No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On Hilbert Covariants
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
Let  $F$ denote a binary form of order
$F$ denote a binary form of order  $d$ over the complex numbers. If
$d$ over the complex numbers. If  $r$ is a divisor of
$r$ is a divisor of  $d$ , then the Hilbert covariant
$d$ , then the Hilbert covariant 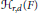 ${{H}_{r,\,d}}\,\left( F \right)$ vanishes exactly when
${{H}_{r,\,d}}\,\left( F \right)$ vanishes exactly when  $F$ is the perfect power of an order
$F$ is the perfect power of an order  $r$ form. In geometric terms, the coefficients of
$r$ form. In geometric terms, the coefficients of 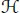 $H$ give defining equations for the image variety
$H$ give defining equations for the image variety 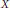 $X$ of an embedding
$X$ of an embedding 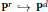 ${{\text{P}}^{r}}\,\to \,{{\text{P}}^{d}}$ . In this paper we describe a new construction of the Hilbert covariant and simultaneously situate it into a wider class of covariants called the Göttingen covariants, all of which vanish on
${{\text{P}}^{r}}\,\to \,{{\text{P}}^{d}}$ . In this paper we describe a new construction of the Hilbert covariant and simultaneously situate it into a wider class of covariants called the Göttingen covariants, all of which vanish on 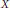 $X$ . We prove that the ideal generated by the coefficients of
$X$ . We prove that the ideal generated by the coefficients of 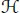 $H$ defines
$H$ defines 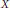 $X$ as a scheme. Finally, we exhibit a generalisation of the Göttingen covariants to
$X$ as a scheme. Finally, we exhibit a generalisation of the Göttingen covariants to 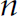 $n$ -ary forms using the classical Clebsch transfer principle.
$n$ -ary forms using the classical Clebsch transfer principle.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2014

