Article contents
Sustainable approach to raw clays for ceramic and refractory applications: insights from updated traditional ternary diagrams
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 September 2024
Abstract
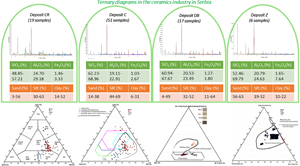
The study analysed 93 samples from four Serbian clay deposits to determine their suitability for ceramics production. The samples were mainly composed of illite and kaolinite. Ternary diagrams were used to classify the samples and evaluate their applicability. Winkler's diagrams, ternary graphs and mineralogical compositions were analysed. The results showed a broader area in these graphs than previously determined for structural ceramics, as well as the potential of these clays for ceramic production. The study used dry-milled, hydraulically semi-dry, pressed and fired samples to assess water absorption and flexural strength and statistical analysis to determine the key parameters influencing final product quality, including that of refractory, wall and floor tiles. This paper evaluates the raw clay materials’ applicability in ceramic production, promoting sustainable use through rapid initial tests, energy savings through dry milling and ecologically sound principles through resource-efficient evaluation.
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Mineralogical Society of the United Kingdom and Ireland
Footnotes
Associate Editor: Michele Dondi
References
A correction has been issued for this article:
- 7
- Cited by
Linked content
Please note a has been issued for this article.

