Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tan, Choon-Peng
1982.
A functional form for a particular coefficient of ergodicity.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 04,
p.
858.
Tan, Choon-Peng
1982.
A functional form for a particular coefficient of ergodicity.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 4,
p.
858.
Tan, Choon-Peng
1983.
Coefficients of ergodicity with respect to vector norms.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 02,
p.
277.
Seneta, E.
1983.
Spectrum localization by ergodicity coefficients for stochastic matrices.
Linear and Multilinear Algebra,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 4,
p.
343.
Seneta, E.
1984.
Explicit forms for ergodicity coefficients and spectrum localization.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 60,
Issue. ,
p.
187.
Rothblum, Uriel G.
1984.
Explicit Solutions to Optimization Problems on the Intersections of the Unit Ball of the $l_1 $ and $l_\infty $ Norms with a Hyperplane.
SIAM Journal on Algebraic Discrete Methods,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 4,
p.
619.
Seneta, E
1984.
On the limiting set of nonnegative matrix products.
Statistics & Probability Letters,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 3,
p.
159.
Wrobel, A.
1984.
On Markovian decision models with a finite skeleton.
Zeitschrift für Operations Research,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 1,
p.
17.
Rothblum, Uriel G.
and
Tan, Choon Peng
1985.
Upper bounds on the maximum modulus of subdominant eigenvalues of nonnegative matrices.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 66,
Issue. ,
p.
45.
Aldous, David
and
Diaconis, Persi
1987.
Strong uniform times and finite random walks.
Advances in Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 1,
p.
69.
Rhodius, Adolf
1988.
The maximal value for coefficients of ergodicity.
Stochastic Processes and their Applications,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 1,
p.
141.
Rhodius, Adolf
1989.
On almost scrambling stochastic matrices.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 126,
Issue. ,
p.
79.
Hartfiel, D.J.
and
Seneta, E.
1990.
A note on semigroups of regular stochastic matrices.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 141,
Issue. ,
p.
47.
Wallstrom, Timothy C.
1990.
Ergodicity of finite-energy diffusions.
Transactions of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 318,
Issue. 2,
p.
735.
Seneta, Eugene
1993.
Explicit forms for ergodicity coefficients of stochastic matrices.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 191,
Issue. ,
p.
245.
Hartcfiel, D.J.
1993.
Cyclic markov set-chains.
Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
145.
Seneta, E.
1993.
Sensitivity of finite Markov chains under perturbation.
Statistics & Probability Letters,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 2,
p.
163.
Seneta, E.
1993.
Ergodicity for products of infinite stochastic matrices.
Journal of Theoretical Probability,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 2,
p.
345.
Rhodius, Adolf
1993.
On explicit forms for ergodicity coefficients.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 194,
Issue. ,
p.
71.
Cohen, Joel E.
Iwasa, Yoh
Rautu, Gh.
Beth Ruskai, Mary
Seneta, Eugene
and
Zbaganu, Gh.
1993.
Relative entropy under mappings by stochastic matrices.
Linear Algebra and its Applications,
Vol. 179,
Issue. ,
p.
211.
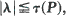 where λ is any non-unit eigenvalue of P. The essential purpose is exposition and unification, with the aid of simple informal proofs.
where λ is any non-unit eigenvalue of P. The essential purpose is exposition and unification, with the aid of simple informal proofs.
