Article contents
Free Lie algebras as modules for symmetric groups
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 April 2009
Abstract
Let r be a positive integer, F a field of odd prime characteristic p, and L the free Lie algebra of rank r over F. Consider L a module for the symmetric group 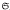 , of all permutations of a free generating set of L. The homogeneous components Ln of L are finite dimensional submodules, and L is their direct sum. For p ≤ r ≤ 2p, the main results of this paper identify the non-porojective indecomposable direct summands of the Ln as Specht modules or dual Specht modules corresponding to certain partitions. For the case r = p, the multiplicities of these indecomposables in the direct decompositions of the Ln are also determined, as are the multiplicities of the projective indecomposables. (Corresponding results for p = 2 have been obtained elsewhere.)
, of all permutations of a free generating set of L. The homogeneous components Ln of L are finite dimensional submodules, and L is their direct sum. For p ≤ r ≤ 2p, the main results of this paper identify the non-porojective indecomposable direct summands of the Ln as Specht modules or dual Specht modules corresponding to certain partitions. For the case r = p, the multiplicities of these indecomposables in the direct decompositions of the Ln are also determined, as are the multiplicities of the projective indecomposables. (Corresponding results for p = 2 have been obtained elsewhere.)
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Australian Mathematical Society 1999
References
- 4
- Cited by

