Article contents
Amplitude modulation of streamwise velocity fluctuations in the roughness sublayer: evidence from large-eddy simulations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 January 2016
Abstract
Recent studies have demonstrated that large- and very-large-scale motions in the logarithmic region of turbulent boundary layers ‘amplitude modulate’ dynamics of the near-wall region (Marusic et al., Science, vol. 329, 2010, pp. 193–196; Mathis et al., J. Fluid Mech., vol. 628, 2009a, pp. 311–337). These contributions prompted development of a predictive model for near-wall dynamics (Mathis et al., J. Fluid Mech., vol. 681, 2011, pp. 537–566) that has promising implications for large-eddy simulations of wall turbulence at high Reynolds numbers (owing to the presence of smaller scales as the wall is approached). Existing studies on the existence of amplitude modulation in wall-bounded turbulence have addressed smooth-wall flows, though high Reynolds number rough-wall flows are ubiquitous. Under such conditions, the production of element-scale vortices ablates the viscous wall region and a new near-wall layer emerges: the roughness sublayer. The roughness sublayer depth scales with aggregate roughness element height, 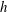 $h$ , and is typically
$h$ , and is typically 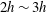 $2h\sim 3h$ . Above the roughness sublayer, Townsend’s hypothesis dictates that turbulence in the logarithmic layer is unaffected by the roughness sublayer (beyond its role in setting the friction velocity and thus inducing a deficit in the mean streamwise velocity known as the roughness function). Here, we present large-eddy simulation results of turbulent channel flow over rough walls. We follow the decoupling procedure outlined in Mathis et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 628, 2009a, 311–337) and present evidence that outer-layer dynamics amplitude modulate the roughness sublayer. Below the roughness element height, we report enormous sensitivity to the streamwise–spanwise position at which flow statistics are measured, owing to spatial heterogeneities in the roughness sublayer imparted by roughness elements. For
$2h\sim 3h$ . Above the roughness sublayer, Townsend’s hypothesis dictates that turbulence in the logarithmic layer is unaffected by the roughness sublayer (beyond its role in setting the friction velocity and thus inducing a deficit in the mean streamwise velocity known as the roughness function). Here, we present large-eddy simulation results of turbulent channel flow over rough walls. We follow the decoupling procedure outlined in Mathis et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 628, 2009a, 311–337) and present evidence that outer-layer dynamics amplitude modulate the roughness sublayer. Below the roughness element height, we report enormous sensitivity to the streamwise–spanwise position at which flow statistics are measured, owing to spatial heterogeneities in the roughness sublayer imparted by roughness elements. For 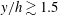 $y/h\gtrsim 1.5$ (i.e. above the cubes, but within the roughness sublayer), topography dependence rapidly declines.
$y/h\gtrsim 1.5$ (i.e. above the cubes, but within the roughness sublayer), topography dependence rapidly declines.
Information
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2016 Cambridge University Press
References
- 67
- Cited by


