Article contents
Large-eddy simulation study of unsteady wake dynamics and geometric sensitivity on a skewed bump
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 December 2019
Abstract
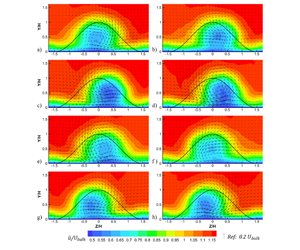
Large-eddy simulations of a skewed bump are performed with the bump at angles of  $10^{\circ }$ and
$10^{\circ }$ and  $50^{\circ }$ with respect to the free stream. The wake has a large separation bubble and unsteady vortex structures that are highly sensitive to the bump angle. The
$50^{\circ }$ with respect to the free stream. The wake has a large separation bubble and unsteady vortex structures that are highly sensitive to the bump angle. The  $10^{\circ }$ bump has secondary separation with forward-facing flow in the main separation bubble. The Reynolds stress suggests large-scale motions in the wake, but are insufficient to understand the shedding dynamics. The quasi-periodic shedding cycle is reconstructed using spectral proper orthogonal decomposition. For the
$10^{\circ }$ bump has secondary separation with forward-facing flow in the main separation bubble. The Reynolds stress suggests large-scale motions in the wake, but are insufficient to understand the shedding dynamics. The quasi-periodic shedding cycle is reconstructed using spectral proper orthogonal decomposition. For the  $10^{\circ }$ case, opposite-sign streamwise vortices are alternately advected downstream in the wake, but only a single vortex is distinguishable in the
$10^{\circ }$ case, opposite-sign streamwise vortices are alternately advected downstream in the wake, but only a single vortex is distinguishable in the  $50^{\circ }$ case. The wake streamwise velocity pulses twice each cycle in the
$50^{\circ }$ case. The wake streamwise velocity pulses twice each cycle in the  $10^{\circ }$ bump, but once per cycle in the
$10^{\circ }$ bump, but once per cycle in the  $50^{\circ }$ bump. The separation bubble and wake oscillate in the spanwise direction. Conditional averaging shows that the vortices are associated with low streamwise velocity and high turbulence. Surface pressures on the bump have negatively skewed distributions in regions on the upstream face and in the separation bubble. In the separation bubble, fluctuations associated with the shedding cycle contribute to the negative skewness.
$50^{\circ }$ bump. The separation bubble and wake oscillate in the spanwise direction. Conditional averaging shows that the vortices are associated with low streamwise velocity and high turbulence. Surface pressures on the bump have negatively skewed distributions in regions on the upstream face and in the separation bubble. In the separation bubble, fluctuations associated with the shedding cycle contribute to the negative skewness.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Cambridge University Press
References
- 5
- Cited by

