Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Takács, Lajos
1970.
On the fluctuations of election returns.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 01,
p.
114.
Takács, Lajos
1970.
On the fluctuations of election returns.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 1,
p.
114.
Charalambides, Ch. A.
2005.
Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences.
Charalambides, Ch. A.
2014.
Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online.

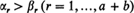 , let
, let 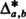 be the number of subscripts
be the number of subscripts 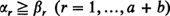 ; and suppose all possible (
; and suppose all possible (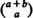 ) voting records are equally probable. The probability distributions of the number of strict and weak lead positions corresponding to
) voting records are equally probable. The probability distributions of the number of strict and weak lead positions corresponding to 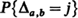 and
and 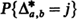 , respectively, have been determined in [4] for
, respectively, have been determined in [4] for 