Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 January 2018
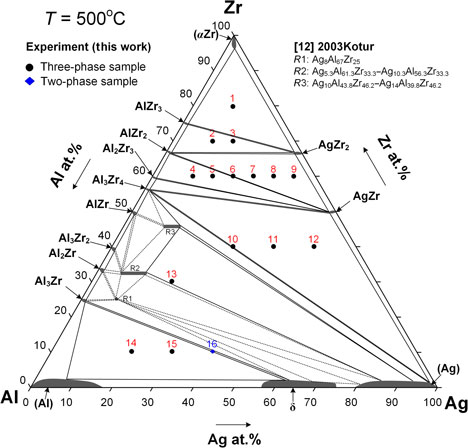
Forty-eight different Ag–Al–Zr ternary alloys were prepared in various compositions to determine the metallic glass region in the Ag–Al–Zr ternary system. Experimental results indicated that the metallic glass region in the Ag–Al–Zr ternary system is Ag20–30Al10–30Zr50–60. The Ag20Al30Zr50 and Ag30Al20Zr50 alloys are supposed to have the best glass-forming ability in the Ag–Al–Zr ternary system. The phase equilibria of the Ag–Al–Zr ternary system at 773 K (500 °C) were investigated and compared with the metallic glass region results in the Ag–Al–Zr ternary system. Ternary isothermal sections of the Ag–Al–Zr system at 773 K (500 °C) were established and two ternary intermetallic phases were observed in this isothermal section.