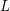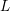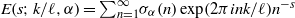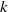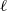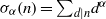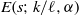Refine search
Actions for selected content:
2 results
Unnormalized differences between zeros of L-functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 2 / February 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2014, pp. 230-252
- Print publication:
- February 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
ZEROS OF THE ESTERMANN ZETA FUNCTION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 94 / Issue 1 / February 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2013, pp. 38-49
- Print publication:
- February 2013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation