No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Optimal linear sofic approximations of countable groups
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 January 2025
Abstract
Let  $G$ be a group. The notion of linear sofic approximations of
$G$ be a group. The notion of linear sofic approximations of  $G$ over an arbitrary field
$G$ over an arbitrary field 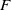 $F$ was introduced and systematically studied by Arzhantseva and Păunescu [3]. Inspired by one of the results of [3], we introduce and study the invariant
$F$ was introduced and systematically studied by Arzhantseva and Păunescu [3]. Inspired by one of the results of [3], we introduce and study the invariant 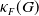 $\kappa _F(G)$ that captures the quality of linear sofic approximations of
$\kappa _F(G)$ that captures the quality of linear sofic approximations of  $G$ over
$G$ over 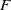 $F$. In this work, we show that when
$F$. In this work, we show that when 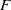 $F$ has characteristic zero and
$F$ has characteristic zero and  $G$ is linear sofic over
$G$ is linear sofic over 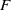 $F$, then
$F$, then 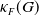 $\kappa _F(G)$ takes values in the interval
$\kappa _F(G)$ takes values in the interval 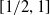 $[1/2,1]$ and
$[1/2,1]$ and 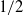 $1/2$ cannot be replaced by any larger value. Further, we show that under the same conditions,
$1/2$ cannot be replaced by any larger value. Further, we show that under the same conditions, 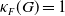 $\kappa _F(G)=1$ when
$\kappa _F(G)=1$ when  $G$ is torsion-free. These results answer a question posed by Arzhantseva and Păunescu [3] for fields of characteristic zero. One of the new ingredients of our proofs is an effective non-concentration estimates for random walks on finitely generated abelian groups, which may be of independent interest.
$G$ is torsion-free. These results answer a question posed by Arzhantseva and Păunescu [3] for fields of characteristic zero. One of the new ingredients of our proofs is an effective non-concentration estimates for random walks on finitely generated abelian groups, which may be of independent interest.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Glasgow Mathematical Journal Trust


