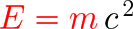Refine search
Actions for selected content:
18 results
Curriculum uitarum: Homer and the many lives of Pythagoras and Empedocles
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Hellenic Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2025, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Pythagoras
-
- Book:
- Ovid and Plato
- Published online:
- 19 June 2025
- Print publication:
- 03 July 2025, pp 92-113
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
9 - Metapontium: Night and Day; Black and White
- from Part II - Aeolian Origins in Myth
-
- Book:
- Aeolic and Aeolians
- Published online:
- 21 November 2024
- Print publication:
- 21 November 2024, pp 236-276
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 3 - Daimones between Plato and Pythagoras
-
- Book:
- Reconstructing Empedocles' Thought
- Published online:
- 01 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 08 February 2024, pp 138-184
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
UNTARNISHED BOOKS AND VANISHED KINGS: NUMA, OVID AND ENNIUS
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 73 / Issue 1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2023, pp. 127-137
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 1 - The Ancient World
-
- Book:
- A History of Western Philosophy of Music
- Published online:
- 18 January 2023
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2023, pp 1-34
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - Psychological Foundations in Ancient Greece
- from Part I - Psychology’s Historical Foundations
-
- Book:
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Published online:
- 04 November 2022
- Print publication:
- 17 November 2022, pp 36-58
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 2 - Long walk to wisdom
- from Part I - The Republic
-
- Book:
- Explorations in Ancient and Modern Philosophy
- Published online:
- 24 March 2022
- Print publication:
- 31 March 2022, pp 73-77
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 2 - Pythagorean Immortality of the Soul?
-
-
- Book:
- Immortality in Ancient Philosophy
- Published online:
- 20 May 2021
- Print publication:
- 03 June 2021, pp 41-65
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 4 - Hyperborea and the Classical Economies of Knowledge
- from Part II - Cosmography, Periods and Genres
-
- Book:
- Cosmography and the Idea of Hyperborea in Ancient Greece
- Published online:
- 08 May 2021
- Print publication:
- 22 April 2021, pp 266-319
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 1 - Hesiod and Daimonification in the Archaic and Classical Periods
-
- Book:
- Posthuman Transformation in Ancient Mediterranean Thought
- Published online:
- 24 December 2020
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021, pp 21-30
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Looking for auctoritas in Ennius’ Annals
- from II - Authority
-
-
- Book:
- Ennius' <I>Annals</I>
- Published online:
- 10 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 April 2020, pp 125-146
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 10 - Immortality: Philosophy, Cinema, Ovid
- from Part V - Eternal Returns
-
- Book:
- Ovid on Screen
- Published online:
- 27 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 341-352
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 1 - When Did Kosmos Become the Kosmos?
-
-
- Book:
- Cosmos in the Ancient World
- Published online:
- 18 June 2019
- Print publication:
- 04 July 2019, pp 22-41
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
How Einstein’s Theory of Relativity Gives us
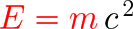 $\color {red} E=m\,\color {black}c^{\,2}$ and the Atomic Bomb
$\color {red} E=m\,\color {black}c^{\,2}$ and the Atomic Bomb
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S338 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 103-106
- Print publication:
- October 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Chapter 14 - Pythagoras in the historical tradition: from Herodotus to Diodorus Siculus
-
-
- Book:
- A History of Pythagoreanism
- Published online:
- 05 May 2014
- Print publication:
- 24 April 2014, pp 296-314
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 1 - Pythagoras
-
-
- Book:
- A History of Pythagoreanism
- Published online:
- 05 May 2014
- Print publication:
- 24 April 2014, pp 24-45
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
11 - Self-definition vis-à-vis the Graeco-Roman world
- from Part III - Community Traditions and Self-Definition
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge History of Christianity
- Published online:
- 28 March 2008
- Print publication:
- 19 January 2006, pp 230-244
-
- Chapter
- Export citation