No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
The Determination of Stresses at Nodal Points from Finite Element Solutions to Elastic Problems
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 July 2016
Extract
The application of matrix displacement methods to elastic problems leads to an array of simultaneous equations, of the form:
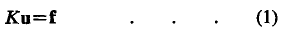
in which K is non-singular. This, when inverted, enables the component deflections u to be determined for any specified loading f. The deformed shape of the system is thus obtained in terms of displacement of the nodes and the latter are used to derive the stress within each element. The stress solution thus lacks precision, since it is not clear as to what point within the element the calculated stress refers. There will be a number of such elements connected to any given node and generally, the computed stress is different within each.
Information
- Type
- Technical Notes
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Royal Aeronautical Society 1971
References
1.
Love, A. E. H.
A Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity, 4th Edition, Dover Publications, New York, 1944.Google Scholar

