The purpose of the present paper is to give a new, simple proof of the theorem of M. Davis, H. Putnam and J. Robinson [1961], which states that every recursively enumerable relation A(a1, …, an) is exponential diophantine, i.e. can be represented in the form
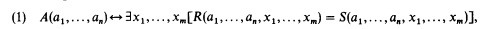
where a1 …, an, x1, …, xm range over natural numbers and R and S are functions built up from these variables and natural number constants by the operations of addition, A + B, multiplication, AB, and exponentiation, AB. We refer to the variables a1,…,an as parameters and the variables x1 …, xm as unknowns.
Historically, the Davis, Putnam and Robinson theorem was one of the important steps in the eventual solution of Hilbert's tenth problem by the second author [1970], who proved that the exponential relation, a = bc, is diophantine, and hence that the right side of (1) can be replaced by a polynomial equation. But this part will not be reproved here. Readers wishing to read about the proof of that are directed to the papers of Y. Matijasevič [1971a], M. Davis [1973], Y. Matijasevič and J. Robinson [1975] or C. Smoryński [1972]. We concern ourselves here for the most part only with exponential diophantine equations until §5 where we mention a few consequences for the class NP of sets computable in nondeterministic polynomial time.
 $\Pi ^0_1$ CLASSES
$\Pi ^0_1$ CLASSES
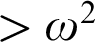 ${>}\ \omega ^2$
-Fickle Recursively Enumerable Turing Degrees
${>}\ \omega ^2$
-Fickle Recursively Enumerable Turing Degrees
 $_2$
SETS
$_2$
SETS