No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 May 2020
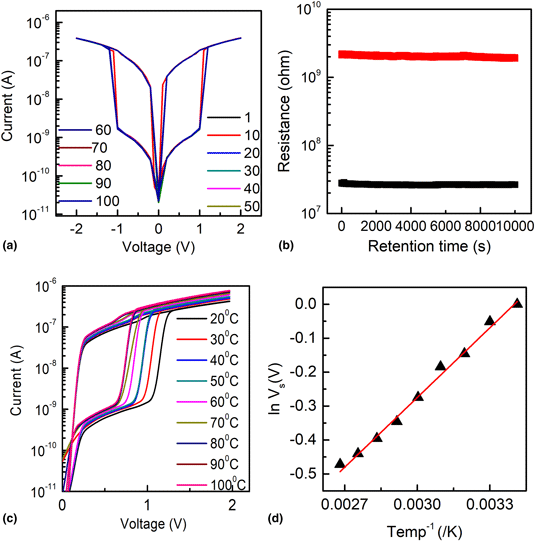
In this work, the authors developed SiC(10 nm)/Ag/SiC(10 nm) thin films showing an electroforming-free resistive switching (RS) effect with a switching ratio of 102. The observed RS effect is attributed to charging and discharging of Ag nanoparticles in the film layer. Further, SiC/Ag/SiC film shows an excellent endurance and retention as well as a good thermal stability of RS characteristics. It is also identified that the switching ratio is invariant but the switching voltage of the device greatly depends on the Ag nanoparticles concentration and the operation temperature of the device. Therefore, SiC/Ag/SiC thin films are attractive for next-generation memory devices with enhanced durability.