David
and
Battiato, Ilenia
2021.
Dynamic Modeling of Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes.
Membranes,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 5,
p.
349.
Ling, B.
Rizzo, C. B.
Battiato, I.
and
de Barros, F. P. J.
2021.
Macroscale transport in channel-matrix systems via integral transforms.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 4,
Zhou, Zuo
Ling, Bowen
Battiato, Ilenia
Husson, Scott M.
and
Ladner, David A.
2021.
Concentration polarization over reverse osmosis membranes with engineered surface features.
Journal of Membrane Science,
Vol. 617,
Issue. ,
p.
118199.
Fan, Shouhong
Blevins, Adrienne
Martinez, Jaylene
and
Ding, Yifu
2022.
Effects of Co-diluent on the pore structure, patterning fidelity, and properties of membranes fabricated by lithographically templated thermally induced phase separation.
Journal of Membrane Science,
Vol. 662,
Issue. ,
p.
121023.
Sitaraman, Hariswaran
and
Battiato, Ilenia
2022.
Impact of large-scale effects on mass transfer and concentration polarization in Reverse Osmosis membrane systems.
Separation and Purification Technology,
Vol. 303,
Issue. ,
p.
122121.
Johnston, Jacob
Lou, Jincheng
and
Tilton, Nils
2022.
Application of projection methods to simulating mass transport in reverse osmosis systems.
Computers & Fluids,
Vol. 232,
Issue. ,
p.
105189.
Sitaraman, Hariswaran
and
Battiato, Ilenia
2022.
Impact of Large-Scale Effects on Mass Transfer and Concentration Polarization in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems.
SSRN Electronic Journal ,
Zampogna, Giuseppe Antonio
Ledda, Pier Giuseppe
and
Gallaire, François
2022.
Transport across thin membranes: Effective solute flux jump.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 8,
Ramanuj, Vimal
Sankaran, Ramanan
Malenica, Luka
Cole, Kyle
Day, Marcus
and
McCutcheon, Jeffrey
2022.
Macrovoid resolved simulations of transport through HPRO relevant membrane geometries.
Journal of Membrane Science,
Vol. 662,
Issue. ,
p.
120958.
Shoukat, Gohar
Idrees, Hassaan
Sajid, Muhammad
Ali, Sara
Ayaz, Yasar
Nawaz, Raheel
and
Ansari, A. R.
2022.
Numerical analysis of permeate flux in reverse osmosis by varying strand geometry.
Scientific Reports,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 1,
Yao, Yinuo
Yu, Siqin
and
Battiato, Ilenia
2023.
Understanding flow dynamics in membrane distillation: Effects of reactor design on polarization.
Separation and Purification Technology,
Vol. 314,
Issue. ,
p.
123664.
Fikri, Sherazade
Lessard, Marie-Hélène
Perreault, Véronique
Doyen, Alain
and
Labrie, Steve
2023.
Candida krusei is the major contaminant of ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis membranes used for cranberry juice production.
Food Microbiology,
Vol. 109,
Issue. ,
p.
104146.
Weber, Ross M.
Ling, Bowen
and
Battiato, Ilenia
2024.
Enforcing global constraints for the dispersion closure problem: τ2-SIMPLE algorithm.
Advances in Water Resources,
Vol. 191,
Issue. ,
p.
104759.
Caspar, Justin
Xue, Guanyang
and
Oztekin, Alparslan
2024.
Performance characteristics on up-scaling vacuum membrane distillation modules.
Desalination,
Vol. 569,
Issue. ,
p.
116994.
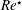 $Re^{\star }$, that accounts for the additional length scales introduced by the membrane modifications, and a membrane performance index,
$Re^{\star }$, that accounts for the additional length scales introduced by the membrane modifications, and a membrane performance index, 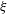 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}$, an aggregate efficiency measure with respect to both clean permeate flux and energy input required to operate the system. Our numerical simulations demonstrate that ‘wiggly’ membranes outperform ‘rough’ membranes for smaller values of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}$, an aggregate efficiency measure with respect to both clean permeate flux and energy input required to operate the system. Our numerical simulations demonstrate that ‘wiggly’ membranes outperform ‘rough’ membranes for smaller values of 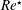 $Re^{\star }$, while the trend is reversed at higher
$Re^{\star }$, while the trend is reversed at higher 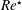 $Re^{\star }$. The proposed approach is able to quantitatively investigate, optimize and guide the design of both morphologically and topologically altered membranes under the same framework, while providing insights into the physical mechanisms controlling the overall system performance.
$Re^{\star }$. The proposed approach is able to quantitatively investigate, optimize and guide the design of both morphologically and topologically altered membranes under the same framework, while providing insights into the physical mechanisms controlling the overall system performance.
