Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Marciani, M.
and
Delplace, P.
2020.
Chiral Maxwell waves in continuous media from Berry monopoles.
Physical Review A,
Vol. 101,
Issue. 2,
Parker, Jeffrey B.
Burby, J. W.
Marston, J. B.
and
Tobias, Steven M.
2020.
Nontrivial topology in the continuous spectrum of a magnetized plasma.
Physical Review Research,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 3,
Iwai, Toshihiro
and
Zhilinskii, Boris
2020.
Bulk-edge correspondence for the Dirac oscillator on the two-torus as a magnetic unit cell.
Journal of Geometry and Physics,
Vol. 156,
Issue. ,
p.
103784.
Tauber, C.
Delplace, P.
and
Venaille, A.
2020.
Anomalous bulk-edge correspondence in continuous media.
Physical Review Research,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 1,
Burns, Keaton J.
Vasil, Geoffrey M.
Oishi, Jeffrey S.
Lecoanet, Daniel
and
Brown, Benjamin P.
2020.
Dedalus: A flexible framework for numerical simulations with spectral methods.
Physical Review Research,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 2,
Favier, Benjamin
and
Knobloch, Edgar
2020.
Robust wall states in rapidly rotating Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 895,
Issue. ,
Parker, Jeffrey B.
Marston, J. B.
Tobias, Steven M.
and
Zhu, Ziyan
2020.
Topological Gaseous Plasmon Polariton in Realistic Plasma.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 124,
Issue. 19,
Upreti, Lavi K.
and
Delplace, Pierre
2020.
Topological chiral interface states beyond insulators.
Physical Review A,
Vol. 102,
Issue. 2,
Xu, Hong-Ya
and
Lai, Ying-Cheng
2020.
Anomalous chiral edge states in spin-1 Dirac quantum dots.
Physical Review Research,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 1,
Delplace, Pierre
and
Venaille, Antoine
2020.
From the geometry of Foucault pendulum to the topology of planetary waves.
Comptes Rendus. Physique,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 2,
p.
165.
Abbaszadeh, Hamed
Fruchart, Michel
van Saarloos, Wim
and
Vitelli, Vincenzo
2021.
Liquid-crystal-based topological photonics.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 118,
Issue. 4,
Hosaka, Yuto
Komura, Shigeyuki
and
Andelman, David
2021.
Hydrodynamic lift of a two-dimensional liquid domain with odd viscosity.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 104,
Issue. 6,
Baardink, Guido
Cassella, Gino
Neville, Luke
Milewski, Paul A.
and
Souslov, Anton
2021.
Complete absorption of topologically protected waves.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 104,
Issue. 1,
Venaille, A.
and
Delplace, P.
2021.
Wave topology brought to the coast.
Physical Review Research,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 4,
Parker, Jeffrey B.
2021.
Topological phase in plasma physics.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 87,
Issue. 2,
Fu, Yichen
and
Qin, Hong
2021.
Topological phases and bulk-edge correspondence of magnetized cold plasmas.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 1,
Graf, Gian Michele
Jud, Hansueli
and
Tauber, Clément
2021.
Topology in Shallow-Water Waves: A Violation of Bulk-Edge Correspondence.
Communications in Mathematical Physics,
Vol. 383,
Issue. 2,
p.
731.
Ren, Chenyang
Fan, Xianping
Xia, Yiling
Chen, Tiancheng
Yang, Liu
Zhong, Jin-Qiang
and
Zhang, H. P.
2021.
Robust propagation of internal coastal Kelvin waves in complex domains.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 2,
Knobloch, Edgar
2022.
Mathematical and Computational Models of Flows and Waves in Geophysics.
p.
1.
Finnigan, Cooper
Kargarian, Mehdi
and
Efimkin, Dmitry K.
2022.
Equatorial magnetoplasma waves.
Physical Review B,
Vol. 105,
Issue. 20,
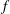 $f$-plane shallow water eigenmodes around band-crossing points in parameter space. In this previous study, the topological invariant was a property of the interface between two hemispheres. Here we ask whether a topological index can be assigned to each hemisphere. We show that this can be done if the shallow water model in the
$f$-plane shallow water eigenmodes around band-crossing points in parameter space. In this previous study, the topological invariant was a property of the interface between two hemispheres. Here we ask whether a topological index can be assigned to each hemisphere. We show that this can be done if the shallow water model in the 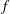 $f$-plane geometry is regularized by an additional odd-viscosity term. We then compute the spectrum of a shallow water model with a sharp equator separating two flat hemispheres, and recover the Kelvin and Yanai waves as two exponentially trapped waves along the equator, with all the other modes delocalized into the bulk. This model provides an exactly solvable example of bulk-interface correspondence in a flow with a sharp interface, and offers a topological interpretation for some of the transition modes described by Iga (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 294, 1995, pp. 367–390). It also paves the way towards a topological interpretation of coastal Kelvin waves along a boundary and, more generally, to an understanding of bulk-boundary correspondence in continuous media.
$f$-plane geometry is regularized by an additional odd-viscosity term. We then compute the spectrum of a shallow water model with a sharp equator separating two flat hemispheres, and recover the Kelvin and Yanai waves as two exponentially trapped waves along the equator, with all the other modes delocalized into the bulk. This model provides an exactly solvable example of bulk-interface correspondence in a flow with a sharp interface, and offers a topological interpretation for some of the transition modes described by Iga (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 294, 1995, pp. 367–390). It also paves the way towards a topological interpretation of coastal Kelvin waves along a boundary and, more generally, to an understanding of bulk-boundary correspondence in continuous media.
