Article contents
(Uniform) convergence of twisted ergodic averages
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 April 2015
Abstract
Let  $T$ be an ergodic measure-preserving transformation on a non-atomic probability space
$T$ be an ergodic measure-preserving transformation on a non-atomic probability space 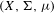 $(X,\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F4},\unicode[STIX]{x1D707})$ . We prove uniform extensions of the Wiener–Wintner theorem in two settings: for averages involving weights coming from Hardy field functions
$(X,\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F4},\unicode[STIX]{x1D707})$ . We prove uniform extensions of the Wiener–Wintner theorem in two settings: for averages involving weights coming from Hardy field functions 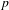 $p$ ,
$p$ , 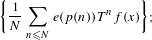 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle \bigg\{\frac{1}{N}\mathop{\sum }_{n\leq N}e(p(n))T^{n}f(x)\bigg\}; & & \displaystyle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle \bigg\{\frac{1}{N}\mathop{\sum }_{n\leq N}e(p(n))T^{n}f(x)\bigg\}; & & \displaystyle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$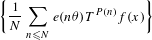 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle \bigg\{\frac{1}{N}\mathop{\sum }_{n\leq N}e(n\unicode[STIX]{x1D703})T^{P(n)}f(x)\bigg\} & & \displaystyle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle \bigg\{\frac{1}{N}\mathop{\sum }_{n\leq N}e(n\unicode[STIX]{x1D703})T^{P(n)}f(x)\bigg\} & & \displaystyle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$ $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\in [0,1]$ . We also give an elementary proof that the above twisted polynomial averages converge pointwise
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\in [0,1]$ . We also give an elementary proof that the above twisted polynomial averages converge pointwise 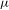 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$ -almost everywhere for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}$ -almost everywhere for 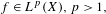 $f\in L^{p}(X),p>1,$ and arbitrary
$f\in L^{p}(X),p>1,$ and arbitrary 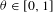 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\in [0,1]$ .
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\in [0,1]$ .
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2015
References
- 8
- Cited by

