No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2024
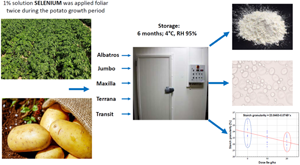
For the proper development of the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), it is essential to provide the plant with micronutrients, including selenium. The availability of the potato for starch industry after harvest is determined by proper storage conditions. Research was undertaken to determine tuber yield, starch yield and quality characteristics of potato starch in relation to cultivar and foliar feeding of plants with selenium during cultivation. Two-factor field experiment was conducted in 2018–2019: I factor – cultivar (Albatros, Jumbo, Maxilla Terrana, Transit), II factor – selenium fertilization (0, 10, 20 g Se/ha). The tests were carried out directly after harvest and after 6 months of tubers storage under constant conditions: temperature 4°C, 95% RH. The highest total tuber and starch yields were obtained by potatoes after application of 20 g Se/ha: 39.42 and 7.94 Mg/ha, respectively. Proportion of large starch grains (>20 μm) was significantly higher for cv. Maxilla – 24.5%. The highest sticking temperature was demonstrated by starch from cv. Maxilla, 69.9°C, while the lowest for the starch of cv. Terrana, 63.3°C. The largest natural losses resulting from transpiration and respiration after long-term storage of tubers received the cv. Transit – 5.0%, and the smallest losses were characterized by the cv. Albatros – 3.9%. Selenium applied during cultivation at dose of 20 g/ha reduced natural losses (−4.3%) and yield starch (−6.2%) and starch content (−1.7%) in tubers. The quality parameters of starch were changed after storage from 0.8 to −3.0%.