No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2016
With HST and WFPC2, galaxies in the Medium Deep Survey can be reliably classified to magnitudes I814 ≲ 22.0 in the F814W band, at a mean redshift 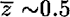 . The main result is the relatively high proportion (~40%) of objects which are in some way irregular or anomalous, and which are of relevance in understanding the origin of the familiar excess population of faint galaxies. These diverse objects include compact galaxies, apparently interacting pairs, galaxies with superluminous starforming regions and diffuse low surface brightness galaxies of various forms. The ‘irregulars’ and ‘peculiar’ galaxies contribute most of the excess counts in the I-band at our limiting magnitude, and may explain the ‘faint blue galaxy’ problem.
. The main result is the relatively high proportion (~40%) of objects which are in some way irregular or anomalous, and which are of relevance in understanding the origin of the familiar excess population of faint galaxies. These diverse objects include compact galaxies, apparently interacting pairs, galaxies with superluminous starforming regions and diffuse low surface brightness galaxies of various forms. The ‘irregulars’ and ‘peculiar’ galaxies contribute most of the excess counts in the I-band at our limiting magnitude, and may explain the ‘faint blue galaxy’ problem.