Introduction
A large body of empirical research documents how patterns of assortative mating are functions of population structure, socio-cultural preferences, social stratification and mobility, and marriage market processes. (For synopses of this evidence, see Buss Reference Buss1985; Mare, Reference Mare1991; Blackwell and Lichter, Reference Blackwell and Lichter2005; Brynin et al., Reference Brynin, Longhi and Pérez2008; Esteve, et al., Reference Esteve, Cortina and Cabré2009; Schwartz, Reference Schwartz2013; Dribe and Stanfors, Reference Dribe and Stanfors2017). Generally, assortative mating is ‘positive’ in the sense that partners tend to share background characteristics such as ethnicity, religion, class, and education. That is, homogamy concerning background characteristics is the rule.
Assortative mating on age is a somewhat different matter. The general rule in almost every society is for the man to be older than the woman, with a large subset of unions in which the man is substantially older than the woman in some societies (Atkinson, and Glass, Reference Atkinson and Glass1985; Casterline et al., Reference Casterline, Williams and McDonald1986; Esteve, et al., Reference Esteve, Cortina and Cabré2009; Carmichael, Reference Carmichael2011; Feng and Ren, Reference Feng and Ren2022). Several explanations have been proposed for this phenomenon. From the evolutionary perspective, younger women are more fecund and offer more reproductive years (Eckland, Reference Eckland1968; Buss and Schmitt, Reference Buss and Schmitt1993). This rationale is reinforced by social exchange theory, with women trading youthfulness for social and economic security, in relative terms, that older men offer (South, Reference South1991; Sprecher, et al., Reference Sprecher, Sullivan and Hatfield1994; Mu and Xie, Reference Mu and Xie2014; Zeng and Liao, Reference Zeng and Liao2021). Indeed, empirical research on partner preference largely confirms the theoretical expectations (Regan et al., Reference Regan, Levin, Sprecher, Christopher and Gate2000; Alterovitz and Mendelsohn, Reference Alterovitz and Mendelsohn2011; Schwarz and Hassebrauck, Reference Schwarz and Hassebrauck2012; Šetinová and Topinková, Reference Šetinová and Topinková2021).
Beyond these general motivations determining preferences for spousal age differences, the more exact form of observed empirical distributions is in part a function of marriage market structures and processes. Population age structure sets constraints on the availability of potential spouses by relative age. The pattern of assortative mating by age can also be affected by who decides the match (the potential spouses versus other family members), where potential partners may be encountered (local community, religious gatherings, school, work), and expectations about inter-family resource exchange (dowry, bridewealth). Rules governing the permissibility of remarriage and multiple marriages also affect spousal age differences. The latter – whether polygamous unions are legal and normatively acceptable – is of special relevance in this research on sub-Saharan Africa.
Drawing on national demographic survey data, this research examines levels and trends in spousal age differences in sub-Saharan Africa over marriage cohorts spanning a four-decade period from 1980 to 2019. There has been no recent systematic effort at a comprehensive description of the sort that this paper provides. Trends in the age at first marriage for women are abundantly documented (Garenne, Reference Garenne2004; Mensch, et al., Reference Mensch, S Singh and Casterline2005; Saardchom and Lemaire, Reference Saardchom and Lemaire2005; Jones, and Gubhaju, Reference Jones and Gubhaju2009; Walke, Reference Walke2012); and the average age has increased in most African societies, which in itself is a force towards a narrowing of the spousal age gap. However, the age of marriage for men has also increased over time in sub-Saharan Africa (Calvès et al., Reference Calvès, Kobiané and Martel2007; Palamuleni, Reference Palamuleni2010; Hertrich, Reference Hertrich2013). The net outcome for spousal age difference distributions is difficult to predict without explicit analysis of these distributions.
The extensive research on levels and trends in the age at first marriage of women in sub-Saharan Africa is suggestive of forces determining spousal age differences. Gender discrimination and low educational attainment have traditionally promoted early marriages for women. Over the past few decades, economic growth – with the accompanying increases in female educational attainment and labour force participation – has delayed age at first marriage and expanded marriage market opportunities for women in sub-Saharan Africa. Educational institutions and workplaces provide women with more opportunities to find potential spouses closer in age than was the case in the past (Saardchom and Lemaire, Reference Saardchom and Lemaire2005; Utomo, Reference Utomo2014) while declines in fertility have shrunk marriage markets for men forcing them to search for partners closer in age (Polachek et al., Reference Polachek, Zhang and Zhou2015). There is also the possibility that women have increasingly more decision-making power in choosing spouses, with the expectation that their preferences would shift away from having a husband who is markedly older. While there is little information on the prevalence of arranged marriages in the region, one might infer from the decline in child marriages (Nguyen and Wodon, Reference Nguyen and Wodon2015; Koski, Clark, and Nandi, Reference Koski, Clark and Nandi2017; Male and Wodon, Reference Male and Wodon2018) that on balance women have a greater influence on spousal choices than in the past.
There have been several past multi-country studies of spousal age differences in sub-Saharan Africa. In an analysis of World Fertility Surveys conducted in the late 1970s and early 1980s, Casterline et al., (Reference Casterline, Williams and McDonald1986) showed that on average spousal age differences were larger in sub-Saharan Africa than in any other major region. This present study serves to update Casterline et al. (Reference Casterline, Williams and McDonald1986), among other contributions.
Since then, many studies set in sub-Saharan Africa have shown that the size of the spousal age difference is associated with fertility. In particular, the age difference is negatively associated with the use of contraception (Longfield et al., Reference Longfield, Glick, Waithaka and Berman2004; Barbieri, et al., Reference Barbieri, Hertrich and Grieve2005; Manlove et al., Reference Manlove, Ryan and Franzetta2007; Coltabiano and Castiglioni, Reference Coltabiano and Castiglioni2008; Das et al., Reference Das, Gautam, Das and Tripathy2011; Ibisomi, Reference Ibisomi2014). An explanation for this finding is that female autonomy and decision-making power are lower in unions where the age difference is large (Casterline et al., Reference Casterline, Williams and McDonald1986; Abadian, Reference Abadian1996; DiClemente et al., Reference DiClemente, Wingood, Crosby, Sionean, Cobb, Harrington and Oh2002; Carmichael, Reference Carmichael2011), restricting the ability of women to negotiate for contraceptive use. Consistent with this explanation, the age difference between partners is associated with an increased risk of intimate partner violence (Vezina and Hebert, Reference Vezina and Hebert2007; Volpe et al., Reference Volpe, Hardie, Cerulli, Sommers and Morrison-Beedy2013) as well as fears of violence and controlling behaviour (Catallozi et al., Reference Catallozzi, Simon, Davidson, Breitbart and Rickert2011). Further, research on adolescents and young adults indicates that younger women are at greater risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies when their partners are older (Kaestle et al., Reference Kaestle, Morisky and Wiley2002). Larger age differences between partners also increase the likelihood of risky behaviours such as unprotected sex (Ryan et al., Reference Ryan, Franzetta, Manlove and Schelar2008; Volpe et al., Reference Volpe, Hardie, Cerulli, Sommers and Morrison-Beedy2013). Spousal age differences at marriage may also have implications for other outcomes such as marital stability (Lehrer, Reference Lehrer2008) and health (Drefahl Reference Drefahl2010; Kim, et al., Reference Kim, Park and Lee2015).
Globally, age differences between spouses have narrowed over time (Atkinson and Glass, Reference Atkinson and Glass1985; Tabutin et al., Reference Tabutin, Schoumaker and Rabenoro2004; Esteve, et al., Reference Esteve, Cortina and Cabré2009; Utomo, Reference Utomo2014) although some recent research indicates that spousal age differences have begun to increase in a few countries (Poppel et al., Reference Poppel, Liefbroer, Vermunt and Smeenk2001; Kolk, Reference Kolk2015; Mu & Xie, Reference Mu and Xie2014). In sub-Saharan Africa, research almost two decades ago showed that spousal age differences had narrowed yet remained substantially higher than in other regions (Tabutin et al., Reference Tabutin, Schoumaker and Rabenoro2004; Barbieri et al., Reference Barbieri, Hertrich and Grieve2005). More recent research confirms the same, that is, larger spousal differences in sub-Saharan Africa compared to other regions (Feng and Ren, Reference Feng and Ren2022; Ausubel et al., Reference Ausubel, Kramer, Shi and Hackett2022).
To explain this feature of the demography of marriage in sub-Saharan Africa, one can point to several other features of the region’s social and cultural systems. The bridewealth system, practiced in most of sub-Saharan Africa, by its nature necessitates men to marry at older ages so that they can acquire the requisite financial resources to complete marriage rites. Isiugo-Abanihe (Reference Isiugo-Abanihe1995) specifically linked the high bridewealth costs to rising ages at marriage in Nigeria two decades ago, and more recent literature has shown that income constraints are correlated with delays in marriage formation for men (Calvès and Depledge, Reference Calvès and Depledge2007; Calvès et al., Reference Calvès, Kobiané and Martel2007.; Mondain et al., Reference Mondain, LeGrand and Sabourin2007). The bridewealth requirements for men coupled with the preference for a youthful wife (as noted above) accounts for the relatively larger age gaps observed in this setting. The relatively high occurrence of polygyny in this context also promotes the marriage of men to much younger women.
There is also the logic of high fertility. A society with high fertility desires (Dodoo, Reference Dodoo1993; Bongaarts and Casterline, Reference Bongaarts and Casterline2013; Casterline and Agyei-Mensah, Reference Casterline and Agyei-Mensah2017) would emphasise fecundity and by extension youthfulness in wives. That may be one of the main reasons why women in sub-Saharan Africa have the lowest age at first marriage (Saardchom and Lemaire, Reference Saardchom and Lemaire2005; Carmichael Reference Carmichael2011). Consistent with this argument, Buss et al., (Reference Buss, Shackelford and LeBlanc2000), in their cross-cultural study, found that fertility preferences are correlated with desired spousal age differences for men but not for women. Also relevant, by affecting women’s age at first marriage, is low educational attainment and poverty that encourages families to push young girls out for marriage.
Methods
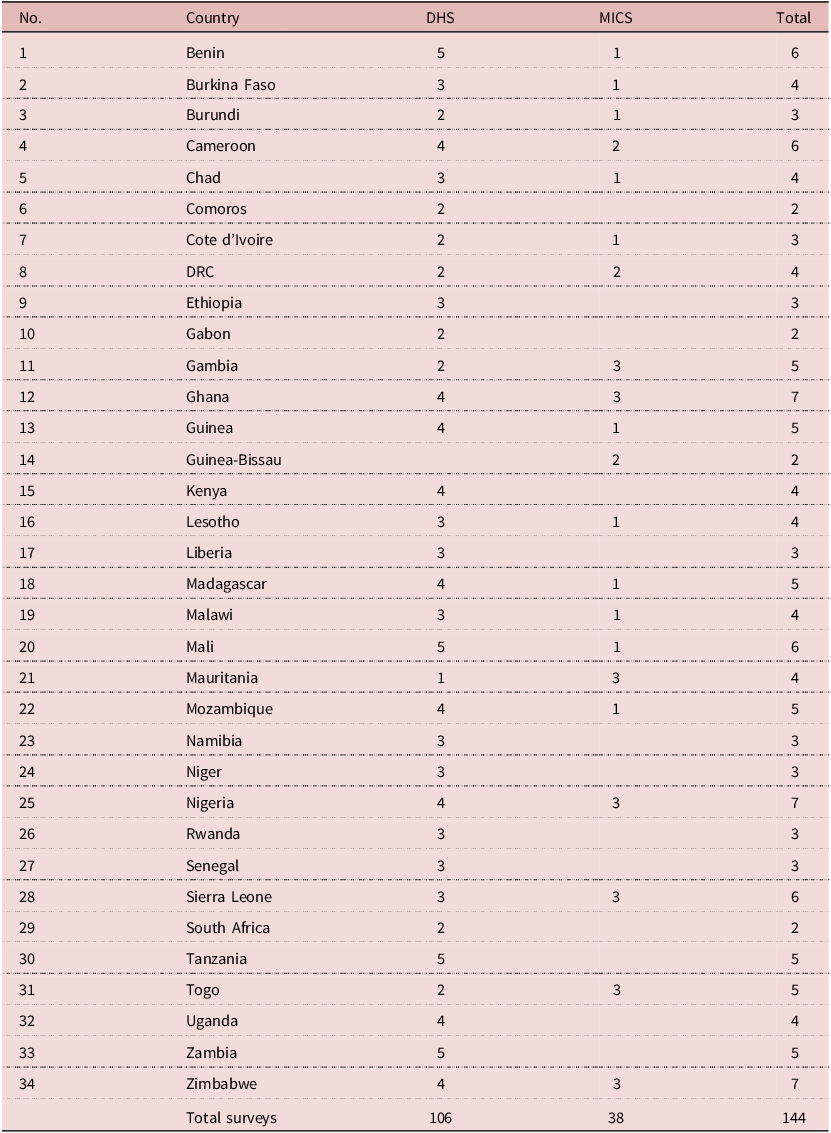
This study examines levels and trends in spousal age differences in 34 countries in sub-Saharan Africa using Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS). Data were pooled from 144 surveys – 106 DHS and 38 MICS – that collected information on partner age in the women’s questionnaire. The data span surveys conducted from 1980 to 2020 (see Table 1 for list of countries). The pooled dataset excludes countries that have only one survey over the period. Countries in which the first and last surveys were less than 10 years apart were also excluded, as adequate time is required between surveys for a stronger basis for studying historical trends.
Table 1. Surveys in Sample
The sample comprises currently married women in their first union as information on partner age is only asked of the current partner. The analysis adopts a marriage cohort approach by classifying women into five-year cohorts based on their year of first marriage. Due to relatively small sample sizes, women married before 1980 and after 2019 were excluded from the analysis.
The outcome variable is a spousal age difference, calculated by subtracting the age of the woman from the age of the husband reported by the woman. Women for whom partner information was missing were excluded from the sample. The age difference distribution was winsorized (Wilcox Reference Wilcox2005) to remove outliers. The original range for the spousal age difference was -39 to 80 years (mean spousal age difference of 8.4 years) stemming from values for reported partner ages that are implausibly high or low. Winsorization involved deleting observations that fell below the 1st percentile and above the 99th percentile of the sample. After winsorization, the age difference ranged from -38 to 41 years (mean spousal age difference of 8.2).
The analysis involved a linear regression predicting the spousal age difference. The focal independent variables were age at marriage for women and educational attainment of women. The control variables in the linear regression were the woman’s religion, partner’s education, type of place of residence, and monogamous versus polygamous union. The regression also included fixed effects for the country; hence, the other coefficients can be regarded as (average) within-country effects.
Multiple models are presented: a base model that controls for marriage cohort and country, a second model that adds age at first marriage, a third that adds women’s level of education, and the fourth model that includes all the covariates. An important feature of this equation is the inclusion of fixed effects for the country. Therefore, the coefficients for marriage cohorts pertain to within-country trends. Finally, a fifth model that includes all the covariates and an interaction between age at marriage and marriage cohorts. The purpose of running the interaction term is to determine whether the correlation between women’s age at marriage and spousal age difference varies by year of marriage.
Results
Figure 1 summarises the trends in the spousal age difference at first marriage by country and year of marriage, ranked by the average spousal age difference of the country. There are substantial variations by country in spousal age differences ranging from 12.9 years in Gambia to 4.5 in Rwanda. The highest spousal age differences are observed in West African countries while countries in Eastern and Southern Africa have relatively lower age differences. The chart indicates that the spousal age difference at first marriage has generally declined with marked cross-national variation in the levels and differentials across marriage cohorts. For most countries, the mean age difference was lowest in the most recent marriage cohort. Exceptions include Burkina Faso, Comoros, and Tanzania where the lowest mean age differences were recorded in the mid-2000s.
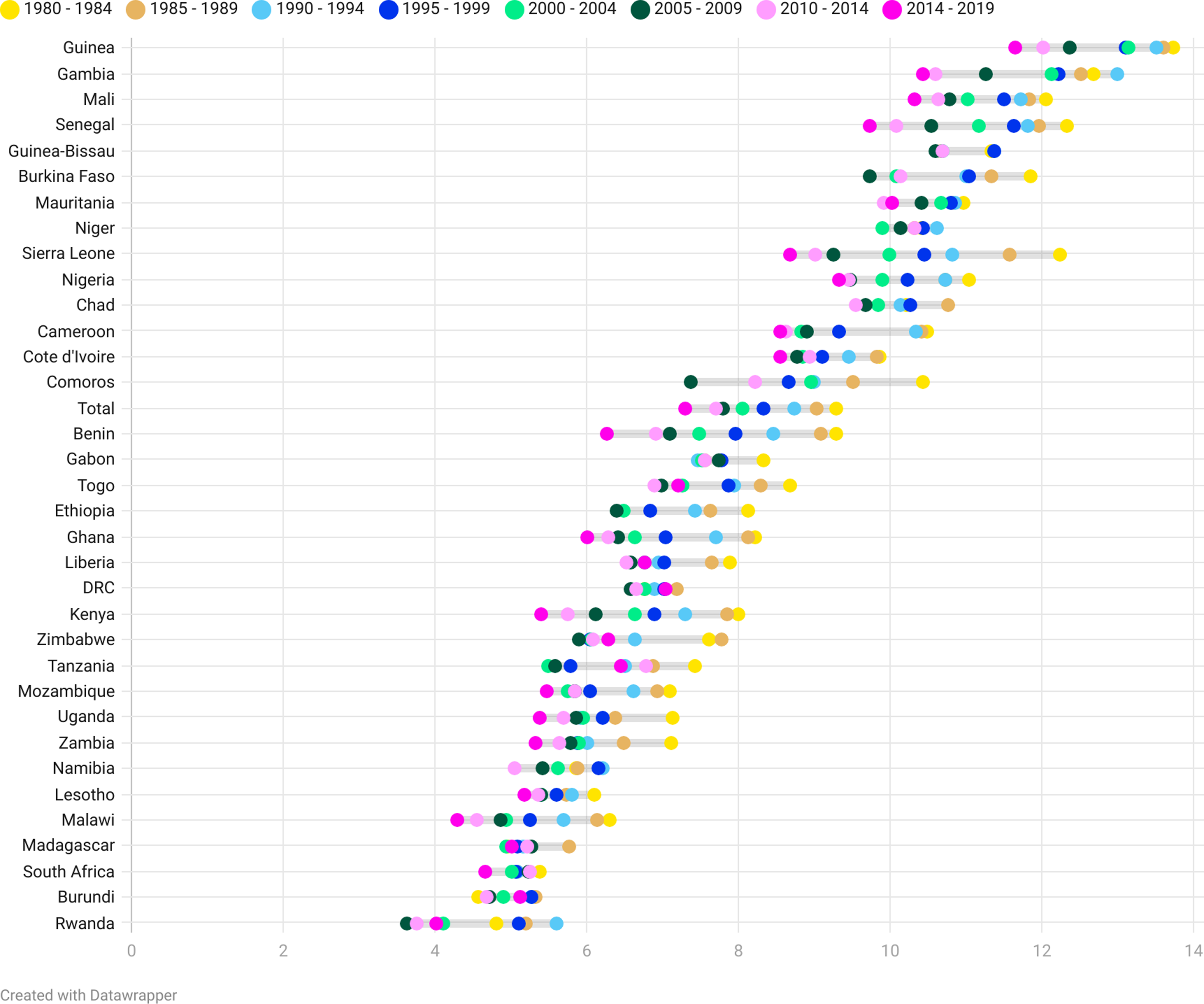
Figure 1. Spousal Age Difference by Marriage Cohort and Country.
Figure 2 further quantifies the magnitude of the change over time. The mean spousal age difference for the overall sample on average declined by 2.0 years between the earliest and most recent cohorts. Age difference predominantly decreased across countries with 31 out of the 34 countries recording a decline. The change in the countries where spousal age difference declined ranged from over 3 years in Sierra Leone to a month in Niger. The three countries that had minor increments between their earliest and most recent cohorts were Madagascar, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and Burundi where spousal age difference increased by less than a year.
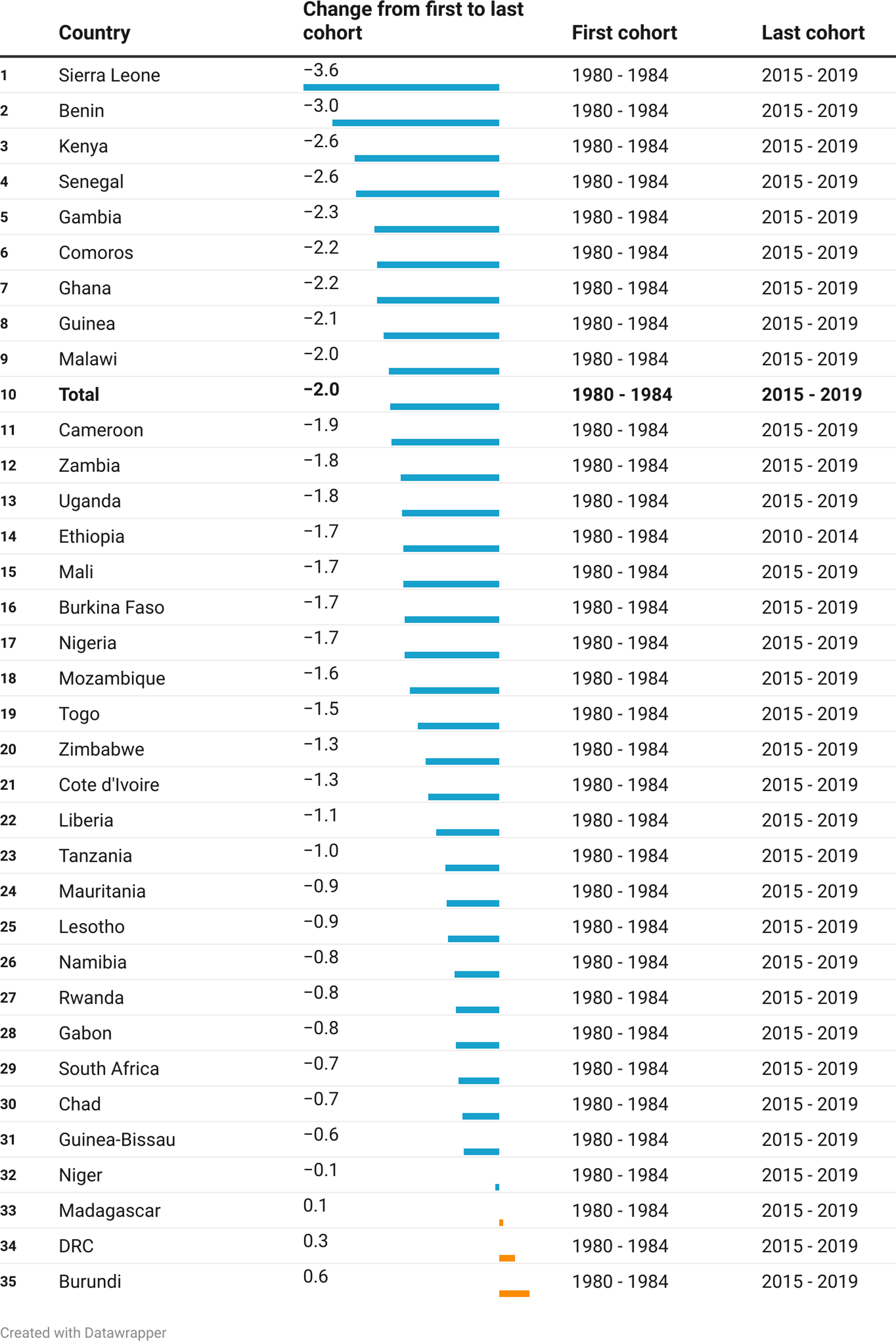
Figure 2. Change in Spousal Age Difference by Cohort and Country.
Table 2 presents descriptive statistics of the sample. The mean spousal age difference for women in first union is 8.2 years. Marriage cohorts for 2000–2004 and 1995–1995, respectively, make up the largest share of the sample.
Table 2. Descriptive Statistics of Sample
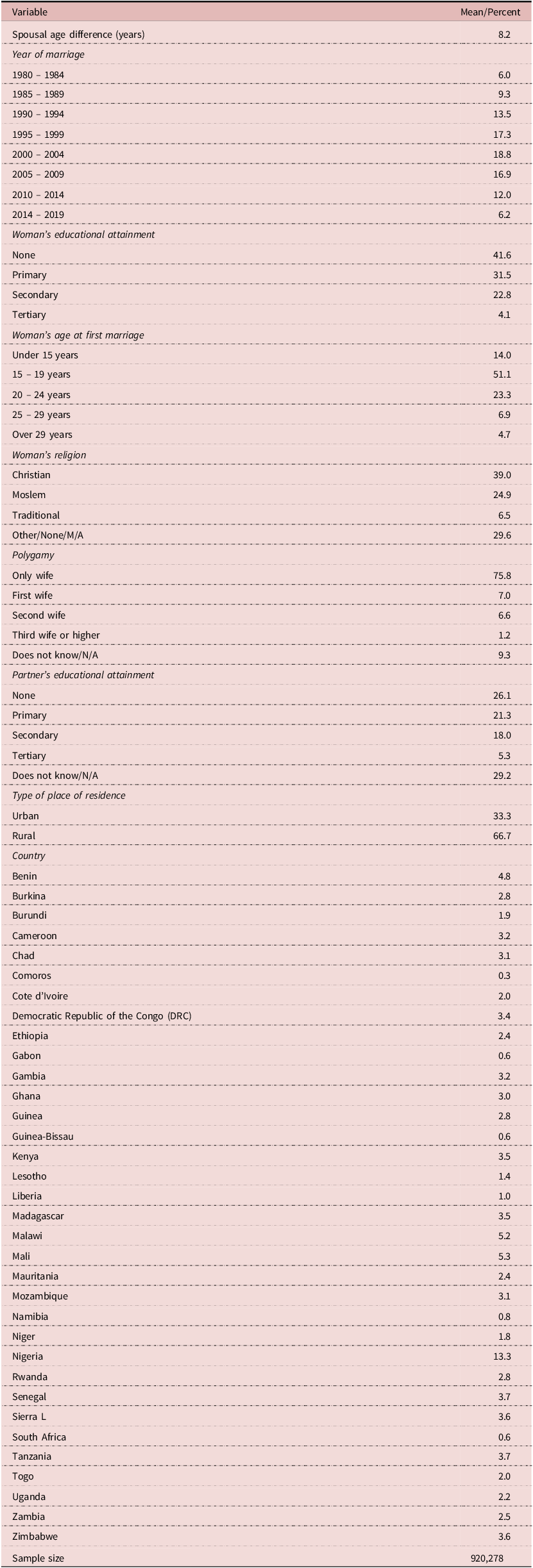
Table 3 presents the trends in age at first marriage for women in the first union and their partners. The mean age at which women marry for the first time has steadily increased, from 16.5 years in 1980–1984 to 20.7 years in 2014–2019. The mean age of the husbands of women in sample has also increased, although at a slower pace compared to wives’ age; it rose from 25.7 years in 1980–1984 to 28.0 years in 2014–2019. Over the years, the mean age difference at first marriage has decreased, from 9.3 years in the 1980–1984 marriage cohort to 7.3 years in the 2014–2019 cohort. Age at marriage increases for both women and men in successive cohorts with that of women (4.2) increasing by two more years more than husbands (2.2), when comparing the earliest and most recent cohorts. Overall, the trends reflect societal shifts over the four-decade period, with both women and men marrying later in life. However, the increase in age at marriage has been greater for women, thus leading to a narrowing of spousal age gaps over time.
Table 3. Trends in Age Difference at First Marriage, and Age at First Marriage for Women and their Husbands
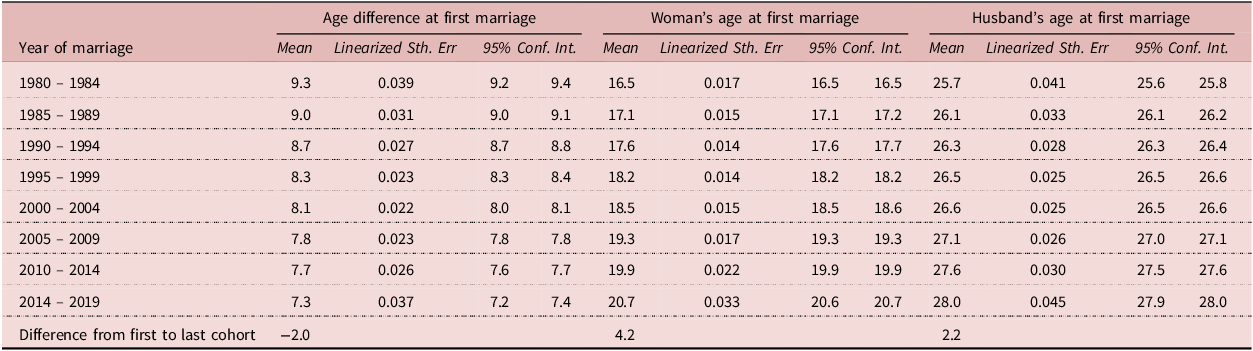
Table 4 presents the results of the regressions predicting the spousal age difference for women in the first union. Model 1 estimates that spousal age difference for a couple in the most recent marriage cohort, that is, 2014 to 2019 is more than a year and a half (1.7 years) lower than a couple in the earliest marriage cohort (1980–1984).
Table 4. Results of Linear Regression Predicting Spousal Age Difference at First Marriage
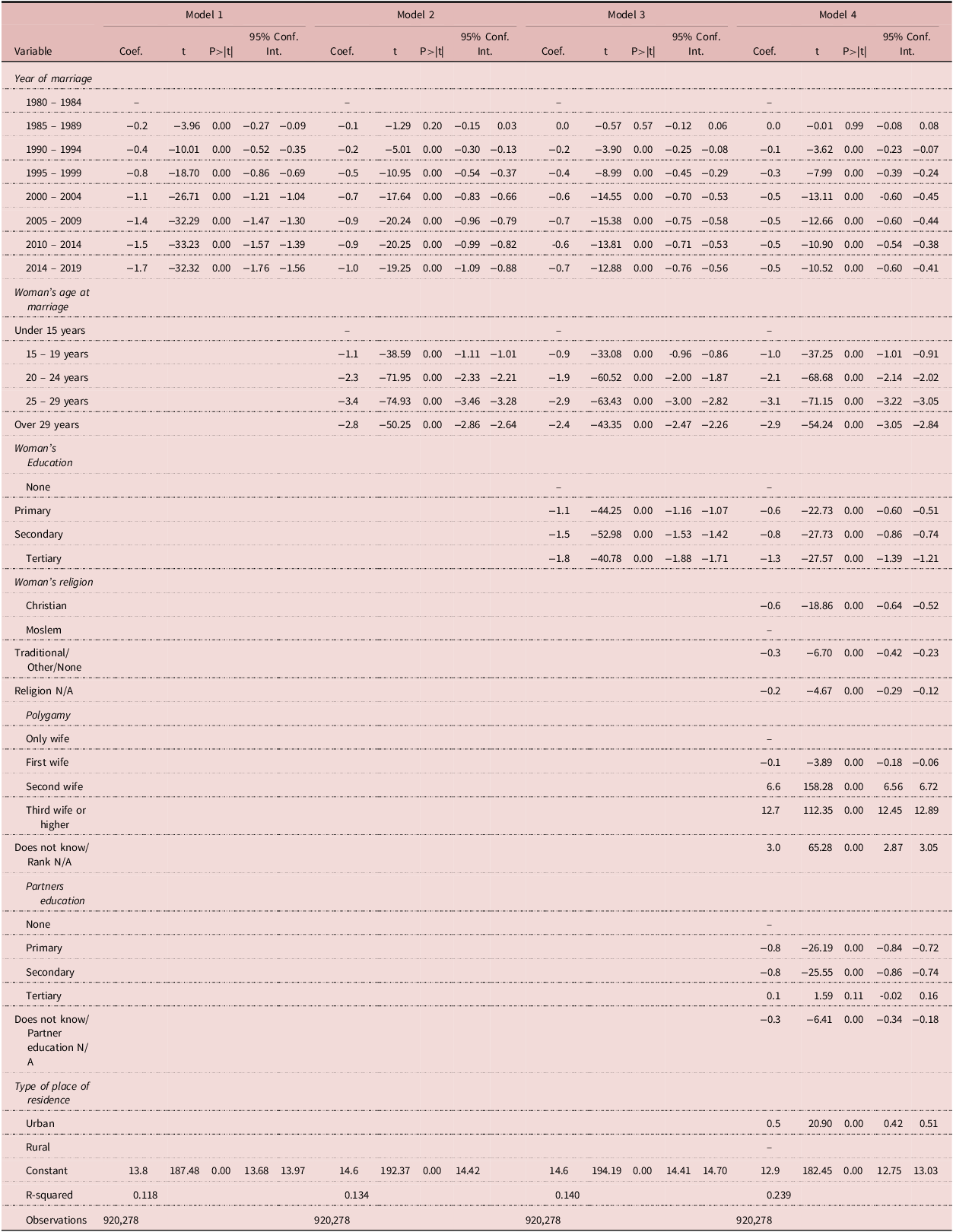
Note: The models also control for country of residence.
The addition of age at first marriage in Model 2 reduces the size of the coefficient for all marriage cohorts and for the most recent marriage cohort by almost half. This means that once age at first marriage is controlled for, the age difference declined by about a year between the earliest and most recent marriage cohorts. Age at marriage is statistically significantly correlated with spousal age difference with women who married above 29 years having a spousal age difference that is almost 3 years smaller than those who married before 15 years.
The inclusion of educational attainment in Model 3 further reduces the sizes of the coefficients, although with a smaller decline than that recorded between Models 1 and 2. Educational attainment is also a statistically significant predictor of spousal age difference: women with some education have a spousal age difference that is at least a year smaller than that of women with no education.
Model 4 which includes all covariates indicates that between 1980–1984 and 2014–2019, the spousal age difference for women in first marriage declined by about six months (0.5 years). With respect to the other covariates, statistically significant predictors of spousal age difference include polygamy, religion, partner education, and type of place of residence.
In all models, the year of marriage is consistently associated with a decline in spousal age difference and the coefficients are statistically significant. The size of the coefficients generally increases as the years progress, particularly from 1995 to 1999 marriage cohort onwards, with the largest negative effects observed in the more recent cohorts (2000–2004, 2005–2009, 2010–2014, and 2014–2019).
Figure 3 shows the coefficients of the interaction terms estimated in Model 5. The results suggest that the observed time trends may be largely driven by women who marry after 29 years of age. For women in the other categories, the time trend does not significantly differ compared to women who were married before 15 years, but a steady and substantial decline is observed for women marrying after 29 years.
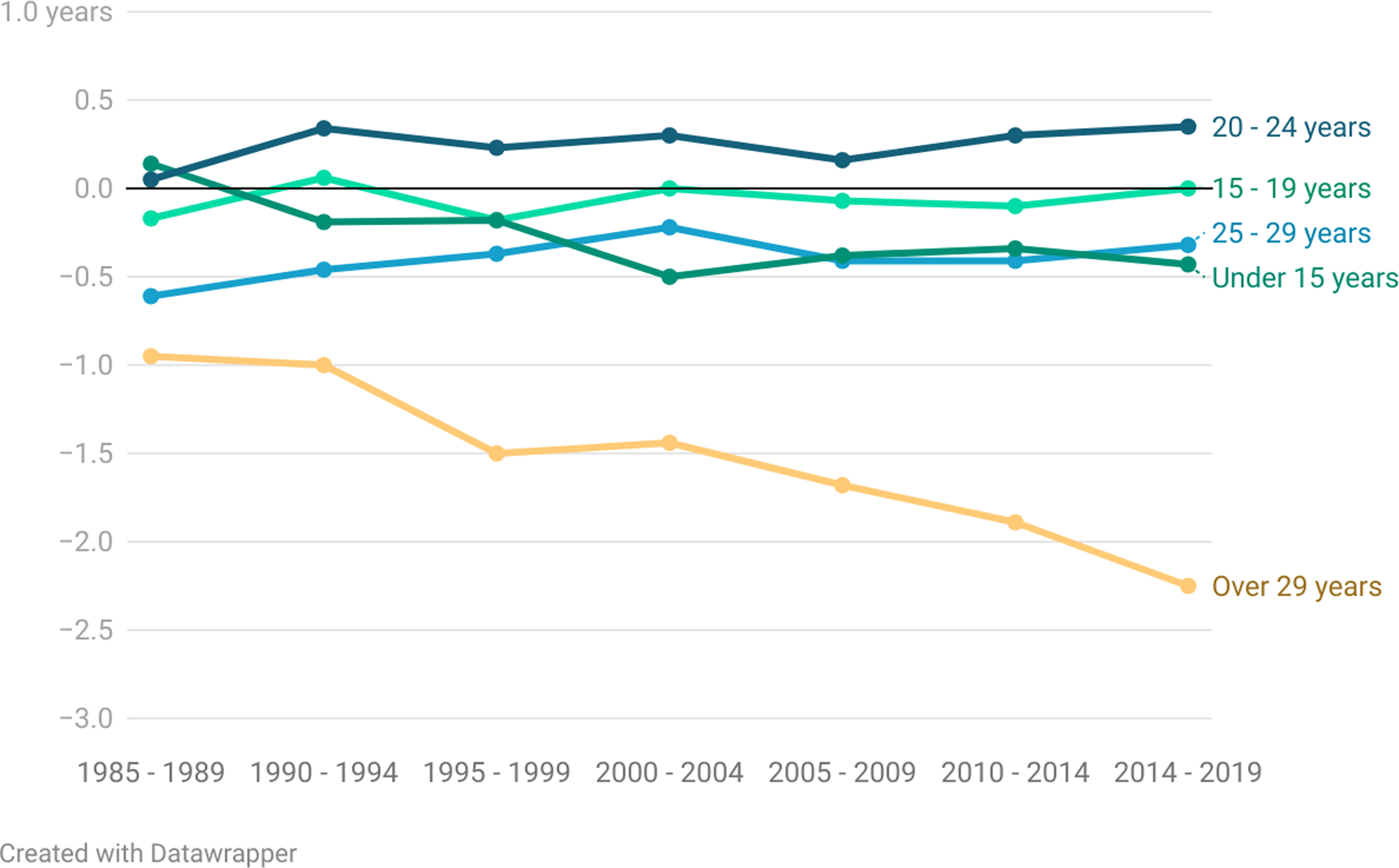
Figure 3. Results of Linear Regression Predicting Spousal Age Difference at First Marriage with Interaction between Age at First Marriage and Marriage Cohort.
Discussion
A deeper understanding of the differences between the ages of spouses is significant because it has implications for understanding a plethora of demographic processes – family formation and marriage markets, fertility and fertility transitions, and age structural differences, between and among countries and world regions. In sub-Saharan Africa, it also provides a nuanced understanding of cross-cultural differences such as ethnolinguistic differences and divides, as evidenced in some of the findings presented in this paper where women whose religion is Islam tend to have a larger spousal age difference than women in other religions. The observed national and regional differences are perhaps a reflection of both the ethnolinguistic and cultural differences, particularly between the Eastern/Southern African and the Western/Central African countries. Another explanation could be due to differences in levels of economic development across the different sub-regions as spousal age difference is negatively correlated with per capita GDP (Feng and Ren, Reference Feng and Ren2022).
Second, age differences between spouses have implications for power dynamics within households. Husbands who marry younger women may have higher social standing and greater economic resources, and this, in turn, can lead to a power imbalance in the marriage favouring men. This generates lower autonomy for the woman in the household, possibly compounded by less education, less access to economic resources, and a lack of extra-familial relationships. They may also lack the ability to contribute equally to decision-making within the household on matters conjugal in nature such as decisions regarding the use of family planning, when and how many children to have, and the autonomy to seek care for themselves and their children, among many others (Bawah et al., Reference Bawah, Phillips, Asuming, Bangha and Vaughan-Smith2013; Drefahl, Reference Drefahl2010, Kitila et al., Reference Kitila, Terfa, Akuma, Olika and Olika2020).
The results indicate that age at first marriage and education attainment partly account for the observed time trend. This study shows that while age differences between spouses have historically been wide, in recent decades, there has been a narrowing of the gap due in part to increases in women’s educational attainment and age at first marriage. As the literature suggests, as cited earlier in this paper, as more women experience formal schooling and attain higher levels of education, they are more likely to find partners of their age, for multiple reasons. First, formal schooling leads women to marry later, and everything else being equal a shift in the distribution of women’s ages at first marriage toward a later age also produces a narrowing of the spousal age difference. Second, as an institutional setting for meeting a potential spouse, schools tend to be decidedly age-graded, and this makes them a force towards age homophily; this is a marriage market effect.
The paper makes two main contributions to the literature on spousal age differences in marriage. The first is the scope of the analysis: a large number of surveys analysed encompass a relatively large expanse of time and space, providing a comprehensive picture of the dynamics of spousal differences in terms of both changes over time and across different regions in sub-Saharan Africa. The historical span is especially important – four decades – given the principal goal of examining changes that have occurred in marriage patterns over time. To the knowledge of the authors, no existing study on spousal age differences in sub-Saharan Africa has pooled data over such a long period across a broad range of countries. In summary, this paper provides a detailed description of trends and some information on some of the explanatory factors for the trends.
A second contribution is methodological: the estimation of country-fixed effects allows for an examination of cross-national variation that can be attributed in part to sociolinguistic differences not controlled for in the analysis. The estimated fixed effects for the country are revealing of cross-national variation that might be attributed to sociolinguistic factors not controlled for in the analysis. The countries with the highest age differences are from West Africa, and the lowest differences are observed in Southern Africa. Age differences are also higher in Francophone countries compared to Anglophone and Lusophone countries. These variables, however, have high collinearity with country and thus attempts to include them in the regressions were unsuccessful.
The marginal reduction in spousal age difference despite increasing age at first marriage in sub-Saharan Africa is suggestive of the male age at first marriage keeping pace with that of females. Increasing educational attainment for males would also be expected to delay their age at first marriage as well. Other factors such as increasing cost of living, high unemployment rates, and stagnant wages may make it difficult for young men to accumulate the necessary resources to fulfil customary bridewealth requirements. These findings may also reflect strong cultural preferences for larger spousal age differences. The persistent spousal age difference of this magnitude has implications for power dynamics within marriages and for women’s autonomy as much younger wives may have less decision-making power and be more vulnerable to domestic violence.
Disclosure Statements
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial entity, or not-for-profit organisation.
Competing interests
The authors declare none.
Ethical standard
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.









