Article contents
Variational formulation of marine ice-sheet and subglacial-lake grounding-line dynamics
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 May 2021
Abstract
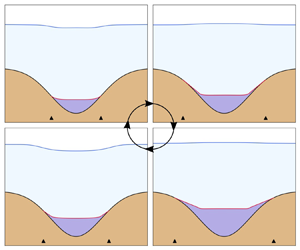
Grounding lines exist where land-based glacial ice flows on to a body of water. Accurately modelling grounding-line migration at the ice–ocean interface is essential for estimating future ice-sheet mass change. On the interior of ice sheets, the shores of subglacial lakes are also grounding lines. Grounding-line positions are sensitive to water volume changes such as sea-level rise or subglacial-lake drainage. Here, we introduce numerical methods for simulating grounding-line dynamics in the marine ice sheet and subglacial-lake settings. Variational inequalities arise from contact conditions that relate normal stress, water pressure and velocity at the base. Existence and uniqueness of solutions to these problems are established using a minimisation argument. A penalty method is used to replace the variational inequalities with variational equations that are solved using a finite-element method. We illustrate the grounding-line response to tidal cycles in the marine ice-sheet problem and filling–draining cycles in the subglacial-lake problem. We introduce two computational benchmarks where the known lake volume change is used to measure the accuracy of the numerical method.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 10
- Cited by


