No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Asymptotic behaviors of subcritical branching killed Brownian motion with drift
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 May 2025
Abstract
In this paper, we study asymptotic behaviors of a subcritical branching Brownian motion with drift 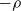 $-\rho$, killed upon exiting
$-\rho$, killed upon exiting 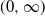 $(0, \infty)$, and offspring distribution
$(0, \infty)$, and offspring distribution 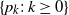 $\{p_k{:}\; k\ge 0\}$. Let
$\{p_k{:}\; k\ge 0\}$. Let 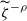 $\widetilde{\zeta}^{-\rho}$ be the extinction time of this subcritical branching killed Brownian motion,
$\widetilde{\zeta}^{-\rho}$ be the extinction time of this subcritical branching killed Brownian motion,  $\widetilde{M}_t^{-\rho}$ the maximal position of all the particles alive at time t and
$\widetilde{M}_t^{-\rho}$ the maximal position of all the particles alive at time t and 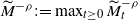 $\widetilde{M}^{-\rho}:\!=\max_{t\ge 0}\widetilde{M}_t^{-\rho}$ the all-time maximal position. Let
$\widetilde{M}^{-\rho}:\!=\max_{t\ge 0}\widetilde{M}_t^{-\rho}$ the all-time maximal position. Let 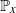 $\mathbb{P}_x$ be the law of this subcritical branching killed Brownian motion when the initial particle is located at
$\mathbb{P}_x$ be the law of this subcritical branching killed Brownian motion when the initial particle is located at 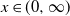 $x\in (0,\infty)$. Under the assumption
$x\in (0,\infty)$. Under the assumption 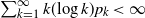 $\sum_{k=1}^\infty k ({\log}\; k) p_k <\infty$, we establish the decay rates of
$\sum_{k=1}^\infty k ({\log}\; k) p_k <\infty$, we establish the decay rates of 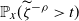 $\mathbb{P}_x(\widetilde{\zeta}^{-\rho}>t)$ and
$\mathbb{P}_x(\widetilde{\zeta}^{-\rho}>t)$ and 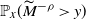 $\mathbb{P}_x(\widetilde{M}^{-\rho}>y)$ as t and y respectively tend to
$\mathbb{P}_x(\widetilde{M}^{-\rho}>y)$ as t and y respectively tend to  $\infty$. We also establish the decay rate of
$\infty$. We also establish the decay rate of 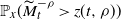 $\mathbb{P}_x(\widetilde{M}_t^{-\rho}> z(t,\rho))$ as
$\mathbb{P}_x(\widetilde{M}_t^{-\rho}> z(t,\rho))$ as 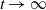 $t\to\infty$, where
$t\to\infty$, where 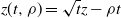 $z(t,\rho)=\sqrt{t}z-\rho t$ for
$z(t,\rho)=\sqrt{t}z-\rho t$ for 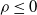 $\rho\leq 0$ and
$\rho\leq 0$ and  $z(t,\rho)=z$ for
$z(t,\rho)=z$ for 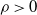 $\rho>0$. As a consequence, we obtain a Yaglom-type limit theorem.
$\rho>0$. As a consequence, we obtain a Yaglom-type limit theorem.
Keywords
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Applied Probability Trust


