Article contents
An Endpoint Alexandrov Bakelman Pucci Estimate in the Plane
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 January 2019
Abstract
The classical Alexandrov–Bakelman–Pucci estimate for the Laplacian states 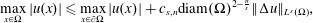 $$\begin{eqnarray}\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|\leqslant \max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x2202}\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|+c_{s,n}\text{diam}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})^{2-\frac{n}{s}}\Vert \unicode[STIX]{x0394}u\Vert _{L^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})},\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|\leqslant \max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x2202}\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|+c_{s,n}\text{diam}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})^{2-\frac{n}{s}}\Vert \unicode[STIX]{x0394}u\Vert _{L^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})},\end{eqnarray}$$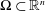 $\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}\subset \mathbb{R}^{n}$,
$\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}\subset \mathbb{R}^{n}$, 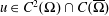 $u\in C^{2}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})\cap C(\overline{\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}})$ and
$u\in C^{2}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})\cap C(\overline{\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}})$ and 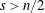 $s>n/2$. The inequality fails for
$s>n/2$. The inequality fails for 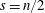 $s=n/2$. A Sobolev embedding result of Milman and Pustylnik, originally phrased in a slightly different context, implies an endpoint inequality: if
$s=n/2$. A Sobolev embedding result of Milman and Pustylnik, originally phrased in a slightly different context, implies an endpoint inequality: if 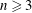 $n\geqslant 3$ and
$n\geqslant 3$ and 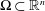 $\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}\subset \mathbb{R}^{n}$ is bounded, then
$\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}\subset \mathbb{R}^{n}$ is bounded, then 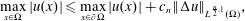 $$\begin{eqnarray}\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|\leqslant \max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x2202}\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|+c_{n}\Vert \unicode[STIX]{x0394}u\Vert _{L^{\frac{n}{2},1}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})},\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|\leqslant \max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x2202}\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|+c_{n}\Vert \unicode[STIX]{x0394}u\Vert _{L^{\frac{n}{2},1}(\unicode[STIX]{x03A9})},\end{eqnarray}$$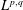 $L^{p,q}$ is the Lorentz space refinement of
$L^{p,q}$ is the Lorentz space refinement of 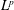 $L^{p}$. This inequality fails for
$L^{p}$. This inequality fails for 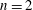 $n=2$, and we prove a sharp substitute result: there exists
$n=2$, and we prove a sharp substitute result: there exists 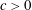 $c>0$ such that for all
$c>0$ such that for all 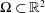 $\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}\subset \mathbb{R}^{2}$ with finite measure,
$\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}\subset \mathbb{R}^{2}$ with finite measure, 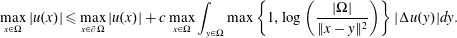 $$\begin{eqnarray}\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|\leqslant \max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x2202}\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|+c\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}\int _{y\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}\max \left\{1,\log \left(\frac{|\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}|}{\Vert x-y\Vert ^{2}}\right)\right\}|\unicode[STIX]{x0394}u(y)|dy.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|\leqslant \max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x2202}\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}|u(x)|+c\max _{x\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}\int _{y\in \unicode[STIX]{x03A9}}\max \left\{1,\log \left(\frac{|\unicode[STIX]{x03A9}|}{\Vert x-y\Vert ^{2}}\right)\right\}|\unicode[STIX]{x0394}u(y)|dy.\end{eqnarray}$$
Keywords
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Canadian Mathematical Society 2018
References
- 2
- Cited by

