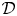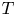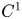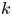Refine search
Actions for selected content:
5 results
Involutivity of distributions at points of superdense tangency with respect to normal currents
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2023, pp. 508-524
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GEOMETRIC SYMMETRY TECHNIQUES FOR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 93 / Issue 2 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2015, pp. 342-344
- Print publication:
- April 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Moving Frames for Lie Pseudo–Groups
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 60 / Issue 6 / 01 December 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 1336-1386
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Multi-flag systems and ordinary differential equations
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 166 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2016, pp. 1-27
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Helices, Hasimoto Surfaces and Bäcklund Transformations
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / 01 December 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 427-439
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2000
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation