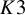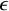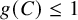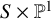1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
In [Reference NesterovNes21],
![]() $\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps to a moduli space of sheaves on a surface S were introduced. When applied to a Hilbert scheme of points
$\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps to a moduli space of sheaves on a surface S were introduced. When applied to a Hilbert scheme of points
![]() $S^{[n]}$
, moduli spaces of
$S^{[n]}$
, moduli spaces of
![]() $\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps
$\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(S^{[n]},\beta )$
interpolate between moduli spaces of stable maps to
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(S^{[n]},\beta )$
interpolate between moduli spaces of stable maps to
![]() $S^{[n]}$
and moduli spaces of one-dimensional subschemes on
$S^{[n]}$
and moduli spaces of one-dimensional subschemes on
![]() $S\times C$
for a moving nodal curve C,
$S\times C$
for a moving nodal curve C,
Zhou’s master-space technique [Reference ZhouZho22] leads to quasimap wall-crossing formulas associated to a variation of the stability parameter
![]() $\epsilon \in {\mathbb {R}}_{>0}$
. By Equation (1.1), these wall-crossing formulas therefore relate the Gromov–Witten (GW) theory of
$\epsilon \in {\mathbb {R}}_{>0}$
. By Equation (1.1), these wall-crossing formulas therefore relate the Gromov–Witten (GW) theory of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
and the Donaldson–Thomas (DT) theory of
$S^{[n]}$
and the Donaldson–Thomas (DT) theory of
![]() $S\times C$
with relative insertions.
$S\times C$
with relative insertions.
The case of moduli spaces of sheaves on a
![]() $K3$
surface requires a special treatment due to the presence of holomorphic symplectic forms and, consequently, the vanishing of the standard virtual fundamental class on
$K3$
surface requires a special treatment due to the presence of holomorphic symplectic forms and, consequently, the vanishing of the standard virtual fundamental class on
![]() ${\overline M}_{g,N}(S^{[n]},\beta )$
. In more precise terms, the vanishing is due to existence of a surjective cosection of the obstruction-theory complex
${\overline M}_{g,N}(S^{[n]},\beta )$
. In more precise terms, the vanishing is due to existence of a surjective cosection of the obstruction-theory complex
![]() ${\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet }$
,
${\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet }$
,
A nontrivial reduced enumerative theory is obtained by taking the cone of
![]() $\sigma $
. The same phenomenon happens on the DT side. The obstruction theory of moduli spaces
$\sigma $
. The same phenomenon happens on the DT side. The obstruction theory of moduli spaces
![]() $\mathrm {Hilb}_{n,\check {\beta }}(S\times C_{g,N})$
admits a surjective cosection, hence the reduction is also necessary. In order to relate the reduced GW theory of
$\mathrm {Hilb}_{n,\check {\beta }}(S\times C_{g,N})$
admits a surjective cosection, hence the reduction is also necessary. In order to relate the reduced GW theory of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
and the reduced DT theory of
$S^{[n]}$
and the reduced DT theory of
![]() $S\times C$
, we have to furnish
$S\times C$
, we have to furnish
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(S^{[n]},\beta )$
with a surjective cosection and, consequently, with a reduced obstruction theory. This is the principle aim of the present work.
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(S^{[n]},\beta )$
with a surjective cosection and, consequently, with a reduced obstruction theory. This is the principle aim of the present work.
Once the reduced wall-crossing formula is established in Theorem 3.7, we proceed to proving the following results:
-
• the (reduced) quantum cohomology of
 $S^{[n]}$
is determined by the relative Pandharipande–Thomas (PT) theory of
$S^{[n]}$
is determined by the relative Pandharipande–Thomas (PT) theory of
 $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
, if S is a
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
, if S is a
 $K3$
surface, conjectured in [Reference OberdieckObe19];
$K3$
surface, conjectured in [Reference OberdieckObe19]; -
• the Hilbert-schemes part of the Igusa cusp form conjecture, conjectured in [Reference Okounkov and PandharipandeOP10];
-
• higher-rank/rank-one DT correspondence with relative insertions for
 $S \times \mathbb {P}^1$
and
$S \times \mathbb {P}^1$
and
 $S \times E$
, if S is a
$S \times E$
, if S is a
 $K3$
surface and E is an elliptic curve;
$K3$
surface and E is an elliptic curve; -
• DT/PT correspondence with relative insertions for
 $S \times \mathbb {P}^1$
, if S is a
$S \times \mathbb {P}^1$
, if S is a
 $K3$
surface.
$K3$
surface.
1.2. Cosection
Let S be a
![]() $K3$
surface and
$K3$
surface and
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
be a projective moduli space of slope stable sheaves on S in a class
$M(\mathbf {v})$
be a projective moduli space of slope stable sheaves on S in a class
![]() $\mathbf {v} \in K_{\mathrm {num}}(S)$
. To give a short motivation for our forthcoming considerations, let us recall the origin of reduced perfect obstruction theory of the GW theory of
$\mathbf {v} \in K_{\mathrm {num}}(S)$
. To give a short motivation for our forthcoming considerations, let us recall the origin of reduced perfect obstruction theory of the GW theory of
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
. Since
$M(\mathbf {v})$
. Since
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
is hyper-Kähler, for any algebraic curve class
$M(\mathbf {v})$
is hyper-Kähler, for any algebraic curve class
![]() $\beta \in H_2(M(\mathbf {v}),{\mathbb {Z}})$
, there exists a deformation of
$\beta \in H_2(M(\mathbf {v}),{\mathbb {Z}})$
, there exists a deformation of
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
over a small disk
$M(\mathbf {v})$
over a small disk
![]() $\Delta $
,
$\Delta $
,
for which the horizontal lift of
![]() $\beta $
is of
$\beta $
is of
![]() $(k,k)$
type only at the central fiber (for our purposes,
$(k,k)$
type only at the central fiber (for our purposes,
![]() $\Delta $
can be replaced by a first-order neighbourhood of the origin
$\Delta $
can be replaced by a first-order neighbourhood of the origin
![]() $\operatorname {Spec} ({\mathbb {C}}[\epsilon ]/\epsilon ^2)$
). In particular, the standard GW invariants vanish. We will call such family a twistor family associated to the class
$\operatorname {Spec} ({\mathbb {C}}[\epsilon ]/\epsilon ^2)$
). In particular, the standard GW invariants vanish. We will call such family a twistor family associated to the class
![]() $\beta $
and refer to [Reference Kool and ThomasKT14, Section 2.1] for more about twistor families in the context of enumerative geometry.
$\beta $
and refer to [Reference Kool and ThomasKT14, Section 2.1] for more about twistor families in the context of enumerative geometry.
To get a nontrivial enumerative theory, we have to remove obstructions that arise via such deformations of
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
. However, in the case of
$M(\mathbf {v})$
. However, in the case of
![]() $\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps, we need twistor families not just of the moduli space
$\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps, we need twistor families not just of the moduli space
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
but of the pair
$M(\mathbf {v})$
but of the pair
![]() $(M(\mathbf {v}),\mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
, where
$(M(\mathbf {v}),\mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
, where
![]() $\mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v})$
is the rigidified stack of all sheaves in the given class [Reference NesterovNes21]. Such twistor families can be given by noncommutative deformations of S. Let us now elaborate on this point by slightly changing the point of view.
$\mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v})$
is the rigidified stack of all sheaves in the given class [Reference NesterovNes21]. Such twistor families can be given by noncommutative deformations of S. Let us now elaborate on this point by slightly changing the point of view.
For simplicity, assume
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[1]}=S$
. A map
$M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[1]}=S$
. A map
![]() $f\colon C \rightarrow S$
of degree
$f\colon C \rightarrow S$
of degree
![]() $\beta $
is determined by its graph on
$\beta $
is determined by its graph on
![]() $S\times C$
. Let I be the associated ideal sheaf of this graph. Deformation theories of I, as a sheaf with fixed determinant, and of f are equivalent. Assuming C is smooth and
$S\times C$
. Let I be the associated ideal sheaf of this graph. Deformation theories of I, as a sheaf with fixed determinant, and of f are equivalent. Assuming C is smooth and
![]() $\beta \neq 0$
, the existence of a first-order twistor family associated to the class
$\beta \neq 0$
, the existence of a first-order twistor family associated to the class
![]() $\beta $
is therefore equivalent to the surjectivity of the following composition
$\beta $
is therefore equivalent to the surjectivity of the following composition
that is, to the existence of a class
![]() $\kappa _{\beta } \in H^1(T_S)$
whose image is nonzero with respect to the composition above, where
$\kappa _{\beta } \in H^1(T_S)$
whose image is nonzero with respect to the composition above, where
![]() $\sigma _I:={\mathrm {tr}}(* \cdot -\mathrm {At}(I))$
for the Atiyah class
$\sigma _I:={\mathrm {tr}}(* \cdot -\mathrm {At}(I))$
for the Atiyah class
![]() $\mathrm {At}(I) \in \operatorname {Ext}^1(I,I\otimes \Omega ^1_{S\times C})$
. To see this, recall that the second map gives the obstruction to deform I along a first-order deformation
$\mathrm {At}(I) \in \operatorname {Ext}^1(I,I\otimes \Omega ^1_{S\times C})$
. To see this, recall that the second map gives the obstruction to deform I along a first-order deformation
![]() $\kappa \in H^1(T_S)$
, while the third map, called semiregularity map [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03], relates obstructions of deforming I to the obstructions of
$\kappa \in H^1(T_S)$
, while the third map, called semiregularity map [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03], relates obstructions of deforming I to the obstructions of
to stay of Hodge type
![]() $(k,k)$
. With these interpretations in mind, it is not difficult to grasp that
$(k,k)$
. With these interpretations in mind, it is not difficult to grasp that
![]() $\kappa _{\beta }$
is indeed our first-order twistor family associated to
$\kappa _{\beta }$
is indeed our first-order twistor family associated to
![]() $\beta $
.
$\beta $
.
The semiregularity map
![]() $\sigma _I$
globalises, that is, there exists a cosection
$\sigma _I$
globalises, that is, there exists a cosection
of the obstruction-theory complex of the moduli space of ideals
![]() $\operatorname {\mathrm {Hilb}}(S\times C)$
. This cosection
$\operatorname {\mathrm {Hilb}}(S\times C)$
. This cosection
![]() $\sigma $
is surjective by the existence of first-order twistor families, if the second Chern character of ideals is equal to
$\sigma $
is surjective by the existence of first-order twistor families, if the second Chern character of ideals is equal to
![]() $(\beta , n)$
for
$(\beta , n)$
for
![]() $\beta \neq 0$
. By the cosection localisation introduced by Kiem–Li [Reference Kiem and LiKL13], the standard virtual fundamental class therefore vanishes. To make the enumerative theory nontrivial, we have to consider the reduced obstruction-theory complex
$\beta \neq 0$
. By the cosection localisation introduced by Kiem–Li [Reference Kiem and LiKL13], the standard virtual fundamental class therefore vanishes. To make the enumerative theory nontrivial, we have to consider the reduced obstruction-theory complex
![]() ${\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet }_{\mathrm {red}}:=\mathrm {cone}(\sigma )[-1]$
. Proving that
${\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet }_{\mathrm {red}}:=\mathrm {cone}(\sigma )[-1]$
. Proving that
![]() ${\mathbb {E}}^\bullet _{\mathrm {red}}$
defines an obstruction theory,
${\mathbb {E}}^\bullet _{\mathrm {red}}$
defines an obstruction theory,
is difficult, we show it under a certain assumption in Proposition A.1. Instead, [Reference Kiem and LiKL13] provides a construction of the reduced virtual fundamental class without an obstruction-theory morphism.
Let us come back to the case of a general moduli space of sheaves
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
. By construction of
$M(\mathbf {v})$
. By construction of
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
, the deformation theory of quasimaps to
$M(\mathbf {v})$
, the deformation theory of quasimaps to
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
is equivalent to the one of sheaves on threefolds of the type
$M(\mathbf {v})$
is equivalent to the one of sheaves on threefolds of the type
![]() $S\times C$
; see [Reference NesterovNes21, Proposition 5.1)] for more details. The obstruction theory of higher-rank sheaves on
$S\times C$
; see [Reference NesterovNes21, Proposition 5.1)] for more details. The obstruction theory of higher-rank sheaves on
![]() $S\times C$
also admits a cosection given by the semiregularity map. We want to show it is surjective. However, already for
$S\times C$
also admits a cosection given by the semiregularity map. We want to show it is surjective. However, already for
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[n]}$
with
$M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[n]}$
with
![]() $n>1$
, there is a problem with the argument presented above. If the degree of
$n>1$
, there is a problem with the argument presented above. If the degree of
![]() $f \colon C \rightarrow S^{[n]}$
is equal to a multiple of the exceptional curve class,Footnote
1
then Equation (1.2) is zero. Indeed, in this case,
$f \colon C \rightarrow S^{[n]}$
is equal to a multiple of the exceptional curve class,Footnote
1
then Equation (1.2) is zero. Indeed, in this case,
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}_{2}(I)=(0,n)$
, and the composition (1.2) is equal to the contraction
${\mathrm {ch}}_{2}(I)=(0,n)$
, and the composition (1.2) is equal to the contraction
![]() $\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}_{2}(I) \rangle $
, which therefore pairs trivially with classes in
$\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}_{2}(I) \rangle $
, which therefore pairs trivially with classes in
![]() $H^1(T_S)$
. The geometric interpretation of this phenomenon is that the exceptional curve class of
$H^1(T_S)$
. The geometric interpretation of this phenomenon is that the exceptional curve class of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
stays of Hodge type
$S^{[n]}$
stays of Hodge type
![]() $(k,k)$
along commutative deformations of S because punctorial Hilbert schemes deform to punctorial Hilbert schemes under commutative deformations of S. To fix the argument, we have to consider classes not just in
$(k,k)$
along commutative deformations of S because punctorial Hilbert schemes deform to punctorial Hilbert schemes under commutative deformations of S. To fix the argument, we have to consider classes not just in
![]() $H^1(T_S)$
, but in a larger space
$H^1(T_S)$
, but in a larger space
that is, we have to consider noncommutative first-order twistor families to prove the surjectivity of the semiregularity map.
1.3. Strategy
For surjectivity of the semiregularity map, we will largely follow [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03, Section 4] and [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Proposition 11] with few extra layers of complications. Firstly, since our threefold
![]() $S\times C$
might be singular (because C is nodal), we have to consider Atiyah classes valued in
$S\times C$
might be singular (because C is nodal), we have to consider Atiyah classes valued in
![]() $\Omega ^1_{S} \boxplus \omega _C$
,
$\Omega ^1_{S} \boxplus \omega _C$
,
instead of
![]() $\Omega ^1_{S} \boxplus {\mathbb {L}}_C=\Omega ^1_{S} \boxplus \Omega ^1_C$
, as the latter does not behave well under degenerations. Chern characters of sheaves are then defined via the Atiyah class of the form as above. Secondly, after establishing the expected correspondence between degrees of quasimaps and Chern characters of sheaves, we allow contractions with classes in
$\Omega ^1_{S} \boxplus {\mathbb {L}}_C=\Omega ^1_{S} \boxplus \Omega ^1_C$
, as the latter does not behave well under degenerations. Chern characters of sheaves are then defined via the Atiyah class of the form as above. Secondly, after establishing the expected correspondence between degrees of quasimaps and Chern characters of sheaves, we allow contractions with classes in
instead of just
![]() $H^1(T_S)$
, unlike in [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03, Section 4]. Proposition 2.3 is a vast extension of [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Proposition 11] and implies surjectivity of the global semiregularity map for higher-rank sheaves, Corollary 3.2.
$H^1(T_S)$
, unlike in [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03, Section 4]. Proposition 2.3 is a vast extension of [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Proposition 11] and implies surjectivity of the global semiregularity map for higher-rank sheaves, Corollary 3.2.
Having constructed a surjective cosection of the obstruction theory, ideally one would like to reduce the obstruction theory. However, due to the involvement of noncommutative geometry in our considerations, we can reduce the obstruction theory only under a certain assumption, which is not unnatural; see Proposition A.1 for more details. For that reason, we do not use our reduced obstruction theory for the construction of the reduced virtual fundamental class. We instead choose to work with reduced classes of [Reference Kiem and LiKL13].
1.4. Applications of the quasimap wall-crossing
1.4.1. Enumerative geometry of
 $S^{[n]}$
$S^{[n]}$
Let E be a fixed elliptic curve. A moduli space of nonconstant maps from E to
![]() $S^{[n]}$
up to translations by E is of reduced virtual dimension 0. Hence, the associated GW invariants do not require insertions, and we can define a virtual count of E inside
$S^{[n]}$
up to translations by E is of reduced virtual dimension 0. Hence, the associated GW invariants do not require insertions, and we can define a virtual count of E inside
![]() $S^{[n]}$
. Applying the reduced wall-crossing to these GW invariants, we obtain that, up to the wall-crossing terms, they are equal to rank-one DT invariants on the Calabi–Yau threefold
$S^{[n]}$
. Applying the reduced wall-crossing to these GW invariants, we obtain that, up to the wall-crossing terms, they are equal to rank-one DT invariants on the Calabi–Yau threefold
![]() $S\times E$
,
$S\times E$
,
In [Reference OberdieckObe21b], the wall-crossing terms are shown to be virtual Euler numbers of certain Quot schemes, which are computed for
![]() $S^{[n]}$
, if S is a
$S^{[n]}$
, if S is a
![]() $K3$
surface. Both theories in Equation (1.3) are subjects of the Igusa cusp form conjecture [Reference Oberdieck and PandharipandeOP16, Conjecture A], which consists of two parts:
$K3$
surface. Both theories in Equation (1.3) are subjects of the Igusa cusp form conjecture [Reference Oberdieck and PandharipandeOP16, Conjecture A], which consists of two parts:
-
• expressing DT invariants of
 $S\times E$
in terms of the Igusa cusp form;
$S\times E$
in terms of the Igusa cusp form; -
• expressing the difference of DT invariants of
 $S\times E$
and GW invariants of
$S\times E$
and GW invariants of
 $S^{[n]}$
associated to E in terms of an explicit correction term.
$S^{[n]}$
associated to E in terms of an explicit correction term.
The first part was proved in a series of papers [Reference Oberdieck and ShenOS20], [Reference Oberdieck and PixtonOP18]. While the second part is therefore a consequence of the reduced quasimap wall-crossing (1.3) together with the computations of [Reference OberdieckObe21b]. This completes the proof of the Igusa cusp form conjecture and provides an expression for GW invariants of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
associated to E. We refer to Section 4.2 for more details about this conjecture.
$S^{[n]}$
associated to E. We refer to Section 4.2 for more details about this conjecture.
In a similar vein, in [Reference OberdieckObe22], a holomorphic anomaly equation is established for
![]() $S^{[n]}$
for genus-0 GW invariants with at most three markings. The proof crucially uses the quisimap wall-crossing, which relates genus-0 GW invariants of
$S^{[n]}$
for genus-0 GW invariants with at most three markings. The proof crucially uses the quisimap wall-crossing, which relates genus-0 GW invariants of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
to PT invariants of
$S^{[n]}$
to PT invariants of
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
and then to GW invariants of
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
and then to GW invariants of
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
by [Reference OberdieckObe21a].
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
by [Reference OberdieckObe21a].
1.4.2. Higher-rank/rank-one DT correspondence for
 $K3\times C$
$K3\times C$
Assume
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
satisfies various assumptions of [Reference NesterovNes21] which are listed in Section 3.1. In particular,
$M(\mathbf {v})$
satisfies various assumptions of [Reference NesterovNes21] which are listed in Section 3.1. In particular,
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
is a smooth projective hyper-Kähler variety. Hence, by [Reference HuybrechtsHuy99, Theorem 4.6], it is deformation equivalent to
$M(\mathbf {v})$
is a smooth projective hyper-Kähler variety. Hence, by [Reference HuybrechtsHuy99, Theorem 4.6], it is deformation equivalent to
![]() $S^{[n]}$
. Using the quasimap wall-crossing on both sides, we can relate higher-rank DT theory to rank-one DT theory. The pictorial representation of this procedure is given in Figure 1.
$S^{[n]}$
. Using the quasimap wall-crossing on both sides, we can relate higher-rank DT theory to rank-one DT theory. The pictorial representation of this procedure is given in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Higher-rank/rank-one DT correspondence.
If
![]() $(g,N)=(0,3)$
, the rank-one DT side of the square is concerned with moduli spaces of one-dimensional subschemes on
$(g,N)=(0,3)$
, the rank-one DT side of the square is concerned with moduli spaces of one-dimensional subschemes on
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
, which are transversal to the vertical divisors over
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
, which are transversal to the vertical divisors over
![]() $\{0,1,\infty \}\subset \mathbb {P}^1$
,
$\{0,1,\infty \}\subset \mathbb {P}^1$
,
We allow
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
to sprout rational tails at
$\mathbb {P}^1$
to sprout rational tails at
![]() $\{0,1,\infty \}$
in order to make the space proper. The resulting space is denoted by
$\{0,1,\infty \}$
in order to make the space proper. The resulting space is denoted by
Intersecting a vertical divisor with a subscheme, we obtain evaluation maps to
![]() $S^{[n]}$
,
$S^{[n]}$
,
Relative insertions are defined to be pullbacks of classes from
![]() $S^{[n]}$
via these evaluation maps. These are the insertions that can be compared to primary GW insertions in Figure 1. For the higher-rank DT side, there exist similar spaces, for the definition of which we refer to Section 4.3.1.
$S^{[n]}$
via these evaluation maps. These are the insertions that can be compared to primary GW insertions in Figure 1. For the higher-rank DT side, there exist similar spaces, for the definition of which we refer to Section 4.3.1.
If
![]() $(g,N)=(0,3)$
, the wall-crossing is trivial; hence, Figure 1 gives us the following relation between DT invariants with relative insertions,
$(g,N)=(0,3)$
, the wall-crossing is trivial; hence, Figure 1 gives us the following relation between DT invariants with relative insertions,
In the case of
![]() $S\times E$
, where E is an elliptic curve, we also get a wall-crossing statement for absolute invariants and equality of certain relative invariants, as is explained in Section 4.3.2.
$S\times E$
, where E is an elliptic curve, we also get a wall-crossing statement for absolute invariants and equality of certain relative invariants, as is explained in Section 4.3.2.
1.4.3.
DT/PT correspondence for
 $K3 \times C$
$K3 \times C$
By results from [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 6.3], there also exists a theory of quasimaps that interpolates between moduli spaces of stable maps to
![]() $S^{[n]}$
and stable pairs on
$S^{[n]}$
and stable pairs on
![]() $S\times C$
in the sense of [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09],
$S\times C$
in the sense of [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09],
The resulting wall-crossing formulas therefore relate the GW theory of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
to the PT theory of
$S^{[n]}$
to the PT theory of
![]() $S\times C$
with relative insertions. We refer to this wall-crossing as perverse quasimap wall-crossing, for more details on this terminology we refer to [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 6.3].
$S\times C$
with relative insertions. We refer to this wall-crossing as perverse quasimap wall-crossing, for more details on this terminology we refer to [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 6.3].
Using both standard and perverse quasimap wall-crossings, we can reduce the DT/PT correspondence for a relative geometry of the form
to the DT/PT correspondence of wall-crossing invariants, as is illustrated in Figure 2. As before, if
![]() $(g,N)=(0,3)$
, the wall-crossing is trivial. We therefore obtain the following relation:
$(g,N)=(0,3)$
, the wall-crossing is trivial. We therefore obtain the following relation:
Note that this is an equality of invariants, unlike the more conventional DT/PT correspondence for Calabi–Yau threefolds which involves dividing by zero-dimensional DT invariants, as it was conjectured in [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09, Conjecture 3.3] and proved in [Reference BridgelandBri11, Theorem 1.1]. This form of DT/PT correspondence is not surprising due to the nature of reduced virtual fundamental classes. Moreover, since we are in the setting of a non-Calabi–Yau relative geometry, the techniques of wall-crossings in derived categories of [Reference Kontsevich and SoibelmanKS08] and [Reference Joyce and SongJS12] cannot be applied to prove wall-crossing statements as above.

Figure 2 DT/PT correspondence.
1.5. Notation and conventions
We work over the field of complex numbers
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}$
. We set
${\mathbb {C}}$
. We set
![]() $e_{{\mathbb {C}}^*}({\mathbb {C}}_{\mathrm {std}})=z,$
where
$e_{{\mathbb {C}}^*}({\mathbb {C}}_{\mathrm {std}})=z,$
where
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}_{\mathrm {std}}$
is the weight 1 representation of
${\mathbb {C}}_{\mathrm {std}}$
is the weight 1 representation of
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
on the vector space
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
on the vector space
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}$
. All functors are derived, unless stated otherwise. Cohomologies and homologies have rational coefficients, unless stated otherwise.
${\mathbb {C}}$
. All functors are derived, unless stated otherwise. Cohomologies and homologies have rational coefficients, unless stated otherwise.
2. Semiregularity map
2.1. Preliminaries
Let S to be a
![]() $K3$
surface over the field of complex numbers
$K3$
surface over the field of complex numbers
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}$
, and let F be a sheaf on
${\mathbb {C}}$
, and let F be a sheaf on
![]() $S\times C$
flat over a nodal curve C. More generally, the following discussion also applies to perfect complexes with the help of [Reference Huybrechts and ThomasHT10]. In particular, we may assume that F is a stable pair in the sense of [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09], which is flat over nodes of C.
$S\times C$
flat over a nodal curve C. More generally, the following discussion also applies to perfect complexes with the help of [Reference Huybrechts and ThomasHT10]. In particular, we may assume that F is a stable pair in the sense of [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09], which is flat over nodes of C.
Consider the Atiyah class
represented by the canonical exact sequence
where
![]() ${\mathcal P}^1(F)$
is the sheaf of principle parts. Composing the Atiyah class with the natural map
${\mathcal P}^1(F)$
is the sheaf of principle parts. Composing the Atiyah class with the natural map
we obtain a class
We then define the Chern character of a sheaf F on
![]() $S \times C$
for a possibly singular C as follows:
$S \times C$
for a possibly singular C as follows:
 $$ \begin{align} {\mathrm{ch}}_{k}(F):= {\mathrm{tr}} \left( \frac{(-1)^k}{k!}\mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F)^k \right) \in H^k(\wedge^k(\Omega^1_{S} \boxplus \omega_{C})). \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} {\mathrm{ch}}_{k}(F):= {\mathrm{tr}} \left( \frac{(-1)^k}{k!}\mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F)^k \right) \in H^k(\wedge^k(\Omega^1_{S} \boxplus \omega_{C})). \end{align} $$
If C is smooth, it agrees with the standard definition of the Chern character. Using the canonical identification
![]() $H^1(\omega _C)\cong {\mathbb {C}}$
, and
$H^1(\omega _C)\cong {\mathbb {C}}$
, and
we get a Künneth’s decomposition of the cohomology
hence
where
With respect to this decomposition above, the Chern character
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)$
has two components
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)$
has two components
such that the first component is determined by the Chern character of a fiber of F over a point
![]() $p\in C$
,
$p\in C$
,
On the other hand, if C is smooth, then
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}$
is determined by the degree of the quasimap associated to F; see [Reference NesterovNes21, Lemma 3.3] for more details. We will show that the definition of
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}$
is determined by the degree of the quasimap associated to F; see [Reference NesterovNes21, Lemma 3.3] for more details. We will show that the definition of
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)$
in Equation (2.1) is compatible with the definition in [Reference NesterovNes21, Definition 3.5] for a singular curve C. So let C be singular, and let
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)$
in Equation (2.1) is compatible with the definition in [Reference NesterovNes21, Definition 3.5] for a singular curve C. So let C be singular, and let
be the normalisation map and
![]() $\pi ^*F_{i}$
be the restriction of
$\pi ^*F_{i}$
be the restriction of
![]() $\pi ^*F$
to the connected components
$\pi ^*F$
to the connected components
![]() $\tilde {C}_{i}$
of
$\tilde {C}_{i}$
of
![]() $\tilde {C}$
. The above decomposition of the Chern character satisfies the following property.
$\tilde {C}$
. The above decomposition of the Chern character satisfies the following property.
Lemma 2.1. Under the identification (2.2), we have
Proof. Firstly, there exist canonical maps making the following diagram commutative:

where the first row is exact on the left, because
![]() $L\pi ^* F\cong \pi ^* F$
, by flatnessFootnote
2
of F over C. The diagram above implies that the pullback of the Atiyah class
$L\pi ^* F\cong \pi ^* F$
, by flatnessFootnote
2
of F over C. The diagram above implies that the pullback of the Atiyah class
![]() $\pi ^*\mathrm {At}(F)$
is mapped to
$\pi ^*\mathrm {At}(F)$
is mapped to
![]() $\mathrm {At}(\pi ^*F)$
with respect to the map
$\mathrm {At}(\pi ^*F)$
with respect to the map
The same holds for
![]() $\pi ^*\mathrm {At}^k(F)$
. Consider now the following commutative diagram:
$\pi ^*\mathrm {At}^k(F)$
. Consider now the following commutative diagram:

such that the first vertical map is the composition
 $$ \begin{align*} R{\mathcal{H} om}(F,F \otimes \Omega_{S\times C}^{k})\rightarrow \pi_*L\pi^* R{\mathcal{H} om}(F,F\otimes \Omega_{S\times C}^{k})&=\pi_*R{\mathcal{H} om}(\pi^*F,\pi^*F\otimes L\pi^*\Omega_{S\times C}^k)\\& \quad \rightarrow \pi_* R{\mathcal{H} om}(\pi^*F,\pi^*F\otimes \pi^*\Omega_{S\times C}^k), \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} R{\mathcal{H} om}(F,F \otimes \Omega_{S\times C}^{k})\rightarrow \pi_*L\pi^* R{\mathcal{H} om}(F,F\otimes \Omega_{S\times C}^{k})&=\pi_*R{\mathcal{H} om}(\pi^*F,\pi^*F\otimes L\pi^*\Omega_{S\times C}^k)\\& \quad \rightarrow \pi_* R{\mathcal{H} om}(\pi^*F,\pi^*F\otimes \pi^*\Omega_{S\times C}^k), \end{align*} $$
where we used that
![]() $L\pi ^*F\cong \pi ^*F$
. Taking the cohomology of the diagram above and using the exactness of
$L\pi ^*F\cong \pi ^*F$
. Taking the cohomology of the diagram above and using the exactness of
![]() $\pi _*$
, we can therefore factor the map
$\pi _*$
, we can therefore factor the map
as follows:
 $$ \begin{align*} \operatorname{Ext}^k(F,F\otimes \Omega_{S\times C}^k) &\rightarrow \operatorname{Ext}^k(\pi^*F,\pi^*F \otimes \pi^*\Omega_{S\times C}^k) \rightarrow \operatorname{Ext}^k(\pi^*F,\pi^*F \otimes \Omega_{S\times \tilde{C}}^k) \\& \rightarrow H^k( \Omega_{S\times \tilde{C}}^k )\cong H^k(\Omega_S^k)\oplus \bigoplus_i H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1})\otimes H^1(\omega_{\tilde{C}_i}) \\&\rightarrow H^k(\Omega_S^k) \oplus H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1})\otimes H^1(\omega_C)\cong H^k(\wedge^k(\Omega^1_{S}\boxplus \omega_C)). \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \operatorname{Ext}^k(F,F\otimes \Omega_{S\times C}^k) &\rightarrow \operatorname{Ext}^k(\pi^*F,\pi^*F \otimes \pi^*\Omega_{S\times C}^k) \rightarrow \operatorname{Ext}^k(\pi^*F,\pi^*F \otimes \Omega_{S\times \tilde{C}}^k) \\& \rightarrow H^k( \Omega_{S\times \tilde{C}}^k )\cong H^k(\Omega_S^k)\oplus \bigoplus_i H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1})\otimes H^1(\omega_{\tilde{C}_i}) \\&\rightarrow H^k(\Omega_S^k) \oplus H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1})\otimes H^1(\omega_C)\cong H^k(\wedge^k(\Omega^1_{S}\boxplus \omega_C)). \end{align*} $$
With respect to the natural identifications
![]() $H^1(\omega _{\tilde {C}_i}) \cong {\mathbb {C}}$
and
$H^1(\omega _{\tilde {C}_i}) \cong {\mathbb {C}}$
and
![]() $H^1(\omega _{C}) \cong {\mathbb {C}}$
, the last map in the sequence becomes
$H^1(\omega _{C}) \cong {\mathbb {C}}$
, the last map in the sequence becomes
 $$\begin{align*}H^k(\Omega_S^k)\oplus \bigoplus_i H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1}) \xrightarrow{(\mathrm{id},+)} H^k(\Omega_S^k)\oplus H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1}).\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}H^k(\Omega_S^k)\oplus \bigoplus_i H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1}) \xrightarrow{(\mathrm{id},+)} H^k(\Omega_S^k)\oplus H^{k-1}(\Omega_S^{k-1}).\end{align*}$$
The claim then follows by tracking the powers of the Atiyah class
![]() $\mathrm {At}^k(F)$
along the maps above.
$\mathrm {At}^k(F)$
along the maps above.
2.2. Semiregularity map
By pulling back classes in
from S to
![]() $S\times C$
, we will treat
$S\times C$
, we will treat
![]() $HT^2(S)$
as classes on
$HT^2(S)$
as classes on
![]() $S\times C$
. Let
$S\times C$
. Let
 $$\begin{align*}\sigma_{i}:= {\mathrm{tr}}\left(* \cdot \frac{(-1)^i}{i!}\mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F)^i \right)\colon \operatorname{Ext}^2(F,F) \rightarrow H^{i+2}(\wedge^i(\Omega^1_{S}\boxplus \omega_C))\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\sigma_{i}:= {\mathrm{tr}}\left(* \cdot \frac{(-1)^i}{i!}\mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F)^i \right)\colon \operatorname{Ext}^2(F,F) \rightarrow H^{i+2}(\wedge^i(\Omega^1_{S}\boxplus \omega_C))\end{align*}$$
be a semiregularity map.
Lemma 2.2. The following diagram is commutative:

Proof. If
![]() $i=0$
, then
$i=0$
, then
![]() $\sigma _{0}={\mathrm {tr}}$
and the commutativity is implied by the following property of the contraction pairing,
$\sigma _{0}={\mathrm {tr}}$
and the commutativity is implied by the following property of the contraction pairing,
The proof is presented in [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03, Proposition 4.2] for
![]() $k=1$
and is the same for other values of k.
$k=1$
and is the same for other values of k.
If
![]() $i=1$
, then for the commutativity of the diagram we have to prove that
$i=1$
, then for the commutativity of the diagram we have to prove that
 $$\begin{align*}\bigg\langle \kappa, {\mathrm{tr}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F)^{k+1}}{k+1!}\right) \bigg\rangle= {\mathrm{tr}} \left( \bigg\langle \kappa, \frac{\mathrm{At}^{k}_{\omega}(F)}{k!} \bigg\rangle\cdot \mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F) \right). \end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\bigg\langle \kappa, {\mathrm{tr}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F)^{k+1}}{k+1!}\right) \bigg\rangle= {\mathrm{tr}} \left( \bigg\langle \kappa, \frac{\mathrm{At}^{k}_{\omega}(F)}{k!} \bigg\rangle\cdot \mathrm{At}_{\omega}(F) \right). \end{align*}$$
If
![]() $\kappa \in H^2({\mathcal O}_S)$
, the equality follows trivially since there is no contraction. The case of
$\kappa \in H^2({\mathcal O}_S)$
, the equality follows trivially since there is no contraction. The case of
![]() $\kappa \in H^1(T_S)$
is treated in [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03, Proposition 4.2]. For
$\kappa \in H^1(T_S)$
is treated in [Reference Buchweitz and FlennerBF03, Proposition 4.2]. For
![]() $\kappa \in H^0(\wedge ^2 T_S)$
, we use the derivation property for contraction with a two-vector field
$\kappa \in H^0(\wedge ^2 T_S)$
, we use the derivation property for contraction with a two-vector field
which can be checked locally on a two-vector field of the form
![]() $V\wedge W$
.
$V\wedge W$
.
Due to the decomposition
there are two ways to contract a class in
![]() $H^i(\wedge ^i(\Omega ^1_{S}\boxplus \omega _C))$
with a class in
$H^i(\wedge ^i(\Omega ^1_{S}\boxplus \omega _C))$
with a class in
![]() $H^{2-k}(\wedge ^kT_S)$
: either via the first component of the decomposition above or via the second. Hence, due to the wedge degree or the cohomological degree, only one component of
$H^{2-k}(\wedge ^kT_S)$
: either via the first component of the decomposition above or via the second. Hence, due to the wedge degree or the cohomological degree, only one component of
![]() $H^i(\wedge ^i(\Omega ^1_{S}\boxplus \omega _C))$
pairs nontrivially with
$H^i(\wedge ^i(\Omega ^1_{S}\boxplus \omega _C))$
pairs nontrivially with
![]() $H^{2-k}(\wedge ^kT_S)$
for a fixed k. It is not difficult to check that contraction with the Chern character,
$H^{2-k}(\wedge ^kT_S)$
for a fixed k. It is not difficult to check that contraction with the Chern character,
is therefore equal to
![]() $\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}} \rangle $
for
$\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}} \rangle $
for
![]() $i=0$
and to
$i=0$
and to
![]() $\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}} \rangle $
for
$\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}} \rangle $
for
![]() $i=1$
. Moreover, using the identification
$i=1$
. Moreover, using the identification
the contraction
![]() $\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}} \rangle $
with classes on
$\langle -,{\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}} \rangle $
with classes on
![]() $S\times C$
is identified with the contraction with classes on S.
$S\times C$
is identified with the contraction with classes on S.
Proposition 2.3. Assume
then there exists
![]() $\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
such that
$\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
such that
In particular, the restriction of the semiregularity map to the traceless part of
![]() $\operatorname {Ext}^2(F,F)$
,
$\operatorname {Ext}^2(F,F)$
,
is nonzero.
Proof. Using a symplectic form on S, we have the following identifications,
After applying these identifications and taking the cohomology, the pairing
which is given by the contraction of classes, becomes the intersection pairing
where
![]() $H\Omega _0(S)=\bigoplus _i H^i(\Omega ^i)$
. In particular, the pairing (2.3) is nondegenerate. We conclude that
$H\Omega _0(S)=\bigoplus _i H^i(\Omega ^i)$
. In particular, the pairing (2.3) is nondegenerate. We conclude that
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}^{\perp }$
and
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}^{\perp }$
and
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}^{\perp }$
are distinct, if and only if
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}^{\perp }$
are distinct, if and only if
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}$
is not a multiple of
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}$
is not a multiple of
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}$
. Hence, there exists a class
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}$
. Hence, there exists a class
![]() $\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
such that
$\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
such that
By Lemma 2.2 and the discussion afterwards, the property
![]() $\langle \kappa , {\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}} \rangle =0$
implies that
$\langle \kappa , {\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}} \rangle =0$
implies that
while the property
![]() $\langle \kappa , {\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}} \rangle =0$
implies that the restriction of the semiregularity map to
$\langle \kappa , {\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}} \rangle =0$
implies that the restriction of the semiregularity map to
![]() $\operatorname {Ext}^2(F,F)_0$
is nonzero, as it is nonzero when applied to the element
$\operatorname {Ext}^2(F,F)_0$
is nonzero, as it is nonzero when applied to the element
![]() $\kappa \cdot \exp (-\mathrm {At}_{\omega }(F))$
.
$\kappa \cdot \exp (-\mathrm {At}_{\omega }(F))$
.
Remark 2.4. From the point of view of quasimaps, the condition
is equivalent to the fact that the quasimap
![]() $f\colon C \rightarrow \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S)$
associated to F is not constant.
$f\colon C \rightarrow \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S)$
associated to F is not constant.
The above result has a following geometric interpretation. With respect to the Hochschild–Kostant–Rosenberg (HKR) isomorphism,
the space
![]() $HT^2(S)$
parametrises first-order noncommutative deformations of S, that is, deformations of
$HT^2(S)$
parametrises first-order noncommutative deformations of S, that is, deformations of
![]() $\mathrm {D}^b(S)$
. Given a first-order deformation
$\mathrm {D}^b(S)$
. Given a first-order deformation
![]() $\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
, the unique horizontal lift of
$\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
, the unique horizontal lift of
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}}$
relative to a Gauss–Manin connection associated to
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}}$
relative to a Gauss–Manin connection associated to
![]() $\kappa $
should stay of Hodge type
$\kappa $
should stay of Hodge type
![]() $(k,k)$
, if and only if
$(k,k)$
, if and only if
![]() ${\langle \kappa , {\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}} \rangle =0}$
. On the other hand,
${\langle \kappa , {\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}} \rangle =0}$
. On the other hand,
![]() $\langle \kappa , \exp (-\mathrm {At}_{\omega }(F))$
gives an obstruction for deforming F on
$\langle \kappa , \exp (-\mathrm {At}_{\omega }(F))$
gives an obstruction for deforming F on
![]() $S\times C$
in the direction
$S\times C$
in the direction
![]() $\kappa $
. Hence, by Lemma 2.2, the semiregularity map
$\kappa $
. Hence, by Lemma 2.2, the semiregularity map
![]() $\sigma _i$
relates obstructions to deform F along
$\sigma _i$
relates obstructions to deform F along
![]() $\kappa $
with obstructions of
$\kappa $
with obstructions of
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}}$
to stay of Hodge type
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d/f}}$
to stay of Hodge type
![]() $(k,k)$
. Proposition 2.3 states that there exists a deformation
$(k,k)$
. Proposition 2.3 states that there exists a deformation
![]() $\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
, for which
$\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
, for which
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}$
stays of Hodge type
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}$
stays of Hodge type
![]() $(k,k)$
, but
$(k,k)$
, but
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}$
does not. From the point of view of quasimaps, this means that the moduli space of stable sheaves M on S associated to the class
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}$
does not. From the point of view of quasimaps, this means that the moduli space of stable sheaves M on S associated to the class
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}$
deforms along
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}$
deforms along
![]() $\kappa $
, but the quasimap associated to F does not.
$\kappa $
, but the quasimap associated to F does not.
For example, let S be a
![]() $K3$
surface associated to a cubic fourfold Y, such that the Fano variety of lines
$K3$
surface associated to a cubic fourfold Y, such that the Fano variety of lines
![]() $F(Y)$
is isomorphic to
$F(Y)$
is isomorphic to
![]() $S^{[2]}$
. Then if we deform Y away from the Hassett divisor [Reference HassettHas00],
$S^{[2]}$
. Then if we deform Y away from the Hassett divisor [Reference HassettHas00],
![]() $F(Y)$
deforms along, but the point class of S does not. Therefore, such deformation of Y will give the first-order noncommutative deformation
$F(Y)$
deforms along, but the point class of S does not. Therefore, such deformation of Y will give the first-order noncommutative deformation
![]() $\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
of S such that
$\kappa \in HT^2(S)$
of S such that
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}=(1,0,-2)$
stays of Hodge type
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {f}}=(1,0,-2)$
stays of Hodge type
![]() $(k,k)$
, but
$(k,k)$
, but
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}=(0,0,k)$
does not. Note that
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}=(0,0,k)$
does not. Note that
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}=(0,0,k)$
corresponds to multiplies of the exceptional curve class in
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)_{\mathrm {d}}=(0,0,k)$
corresponds to multiplies of the exceptional curve class in
![]() $S^{[2]}$
. Indeed, there are no commutative deformations of S that will make
$S^{[2]}$
. Indeed, there are no commutative deformations of S that will make
![]() $(0,0,k)$
non-Hodge because, in this case, the exceptional divisor deforms along with
$(0,0,k)$
non-Hodge because, in this case, the exceptional divisor deforms along with
![]() $S^{[2]}$
.
$S^{[2]}$
.
3. Reduced wall-crossing
3.1. Surjective cosection
We fix a very ample line bundle
![]() ${\mathcal O}_{S}(1)\in \mathop {\mathrm {Pic}}\nolimits (S)$
, a class
${\mathcal O}_{S}(1)\in \mathop {\mathrm {Pic}}\nolimits (S)$
, a class
![]() $\mathbf {v} \in K_{\mathrm {num}}(S)$
and another class
$\mathbf {v} \in K_{\mathrm {num}}(S)$
and another class
![]() $\mathbf {u} \in K_{0}(S)$
such that:
$\mathbf {u} \in K_{0}(S)$
such that:
-
•
 ${\mathrm {rk}}(\mathbf {v})>0$
,
${\mathrm {rk}}(\mathbf {v})>0$
, -
•
 $\chi (\mathbf {v}\cdot \mathbf {u})=1$
,
$\chi (\mathbf {v}\cdot \mathbf {u})=1$
, -
• there are no strictly slope
 ${\mathcal O}_{S}(1)$
-semistable sheaves in the class
${\mathcal O}_{S}(1)$
-semistable sheaves in the class
 $\mathbf {v}$
.
$\mathbf {v}$
.
Let
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
be the moduli space of slope
$M(\mathbf {v})$
be the moduli space of slope
![]() ${\mathcal O}_S(1)$
-stable sheaves on S in the class
${\mathcal O}_S(1)$
-stable sheaves on S in the class
![]() $\mathbf {v}$
. The second assumption implies that
$\mathbf {v}$
. The second assumption implies that
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
is a fine moduli space, while the last assumption implies that
$M(\mathbf {v})$
is a fine moduli space, while the last assumption implies that
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
is smooth and projective. The first two assumptions are made for technical reasons and, in principle, can be dropped. We refer to [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 1.6] for a more detailed discussion about why these assumptions are made.
$M(\mathbf {v})$
is smooth and projective. The first two assumptions are made for technical reasons and, in principle, can be dropped. We refer to [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 1.6] for a more detailed discussion about why these assumptions are made.
Remark 3.1. An example of a moduli space
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
which satisfies the assumptions above will be a moduli space of sheaves in the class
$M(\mathbf {v})$
which satisfies the assumptions above will be a moduli space of sheaves in the class
![]() ${\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf {v})=(2,\alpha ,2k+1)$
for a polarisation such that
${\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf {v})=(2,\alpha ,2k+1)$
for a polarisation such that
![]() $\deg (\alpha )$
is odd (or a generic polarisation that is close to a polarisation for which
$\deg (\alpha )$
is odd (or a generic polarisation that is close to a polarisation for which
![]() $\deg (\alpha )$
is odd). Firstly,
$\deg (\alpha )$
is odd). Firstly,
![]() ${\mathrm {rk}}(\mathbf {v})$
and
${\mathrm {rk}}(\mathbf {v})$
and
![]() $\deg (\mathbf {v})$
are coprime; therefore, there are no strictly slope semistable sheaves. The class
$\deg (\mathbf {v})$
are coprime; therefore, there are no strictly slope semistable sheaves. The class
![]() $\mathbf {u}=[{\mathcal O}_S]-(k+2)[{\mathcal O}_{\mathrm {pt}}]\in K_{0}(S)$
has the property
$\mathbf {u}=[{\mathcal O}_S]-(k+2)[{\mathcal O}_{\mathrm {pt}}]\in K_{0}(S)$
has the property
![]() $\chi (\mathbf {v}\cdot \mathbf {u})=1$
. Moreover, [Reference NesterovNes21, Corollary A.6] holds in this case; therefore, the space
$\chi (\mathbf {v}\cdot \mathbf {u})=1$
. Moreover, [Reference NesterovNes21, Corollary A.6] holds in this case; therefore, the space
![]() $M_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S\times C)$
is a moduli space of all stable sheaves for some suitable polarisation. More specifically, such setup can be arranged on an elliptic
$M_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S\times C)$
is a moduli space of all stable sheaves for some suitable polarisation. More specifically, such setup can be arranged on an elliptic
![]() $K3$
surface.
$K3$
surface.
By [Reference NesterovNes21, Theorem 3.15], there exists an identification between a space of
![]() $\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps
$\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )$
and a certain relative moduli space of sheaves
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )$
and a certain relative moduli space of sheaves
![]() $M^{ \epsilon }_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S \times C_{g,N})$
,
$M^{ \epsilon }_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S \times C_{g,N})$
,
such that the corresponding obstructions theories are isomorphic. The product
![]() $S\times C_{g,N}$
stands for the relative geometry
$S\times C_{g,N}$
stands for the relative geometry
where
![]() $C_{g,N}$
is the universal curve over
$C_{g,N}$
is the universal curve over
![]() ${\overline M}_{g,N}$
. This identification depends on the choice of the class
${\overline M}_{g,N}$
. This identification depends on the choice of the class
![]() $\mathbf {u} \in K_0(S)$
, which we suppress from the notation. For
$\mathbf {u} \in K_0(S)$
, which we suppress from the notation. For
![]() $\epsilon =0^+$
, the
$\epsilon =0^+$
, the
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}$
-valued points of
${\mathbb {C}}$
-valued points of
![]() $M^{0^+}_{\mathbf v, \check {\beta }}(S\times C_{g,N})$
are triples
$M^{0^+}_{\mathbf v, \check {\beta }}(S\times C_{g,N})$
are triples
such that:
-
•
 $(C, \mathbf {p})$
is a prestable nodal curve (no rational tails),
$(C, \mathbf {p})$
is a prestable nodal curve (no rational tails), -
• a sheaf F on
 $S\times C$
flat over C,
$S\times C$
flat over C, -
•
 $ {\mathrm {ch}}(F)=({\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf v), \check \beta )$
,
$ {\mathrm {ch}}(F)=({\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf v), \check \beta )$
, -
•
 $F_p$
is stable for a general
$F_p$
is stable for a general
 $p\in C$
,
$p\in C$
, -
•
 $F_p$
is stable, if p is a node or a marking,
$F_p$
is stable, if p is a node or a marking, -
• the group of automorphisms of
 $(C, \mathbf {p})$
fixing F is finite,
$(C, \mathbf {p})$
fixing F is finite, -
•
 $\det (p_{C*}(p_{S}^{*}\mathbf {u}\otimes F))\cong {\mathcal O}_{C}$
.
$\det (p_{C*}(p_{S}^{*}\mathbf {u}\otimes F))\cong {\mathcal O}_{C}$
.
We will frequently use the identification (3.1) to transfer various constructions from sheaves to quasimaps and vice versa. If
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[n]}$
, then one can consider a moduli space of perverse quasimaps
$M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[n]}$
, then one can consider a moduli space of perverse quasimaps
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )^{\sharp }$
, which admits an identification with a relative moduli space stable pairs of [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09],
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )^{\sharp }$
, which admits an identification with a relative moduli space stable pairs of [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09],
The following discussion applies to both kinds of quasimaps.
Let
 $$ \begin{align*} &\pi\colon S\times {\mathcal C}^{\epsilon}_{g,N} \rightarrow M^{ \epsilon}_{\mathbf{v},\check{\beta}}(S \times C_{g,N}), \\ &{\mathbb{F}} \in \mathrm{Coh}(S\times {\mathcal C}^\epsilon_{g,N}) \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} &\pi\colon S\times {\mathcal C}^{\epsilon}_{g,N} \rightarrow M^{ \epsilon}_{\mathbf{v},\check{\beta}}(S \times C_{g,N}), \\ &{\mathbb{F}} \in \mathrm{Coh}(S\times {\mathcal C}^\epsilon_{g,N}) \end{align*} $$
be the universal threefold and the universal sheaf of
![]() $M^{ \epsilon }_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S \times C_{g,N})$
, respectively. Let
$M^{ \epsilon }_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S \times C_{g,N})$
, respectively. Let
be the universal trace map. The complex
defines a perfect obstruction theory on
![]() $M^{ \epsilon }_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S \times C_{g,N})$
relative to the moduli stack of nodal curves
$M^{ \epsilon }_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S \times C_{g,N})$
relative to the moduli stack of nodal curves
![]() $\mathfrak {M}_{g,N}$
. We construct a cosection of the obstruction theory via the global relative semiregularity map,
$\mathfrak {M}_{g,N}$
. We construct a cosection of the obstruction theory via the global relative semiregularity map,
and since
we have
By the identification (3.1), we get a cosection for the obstruction theory of
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )$
. Surjectivity of the cosection follows from the preceding results.
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )$
. Surjectivity of the cosection follows from the preceding results.
Corollary 3.2. Assuming
![]() $\beta \neq 0$
, the semiregularity map
$\beta \neq 0$
, the semiregularity map
![]() $\mathsf {sr}$
is surjective.
$\mathsf {sr}$
is surjective.
Proof. Under the given assumption, the surjectivity of the semiregularity map
![]() $\mathsf {sr}$
follows from Proposition 2.3 and Lemma 2.1.
$\mathsf {sr}$
follows from Proposition 2.3 and Lemma 2.1.
Consider now the composition
where the first map defined by the following composition,
The composition (3.4) is zero by the same arguments as in Lemma 2.2. The semiregularity map therefore descends to the absolute obstruction theory,

Hence, the results of [Reference Kiem and LiKL13] apply.
The obstruction theory of the master space
![]() $MQ^{\epsilon _0}_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )$
also has a surjective cosection; see [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 7.2] for the definition of the master space. Like in the case of
$MQ^{\epsilon _0}_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}), \beta )$
also has a surjective cosection; see [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 7.2] for the definition of the master space. Like in the case of
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}) \beta )$
, it is constructed by identifying the master space with a moduli spaces of sheaves.
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}) \beta )$
, it is constructed by identifying the master space with a moduli spaces of sheaves.
3.2. Invariants
In what follows, we use Kiem–Li’s construction of reduced virtual fundamental classes via the cosection localisation [Reference Kiem and LiKL13]. By using the identification (3.1), we define
to be the associated reduced virtual fundamental class. From now on, by a virtual fundamental class we always will mean a reduced virtual fundamental class, except for
![]() $\beta =0$
, since the standard virtual fundamental class does not vanish in this case. These classes can be seen as virtual fundamental classes associated to the reduced obstruction-theory complex
$\beta =0$
, since the standard virtual fundamental class does not vanish in this case. These classes can be seen as virtual fundamental classes associated to the reduced obstruction-theory complex
![]() ${\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet }_{\mathrm {red}}$
, defined as the cone of the cosection,
${\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet }_{\mathrm {red}}$
, defined as the cone of the cosection,
However, we are unable to prove that
![]() ${\mathbb {E}}_{\mathrm {red }}^{\bullet }$
defines an obstruction theory in full generality, cf. Proposition A.1. Luckily, Kiem–Li’s class is good enough for all purposes; for example, see [Reference Chang, Kiem and LiCKL17] for the virtual torus localisation of Kiem–Li’s reduced classes.
${\mathbb {E}}_{\mathrm {red }}^{\bullet }$
defines an obstruction theory in full generality, cf. Proposition A.1. Luckily, Kiem–Li’s class is good enough for all purposes; for example, see [Reference Chang, Kiem and LiCKL17] for the virtual torus localisation of Kiem–Li’s reduced classes.
Definition 3.3. We define descendent quasimap invariants,
 $$\begin{align*}\langle \gamma_{1}\psi^{k_1}, \dots, \gamma_{N}\psi^{k_N} \rangle^{M(\mathbf{v}), \epsilon}_{g,N,\beta}:= \int_{[Q^{\epsilon}_{g,N}(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)]^{\mathrm{red}}}\prod^{i=N}_{i=1}{\mathrm{ev}}^{*}_{i}(\gamma_{i})\psi_{i}^{k_{i}},\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\langle \gamma_{1}\psi^{k_1}, \dots, \gamma_{N}\psi^{k_N} \rangle^{M(\mathbf{v}), \epsilon}_{g,N,\beta}:= \int_{[Q^{\epsilon}_{g,N}(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)]^{\mathrm{red}}}\prod^{i=N}_{i=1}{\mathrm{ev}}^{*}_{i}(\gamma_{i})\psi_{i}^{k_{i}},\end{align*}$$
where
![]() $\gamma _{1}, \dots , \gamma _{N} \in H^{*}(M(\mathbf {v}))$
,
$\gamma _{1}, \dots , \gamma _{N} \in H^{*}(M(\mathbf {v}))$
,
![]() $\psi _{1}, \dots \psi _{N}$
are
$\psi _{1}, \dots \psi _{N}$
are
![]() $\psi $
-classes associated to markings and
$\psi $
-classes associated to markings and
![]() $k_{1}, \dots k_{N}$
are nonnegative integers. We similarly define the perverse invariants
$k_{1}, \dots k_{N}$
are nonnegative integers. We similarly define the perverse invariants
![]() $\langle \gamma _{1}\psi ^{k_1}, \dots , \gamma _{N}\psi ^{k_N} \rangle ^{\sharp ,S^{[n]}, \epsilon }_{g,\beta }$
, using perverse quasimaps from [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 6.3]. With respect to the identification (3.1), primary
$\langle \gamma _{1}\psi ^{k_1}, \dots , \gamma _{N}\psi ^{k_N} \rangle ^{\sharp ,S^{[n]}, \epsilon }_{g,\beta }$
, using perverse quasimaps from [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 6.3]. With respect to the identification (3.1), primary
![]() $\epsilon $
-invariants (no
$\epsilon $
-invariants (no
![]() $\psi $
-classes) correspond to relative DT invariants.
$\psi $
-classes) correspond to relative DT invariants.
Consider now the diagram

where
![]() $C_{g,N}$
is the universal curve over
$C_{g,N}$
is the universal curve over
![]() ${\overline M}_{g,N}$
and p is the stabilisation of curves. For the unstable values of g and N, we set the product
${\overline M}_{g,N}$
and p is the stabilisation of curves. For the unstable values of g and N, we set the product
![]() $S\times {\overline M}_{g,N+1}$
to be S.
$S\times {\overline M}_{g,N+1}$
to be S.
Definition 3.4. For a class
![]() $\tilde {\gamma } \in H^l(S\times C_{g,N})$
, define the following operation on cohomology:
$\tilde {\gamma } \in H^l(S\times C_{g,N})$
, define the following operation on cohomology:
The descendent DT invariants are then defined by
By combing Definition 3.3 with the definition above, we obtain a mix of descendent quasimap invariants and descendent DT invariants,
The same applies to the perverse invariants. For
![]() $\epsilon =0^+$
and for a fixed marked curveFootnote
3
$\epsilon =0^+$
and for a fixed marked curveFootnote
3
![]() $(C,\mathbf {p})$
, we denote the invariants above by
$(C,\mathbf {p})$
, we denote the invariants above by
to emphasize that we are considering the DT theory of
![]() $S\times C$
.
$S\times C$
.
3.3. Wall-crossing
We fix a parametrized projective line
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
with a
$\mathbb {P}^1$
with a
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-action,
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-action,
such that
![]() $0:=[0:1]$
and
$0:=[0:1]$
and
![]() $\infty :=[1:0]$
. By convention, we set
$\infty :=[1:0]$
. By convention, we set
where
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}_{\mathrm {std}}$
is the weight 1 representation of
${\mathbb {C}}_{\mathrm {std}}$
is the weight 1 representation of
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
. We now define a Vertex space,
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
. We now define a Vertex space,
to be a moduli space of sheaves F on
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
subject to the following conditions:
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
subject to the following conditions:
-
• F is torsion-free,
-
•
 ${\mathrm {ch}}(F)=({\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf {v}),\check {\beta })$
,
${\mathrm {ch}}(F)=({\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf {v}),\check {\beta })$
, -
• fibers
 $F_p$
are stable for a general
$F_p$
are stable for a general
 $p \in \mathbb {P}^1$
,
$p \in \mathbb {P}^1$
, -
• the fiber
 $F_\infty $
is stable,
$F_\infty $
is stable, -
•
 $\det (p_{C*}(p_{S}^{*}\mathbf {u}\otimes F))\cong {\mathcal O}_{C}$
.
$\det (p_{C*}(p_{S}^{*}\mathbf {u}\otimes F))\cong {\mathcal O}_{C}$
.
By construction, there is a natural evaluation map,
Moreover, by acting on
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
, we obtain a
$\mathbb {P}^1$
, we obtain a
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-action on
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-action on
![]() $V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
. By the same arguments as in Section 3.1, the obstruction theory of
$V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
. By the same arguments as in Section 3.1, the obstruction theory of
![]() $V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
has a surjective cosection. Moreover, the cosection is
$V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
has a surjective cosection. Moreover, the cosection is
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-equivariant. The Vertex space is not proper, but its
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-equivariant. The Vertex space is not proper, but its
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-fixed locus
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-fixed locus
is proper. Indeed, this follows from properness of the space of all prestable quasimaps from
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
and the fact that
$\mathbb {P}^1$
and the fact that
![]() $V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{{\mathbb {C}}^*}$
is just a connected component of its
$V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{{\mathbb {C}}^*}$
is just a connected component of its
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-fixed locus. We can therefore use the virtual torus localisation of reduced classes [Reference Chang, Kiem and LiCKL17] to define its virtual fundamental class,
${\mathbb {C}}^*$
-fixed locus. We can therefore use the virtual torus localisation of reduced classes [Reference Chang, Kiem and LiCKL17] to define its virtual fundamental class,
 $$\begin{align*}[V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)]^{\mathrm{red}}:=\frac{[V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)^{{\mathbb{C}}^*}]^{\mathrm{red}}}{e_{{\mathbb{C}}^*}({\mathcal N}^{\mathrm{vir}})} \in H_*(V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)^{{\mathbb{C}}^*})[z^{\pm}],\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}[V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)]^{\mathrm{red}}:=\frac{[V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)^{{\mathbb{C}}^*}]^{\mathrm{red}}}{e_{{\mathbb{C}}^*}({\mathcal N}^{\mathrm{vir}})} \in H_*(V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)^{{\mathbb{C}}^*})[z^{\pm}],\end{align*}$$
where
![]() ${\mathcal N}^{\mathrm {vir}}$
is the virtual normal complex of
${\mathcal N}^{\mathrm {vir}}$
is the virtual normal complex of
![]() $V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{{\mathbb {C}}^*}$
inside
$V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{{\mathbb {C}}^*}$
inside
![]() $V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
, and z is the equivariant parameter. We are now ready to define Givental’s I-function, introduced in the context of GIT quasimaps in [Reference Ciocan-Fontanine, Kim and MaulikCKM14].
$V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
, and z is the equivariant parameter. We are now ready to define Givental’s I-function, introduced in the context of GIT quasimaps in [Reference Ciocan-Fontanine, Kim and MaulikCKM14].
Definition 3.5. We define
 $$ \begin{align*} I^{\mathbf{v}}_\beta(z)&:= {\mathrm{ev}}_* [V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)]^{\mathrm{red}} \in H^*(M(\mathbf{v}))[z^\pm], \\ \mu^{\mathbf{v}}_\beta(z)&:=[zI^{\mathbf{v}}_\beta(z)]_{z^{\geq 0}} \in H^*(M(\mathbf{v}))[z]. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} I^{\mathbf{v}}_\beta(z)&:= {\mathrm{ev}}_* [V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)]^{\mathrm{red}} \in H^*(M(\mathbf{v}))[z^\pm], \\ \mu^{\mathbf{v}}_\beta(z)&:=[zI^{\mathbf{v}}_\beta(z)]_{z^{\geq 0}} \in H^*(M(\mathbf{v}))[z]. \end{align*} $$
Lemma 3.6. The class
![]() $\mu ^{\mathbf {v}}_\beta (z)$
admits the following expression:
$\mu ^{\mathbf {v}}_\beta (z)$
admits the following expression:
where
![]() $\mu ^{\mathbf {v}}_\beta \in {\mathbb {Q}}$
.
$\mu ^{\mathbf {v}}_\beta \in {\mathbb {Q}}$
.
Proof. This follows from the definition and the fact that the reduced virtual dimension of
![]() $V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
is equal to
$V(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
is equal to
![]() $\dim (M(\mathbf {v}))+1$
.
$\dim (M(\mathbf {v}))+1$
.
The space
![]() ${\mathbb {R}}_{>0} \cup \{0^+,\infty \}$
of
${\mathbb {R}}_{>0} \cup \{0^+,\infty \}$
of
![]() $\epsilon $
-stabilities is divided into chambers, in which the moduli space
$\epsilon $
-stabilities is divided into chambers, in which the moduli space
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
stays the same, and as
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
stays the same, and as
![]() $\epsilon $
crosses the a wall between chambers, the moduli space changes discontinuously. Given a quasimap class
$\epsilon $
crosses the a wall between chambers, the moduli space changes discontinuously. Given a quasimap class
![]() $\beta \in \mathrm {Eff}(M(\mathbf {v}), \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
, then for a class
$\beta \in \mathrm {Eff}(M(\mathbf {v}), \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
, then for a class
![]() $\beta '\in \mathrm {Eff}(M(\mathbf {v}), \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
that appears as a summand of
$\beta '\in \mathrm {Eff}(M(\mathbf {v}), \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
that appears as a summand of
![]() $\beta$
, we define
$\beta$
, we define
and we define the
![]() $\epsilon $
-stability of quasimaps of degree
$\epsilon $
-stability of quasimaps of degree
![]() $\beta '$
with respect to the line bundle
$\beta '$
with respect to the line bundle
![]() ${\mathcal L}_\beta $
, constructed in [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 3.4]. Let
${\mathcal L}_\beta $
, constructed in [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 3.4]. Let
![]() $\epsilon _{0}=1/d_{0} \in {\mathbb {R}}_{>0}$
be a wall for
$\epsilon _{0}=1/d_{0} \in {\mathbb {R}}_{>0}$
be a wall for
![]() $\beta \in \mathrm {Eff}(M(\mathbf {v}), \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
and
$\beta \in \mathrm {Eff}(M(\mathbf {v}), \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}(S,\mathbf {v}))$
and
![]() $\epsilon _-$
,
$\epsilon _-$
,
![]() $\epsilon _+$
be some values that are close to
$\epsilon _+$
be some values that are close to
![]() $\epsilon _{0}$
from the left and the right of the wall, respectively.
$\epsilon _{0}$
from the left and the right of the wall, respectively.
Theorem 3.7. Assuming
![]() $2g-2+N+\epsilon _0\deg (\beta )>0$
, we have
$2g-2+N+\epsilon _0\deg (\beta )>0$
, we have
if
![]() $\deg (\beta )=d_{0}$
, and
$\deg (\beta )=d_{0}$
, and
otherwise.
Sketch of Proof.
As in the case of [Reference NesterovNes21, Theorem 7.5], the results from [Reference ZhouZho22, Section 6] apply almost without change. The difference is that we use reduced classes now. Up to a finite gerbe, the fixed components of the master space which contribute to the wall-crossing formula are of the following form,
 $$\begin{align*}\widetilde{Q}^{\epsilon_+}_{g,N+k}(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta') \times_{M(\mathbf{v})^{k}} \prod_{i=1}^k V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta_i)^{{\mathbb{C}}^*},\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\widetilde{Q}^{\epsilon_+}_{g,N+k}(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta') \times_{M(\mathbf{v})^{k}} \prod_{i=1}^k V(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta_i)^{{\mathbb{C}}^*},\end{align*}$$
where
![]() $\beta =\beta '+\beta _{1}+\dots +\beta _{k}$
and
$\beta =\beta '+\beta _{1}+\dots +\beta _{k}$
and
![]() $\deg (\beta _i)=d_{0}$
. Recall that
$\deg (\beta _i)=d_{0}$
. Recall that
![]() $\widetilde {Q}^{\epsilon _+}_{g,N+k}(M(\mathbf {v})\beta ')$
is the base change of
$\widetilde {Q}^{\epsilon _+}_{g,N+k}(M(\mathbf {v})\beta ')$
is the base change of
![]() $Q^{\epsilon _+}_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
from
$Q^{\epsilon _+}_{g,N}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
from
![]() $\mathfrak {M}_{g,N}$
to
$\mathfrak {M}_{g,N}$
to
![]() $\widetilde {\mathfrak {M}}_{g,N,d}$
, where the latter is the moduli space of curves with entangled tails. The reduced class of a product splits as a product of reduced and nonreduced classes on its factors (cf. [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Section 3.9]). Hence, by Corollary 3.2 and [Reference Kiem and LiKL13], it vanishes, unless
$\widetilde {\mathfrak {M}}_{g,N,d}$
, where the latter is the moduli space of curves with entangled tails. The reduced class of a product splits as a product of reduced and nonreduced classes on its factors (cf. [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Section 3.9]). Hence, by Corollary 3.2 and [Reference Kiem and LiKL13], it vanishes, unless
![]() $\beta '=0$
and
$\beta '=0$
and
![]() $k=1$
. In this case,
$k=1$
. In this case,
Using the analysis presented in [Reference ZhouZho22, Section 7] and Lemma 3.6, we get that the contribution of this component to the wall-crossing is
this concludes the argument.
Applying Theorem 3.7 inductively to all walls on the way from
![]() $\epsilon =0^+$
to
$\epsilon =0^+$
to
![]() $\epsilon =\infty $
, we obtain the following result.
$\epsilon =\infty $
, we obtain the following result.
Corollary 3.8. Assuming
![]() $(g,N)\neq (0,1)$
, we have
$(g,N)\neq (0,1)$
, we have
Another immediate corollary of the wall-crossing formula is the following expression for the wall-crossing invariants.
Corollary 3.9. We have
Proof. The result follows from Corollary 3.8 applied to the invariants ![]() for
for
![]() $\epsilon \in \{0^+, \infty \}$
and the string equation on the GW side.
$\epsilon \in \{0^+, \infty \}$
and the string equation on the GW side.
There are invariants that are not covered by the results above and of great interest for us – those of a fixed elliptic curve. Let E be a fixed elliptic curve and
![]() $Q^\epsilon _{E}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{\bullet }$
be the fiber of
$Q^\epsilon _{E}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{\bullet }$
be the fiber of
over the stacky point
![]() $[E]/E \in {\overline M}_{1,0}({\mathbb {C}})$
. In other words,
$[E]/E \in {\overline M}_{1,0}({\mathbb {C}})$
. In other words,
![]() $Q^\epsilon _{E}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{\bullet }$
is the moduli space of
$Q^\epsilon _{E}(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )^{\bullet }$
is the moduli space of
![]() $\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps, whose smoothing of the domain is E, and maps are considered up translations of E. For
$\epsilon $
-stable quasimaps, whose smoothing of the domain is E, and maps are considered up translations of E. For
![]() $\beta \neq 0$
, we define
$\beta \neq 0$
, we define
 $$\begin{align*}\langle \emptyset \rangle^{M(\mathbf{v}),\epsilon}_{E,\beta}:=\int_{[Q^{\epsilon}_{E}(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)^{\bullet}]^{\mathrm{red}}}1.\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\langle \emptyset \rangle^{M(\mathbf{v}),\epsilon}_{E,\beta}:=\int_{[Q^{\epsilon}_{E}(M(\mathbf{v}),\beta)^{\bullet}]^{\mathrm{red}}}1.\end{align*}$$
Theorem 3.10. Assuming
![]() $\beta \neq 0$
, we have
$\beta \neq 0$
, we have
if
![]() $\deg (\beta )=d_{0}$
and
$\deg (\beta )=d_{0}$
and
otherwise.
Sketch of Proof.
As in Theorem 3.7, the only case when the contribution from the wall-crossing components is nonzero is the one of
![]() $\beta '=0$
and
$\beta '=0$
and
![]() $k=1$
. In this case,
$k=1$
. In this case,
and the obstruction bundle is the tangent bundle
![]() $T_{M(\mathbf {v})}$
. Hence, the virtual fundamental class is
$T_{M(\mathbf {v})}$
. Hence, the virtual fundamental class is
![]() $\chi (M(\mathbf {v}))[\mathrm {pt}]$
. The corresponding wall-crossing term is therefore equal to
$\chi (M(\mathbf {v}))[\mathrm {pt}]$
. The corresponding wall-crossing term is therefore equal to
this concludes the argument.
As before, by applying Theorem 3.10 inductively, we obtain the following result.
Corollary 3.11. Assuming
![]() $\beta \neq 0$
, we have
$\beta \neq 0$
, we have
4. Applications
4.1. Genus-0 invariants of
 $S^{[n]}$
$S^{[n]}$
We start with genus-0 three-point quasimap invariants of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
. The moduli space of
$S^{[n]}$
. The moduli space of
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
with three marked points is a point. Hence, by fixing markings, we can identify moduli spaces of
$\mathbb {P}^1$
with three marked points is a point. Hence, by fixing markings, we can identify moduli spaces of
![]() $0^+$
-stable quasimaps with one-dimensional subschemes/stable pairs on
$0^+$
-stable quasimaps with one-dimensional subschemes/stable pairs on
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
relative to the divisor
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
relative to the divisor
![]() $S_{0,1,\infty } \subset S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
. In the notation introduced in Equations (1.4) and (3.1), we therefore obtain
$S_{0,1,\infty } \subset S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
. In the notation introduced in Equations (1.4) and (3.1), we therefore obtain
 $$ \begin{align} \begin{split} Q^{0^+}_{0,3}(S^{[n]}, \beta)&\cong \mathrm{Hilb}^{0^+}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times C_{0,3}) =\mathrm{Hilb}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times \mathbb{P}^1/S_{0,1, \infty}),\\ Q^{0^+}_{0,3}(S^{[n]}, \beta)^\sharp&\cong \mathrm{P}^{0^+}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times C_{0,3}) =\mathrm{P}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times \mathbb{P}^1/S_{0,1, \infty}) \end{split} \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \begin{split} Q^{0^+}_{0,3}(S^{[n]}, \beta)&\cong \mathrm{Hilb}^{0^+}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times C_{0,3}) =\mathrm{Hilb}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times \mathbb{P}^1/S_{0,1, \infty}),\\ Q^{0^+}_{0,3}(S^{[n]}, \beta)^\sharp&\cong \mathrm{P}^{0^+}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times C_{0,3}) =\mathrm{P}_{n,\check{\beta}}(S\times \mathbb{P}^1/S_{0,1, \infty}) \end{split} \end{align} $$
such that relative insertions correspond to primary quasimap insertions. Moreover, by Corollary 3.8 and the string equation, the wall-crossing is trivial for primary invariants, if
![]() $(g,N)=(0,3)$
. We therefore obtain that
$(g,N)=(0,3)$
. We therefore obtain that
In light of the identification (4.1), we obtain the following result.
Corollary 4.1. We have
On one hand, the result above together with the PT/GW correspondence for
![]() $K3$
geometries of [Reference OberdieckObe21a, Theorem 1.2] confirm the conjecture proposed in [Reference OberdieckObe19, Conjecture 1]. The conjecture claimed that the relative GW theory of
$K3$
geometries of [Reference OberdieckObe21a, Theorem 1.2] confirm the conjecture proposed in [Reference OberdieckObe19, Conjecture 1]. The conjecture claimed that the relative GW theory of
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
and the genus-0 three-point GW theory of
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
and the genus-0 three-point GW theory of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
are equivalent after the change of variables
$S^{[n]}$
are equivalent after the change of variables
![]() $y=-e^{iu}$
. In fact, Corollary 4.1 is a more natural form of [Reference OberdieckObe19, Conjecture 1], as it asserts equality of invariants without any change of variables. On the other hand, Corollary 4.1 provides a DT/PT correspondence with relative insertions for
$y=-e^{iu}$
. In fact, Corollary 4.1 is a more natural form of [Reference OberdieckObe19, Conjecture 1], as it asserts equality of invariants without any change of variables. On the other hand, Corollary 4.1 provides a DT/PT correspondence with relative insertions for
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
. More generally, the results above can be restated for a relative geometry
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
. More generally, the results above can be restated for a relative geometry
such that
![]() $N>2$
. In this case, by the string equation, the wall-crossing is also trivial for primary insertions.
$N>2$
. In this case, by the string equation, the wall-crossing is also trivial for primary insertions.
4.2. Genus-1 invariants of
 $S^{[n]}$
and Igusa cusp form conjecture
$S^{[n]}$
and Igusa cusp form conjecture
In this section, we will consider perverse quasimaps. In this case,
![]() $0^+$
-stable quasimaps correspond to stable pairs. Let us firstly establish a relation between degrees
$0^+$
-stable quasimaps correspond to stable pairs. Let us firstly establish a relation between degrees
![]() $\beta $
of quasimaps and Chern characters
$\beta $
of quasimaps and Chern characters
![]() $\check {\beta }$
of the associated stable pairs.
$\check {\beta }$
of the associated stable pairs.
Firstly, the homology
![]() $H_2(S^{[n]},{\mathbb {Z}})$
admits a Nakajima basis
$H_2(S^{[n]},{\mathbb {Z}})$
admits a Nakajima basis
 $$ \begin{align*} H_2(S,{\mathbb{Z}}) \oplus {\mathbb{Z}} &\xrightarrow{\sim} H_2(S^{[n]},{\mathbb{Z}}), \\ (\gamma, k) &\mapsto C_{\gamma}+kA, \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} H_2(S,{\mathbb{Z}}) \oplus {\mathbb{Z}} &\xrightarrow{\sim} H_2(S^{[n]},{\mathbb{Z}}), \\ (\gamma, k) &\mapsto C_{\gamma}+kA, \end{align*} $$
where the classes above are defined in terms of Nakajima operators as follows:
We refer to [Reference OberdieckObe18a, Section 1] for the notation and the definition of Nakajima operators in the similar context. In more geometric terms, if a class
![]() $\gamma $
is represented by a curve
$\gamma $
is represented by a curve
![]() $\Gamma \subset S$
, then the class
$\Gamma \subset S$
, then the class
![]() $C_\gamma $
is represented by the curve
$C_\gamma $
is represented by the curve
![]() $\Gamma _n \subset S^{[n]}$
which is given by letting one point move along
$\Gamma _n \subset S^{[n]}$
which is given by letting one point move along
![]() $\Gamma $
and keeping
$\Gamma $
and keeping
![]() $n-1$
other distinct points fixed. The class A is given by the locus of length-2 nonreduced structures on a fixed point
$n-1$
other distinct points fixed. The class A is given by the locus of length-2 nonreduced structures on a fixed point
![]() $p\in S$
, keeping other
$p\in S$
, keeping other
![]() $n-2$
reduced points fixed.
$n-2$
reduced points fixed.
Given now a quasimap
![]() $f \colon C \rightarrow \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}^{\sharp }(S,\mathbf {v})$
. By [Reference NesterovNes21, Corollary 6.8], the objects associated to such quasimaps are stable pairs on
$f \colon C \rightarrow \mathfrak {Coh}_{r}^{\sharp }(S,\mathbf {v})$
. By [Reference NesterovNes21, Corollary 6.8], the objects associated to such quasimaps are stable pairs on
![]() $S\times C$
, hence the class
$S\times C$
, hence the class
![]() $-\check {\beta }$
is of the following form
$-\check {\beta }$
is of the following form
where the negative sign amounts to considering Chern characters of subschemes rather than their ideals. For simplicity we will denote a class
![]() $-\check {\beta }$
just by
$-\check {\beta }$
just by
![]() $(\gamma , k)$
. The decomposition above and the one given by Nakajima basis are related. If we consider a map
$(\gamma , k)$
. The decomposition above and the one given by Nakajima basis are related. If we consider a map
![]() $f \colon C \rightarrow S^{[n]}$
of degree
$f \colon C \rightarrow S^{[n]}$
of degree
![]() $\beta $
(in the sense of quasimaps) such that
$\beta $
(in the sense of quasimaps) such that
![]() $-\check {\beta }=(\gamma , k)$
, then by [Reference OberdieckObe18a, Lemma 2] we have
$-\check {\beta }=(\gamma , k)$
, then by [Reference OberdieckObe18a, Lemma 2] we have
Hence, from now on, we will write degrees of quasimaps
![]() $\beta $
in terms of
$\beta $
in terms of
![]() $-\check {\beta }$
, which by Equation (4.3) also corresponds to writing degrees in terms Nakajima basis in the case
$-\check {\beta }$
, which by Equation (4.3) also corresponds to writing degrees in terms Nakajima basis in the case
![]() $\epsilon =\infty $
.
$\epsilon =\infty $
.
Consider now a generic projective
![]() $K3$
surface S with of Picard rank 1 such that
$K3$
surface S with of Picard rank 1 such that
By the previous discussion and [Reference NesterovNes21, Corollary 6.8], we have the following identification of moduli spaces
As before, the superscript on the moduli space on the left indicates that we consider maps up to translations of E. For the same reason, we take the quotient by E on the left. On the other hand,
Consider now the following two generating series,
 $$ \begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}(p,q,\tilde{q})&:=\sum_{n\geq0}\sum_{h\geq0}\sum_{k\in {\mathbb{Z}}}(-p)^{k}q^{h-1}\tilde{q}^{n-1} \langle \emptyset \rangle^{S^{[n]},0^+}_{E,(\beta_{h},k)},\\ \mathsf{GW}(p,q,\tilde{q})&:=\sum_{n>0}\sum_{h\geq0}\sum_{k\geq0} (-p)^{k}q^{h-1}\tilde{q}^{n-1}\langle \emptyset \rangle^{S^{[n]},\infty}_{E,(\beta_{h},k)}. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}(p,q,\tilde{q})&:=\sum_{n\geq0}\sum_{h\geq0}\sum_{k\in {\mathbb{Z}}}(-p)^{k}q^{h-1}\tilde{q}^{n-1} \langle \emptyset \rangle^{S^{[n]},0^+}_{E,(\beta_{h},k)},\\ \mathsf{GW}(p,q,\tilde{q})&:=\sum_{n>0}\sum_{h\geq0}\sum_{k\geq0} (-p)^{k}q^{h-1}\tilde{q}^{n-1}\langle \emptyset \rangle^{S^{[n]},\infty}_{E,(\beta_{h},k)}. \end{align*} $$
The series are well defined because
![]() $(S,\beta )$
and
$(S,\beta )$
and
![]() $(S',\beta ')$
are deformation equivalent, if and only if
$(S',\beta ')$
are deformation equivalent, if and only if
where
![]() $\mathrm {div}(\beta )$
is the divisibility of the class. In our case, the classes
$\mathrm {div}(\beta )$
is the divisibility of the class. In our case, the classes
![]() $\beta _{h}$
are primitive by definition. In [Reference Oberdieck and ShenOS20] and [Reference Oberdieck and PixtonOP18], it was proved that
$\beta _{h}$
are primitive by definition. In [Reference Oberdieck and ShenOS20] and [Reference Oberdieck and PixtonOP18], it was proved that
where
![]() $\chi _{10}(p,q,\tilde {q})$
is the Igusa cusp form, we refer to [Reference Oberdieck and PixtonOP18, Section 0.2] for its definition. We can view both series as generating series of quasimaps for
$\chi _{10}(p,q,\tilde {q})$
is the Igusa cusp form, we refer to [Reference Oberdieck and PixtonOP18, Section 0.2] for its definition. We can view both series as generating series of quasimaps for
![]() $\epsilon \in \{0^+,\infty \}$
. Using Corollary 3.11, we obtain
$\epsilon \in \{0^+,\infty \}$
. Using Corollary 3.11, we obtain
The wall-crossing invariants
![]() $\mu ^{n,\sharp }_{(\beta _{h},k)}$
are equal to virtual Euler characteristics of Quot schemes, as it is explained in [Reference OberdieckObe21b]. In the same article, wall-crossing invariants are also explicitly computed for
$\mu ^{n,\sharp }_{(\beta _{h},k)}$
are equal to virtual Euler characteristics of Quot schemes, as it is explained in [Reference OberdieckObe21b]. In the same article, wall-crossing invariants are also explicitly computed for
![]() $S^{[n]}$
(see [Reference OberdieckObe21b, Theorem 1.2]),
$S^{[n]}$
(see [Reference OberdieckObe21b, Theorem 1.2]),
 $$\begin{align*}\sum_{n\geq0}\sum_{h\geq0}\sum_{k\in {\mathbb{Z}}} (-p)^{k}q^{h-1}\tilde{q}^{n-1} \mu^{n,\sharp}_{(\beta_{h},k)} \chi(S^{[n]})=\frac{1}{\Theta^2\Delta}\frac{1}{\tilde{q}}\prod_{n\geq1}\frac{1}{(1-(\tilde{q} G)^n)^{24}},\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\sum_{n\geq0}\sum_{h\geq0}\sum_{k\in {\mathbb{Z}}} (-p)^{k}q^{h-1}\tilde{q}^{n-1} \mu^{n,\sharp}_{(\beta_{h},k)} \chi(S^{[n]})=\frac{1}{\Theta^2\Delta}\frac{1}{\tilde{q}}\prod_{n\geq1}\frac{1}{(1-(\tilde{q} G)^n)^{24}},\end{align*}$$
where
 $$ \begin{align*} \Theta(p,q)&=(p^{1/2}-p^{1/2})\prod_{m\geq1} \frac{(1-pq^m)(1-p^{-1}q^m)}{(1-q^m)^2} ,\\ G(p,q)&=-\Theta(p,q)^2 \left(p\frac{d}{dp}\right)^2\log(\Theta(p,q)), \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \Theta(p,q)&=(p^{1/2}-p^{1/2})\prod_{m\geq1} \frac{(1-pq^m)(1-p^{-1}q^m)}{(1-q^m)^2} ,\\ G(p,q)&=-\Theta(p,q)^2 \left(p\frac{d}{dp}\right)^2\log(\Theta(p,q)), \end{align*} $$
and
![]() $\Delta (q)=q\prod _{n\geq 1}(1-q^n)^{24}.$
We therefore obtain the following corollary, which confirms the first equality in [Reference Oberdieck and PandharipandeOP16, Conjecture A].
$\Delta (q)=q\prod _{n\geq 1}(1-q^n)^{24}.$
We therefore obtain the following corollary, which confirms the first equality in [Reference Oberdieck and PandharipandeOP16, Conjecture A].
Corollary 4.2. We have
 $$\begin{align*}\mathsf{PT}(p,q,\tilde{q})=\mathsf{GW}(p,q,\tilde{q})+ \frac{1}{\Theta^2\Delta}\frac{1}{\tilde{q}}\prod_{n\geq1}\frac{1}{(1-(\tilde{q} G)^n)^{24}}.\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\mathsf{PT}(p,q,\tilde{q})=\mathsf{GW}(p,q,\tilde{q})+ \frac{1}{\Theta^2\Delta}\frac{1}{\tilde{q}}\prod_{n\geq1}\frac{1}{(1-(\tilde{q} G)^n)^{24}}.\end{align*}$$
As in the case of [Reference OberdieckObe19, Conjecture 1], the statement of [Reference Oberdieck and PandharipandeOP16, Conjecture A] involved the relative GW theory of
![]() $S\times E$
instead of the relative DT theory of
$S\times E$
instead of the relative DT theory of
![]() $S\times E$
. In light of our wall-crossing, the latter should be considered more natural in this context. Nevertheless, the two are equivalent by [Reference OberdieckObe21a].
$S\times E$
. In light of our wall-crossing, the latter should be considered more natural in this context. Nevertheless, the two are equivalent by [Reference OberdieckObe21a].
4.3. Higher-rank DT invariants
Under our assumptions, a moduli space
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
is deformation equivalent to a punctorial Hilbert scheme
$M(\mathbf {v})$
is deformation equivalent to a punctorial Hilbert scheme
![]() $S^{[n]}$
, where
$S^{[n]}$
, where
![]() $2n=\dim (M(\mathbf {v}))$
. Since we are working with reduced classes, in order to use the deformation invariance of GW theory, we have to deform
$2n=\dim (M(\mathbf {v}))$
. Since we are working with reduced classes, in order to use the deformation invariance of GW theory, we have to deform
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
together with a curve class
$M(\mathbf {v})$
together with a curve class
![]() $\beta $
. In this case, we might need to deform
$\beta $
. In this case, we might need to deform
![]() $(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
to a Hilbert scheme of points
$(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
to a Hilbert scheme of points
![]() $(S^{\prime [n]},\beta ')$
on another
$(S^{\prime [n]},\beta ')$
on another
![]() $K3$
surface
$K3$
surface
![]() $S'$
. We conclude that the reduced GW theory of
$S'$
. We conclude that the reduced GW theory of
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
in the class
$M(\mathbf {v})$
in the class
![]() $\beta $
is equivalent to the one of
$\beta $
is equivalent to the one of
![]() $S^{\prime [n]}$
in the class
$S^{\prime [n]}$
in the class
![]() $\beta '$
. Applying the quasimap wall-crossing both to
$\beta '$
. Applying the quasimap wall-crossing both to
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
and to
$M(\mathbf {v})$
and to
![]() $S^{\prime [n]}$
, we can therefore express higher-rank DT invariants of a threefold
$S^{\prime [n]}$
, we can therefore express higher-rank DT invariants of a threefold
![]() $S\times C$
in terms of rank-one DT invariants and wall-crossing invariants.
$S\times C$
in terms of rank-one DT invariants and wall-crossing invariants.
4.3.1.
 $K3\times \mathbb {P}^1$
$K3\times \mathbb {P}^1$
Let us firstly consider invariants on
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
relative to
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
relative to
![]() $S_{0,1,\infty }$
. As previously, by fixing the markings, we obtain
$S_{0,1,\infty }$
. As previously, by fixing the markings, we obtain
The
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}$
-valued points of
${\mathbb {C}}$
-valued points of
![]() $M_{\mathbf {v},\check \beta }(S\times \mathbb {P}^1/S_{0,1, \infty })$
are triples
$M_{\mathbf {v},\check \beta }(S\times \mathbb {P}^1/S_{0,1, \infty })$
are triples
![]() $(P,\{0,1,\infty \}, F)$
satisfying the same conditions as triples in Equation (3.2) such that:
$(P,\{0,1,\infty \}, F)$
satisfying the same conditions as triples in Equation (3.2) such that:
-
•
 $(P, \{0,1,\infty \})$
is a marked curve without rational tails,Footnote
4
whose smoothingFootnote
5
is
$(P, \{0,1,\infty \})$
is a marked curve without rational tails,Footnote
4
whose smoothingFootnote
5
is
 $(\mathbb {P}^1, \{0,1,\infty \})$
.
$(\mathbb {P}^1, \{0,1,\infty \})$
.
Moreover, as in the case of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
, there is no wall-crossing by Theorem 3.8 and the string equation, therefore
$S^{[n]}$
, there is no wall-crossing by Theorem 3.8 and the string equation, therefore
Choose a deformation of
![]() $(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
to
$(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
to
![]() $(S^{\prime [n]},\beta ')$
which keeps the curve class
$(S^{\prime [n]},\beta ')$
which keeps the curve class
![]() $\beta $
algebraic. The deformation gives an identification of cohomologies
$\beta $
algebraic. The deformation gives an identification of cohomologies
which we use to identify curve classes
![]() $\beta $
and
$\beta $
and
![]() $\beta '$
and insertions
$\beta '$
and insertions
![]() $\gamma _1,\dots , \gamma _N$
on both sides. With respect to this identification, we have
$\gamma _1,\dots , \gamma _N$
on both sides. With respect to this identification, we have
Passing from quasimaps to sheaves and using Equation 4.4, we obtain the following result.
Corollary 4.3. Given a deformation of
![]() $(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
to
$(M(\mathbf {v}),\beta )$
to
![]() $(S^{\prime [n]},\beta ')$
. Identifying cohomologies of
$(S^{\prime [n]},\beta ')$
. Identifying cohomologies of
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})$
and
$M(\mathbf {v})$
and
![]() $S^{\prime [n]}$
, we have
$S^{\prime [n]}$
, we have
4.3.2.
 $K3\times E$
$K3\times E$
Consider now
![]() $S\times E$
, where E is an elliptic curve. If
$S\times E$
, where E is an elliptic curve. If
![]() $M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[n]}$
, then invariants
$M(\mathbf {v})=S^{[n]}$
, then invariants ![]() from Corollary 3.9 are called rubber DT invariants on
from Corollary 3.9 are called rubber DT invariants on
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
. These are invariants associated to the moduli space of subschemes on
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
. These are invariants associated to the moduli space of subschemes on
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
relative to the divisor
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
relative to the divisor
![]() $S_{0,\infty }$
up to the
$S_{0,\infty }$
up to the
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}^{*}$
-action coming from
${\mathbb {C}}^{*}$
-action coming from
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
-factor which fixes
$\mathbb {P}^1$
-factor which fixes
![]() $0$
and
$0$
and
![]() $\infty $
,
$\infty $
,
These invariants can be rigidified to standard relative DT invariants with absolute insertions. In fact, this holds more generally for any
![]() $\mathbf {v}$
and also for genus-1 invariants
$\mathbf {v}$
and also for genus-1 invariants
![]() $\langle \emptyset \rangle ^{M(\mathbf {v}),0^+}_{E,\beta }$
.
$\langle \emptyset \rangle ^{M(\mathbf {v}),0^+}_{E,\beta }$
.
Lemma 4.4. We have

where
![]() $D \in H^2(S)$
,
$D \in H^2(S)$
,
![]() $\omega \in H^2(C)$
is the point class, and
$\omega \in H^2(C)$
is the point class, and
![]() $\check {\beta }_1 \in H^2(S)$
is the component of
$\check {\beta }_1 \in H^2(S)$
is the component of
![]() $\check {\beta }$
of cohomological degree 2.
$\check {\beta }$
of cohomological degree 2.
Proof. The proof is exactly the same as in [Reference Maulik and OblomkovMO09, Lemma 3.3]. For
![]() $S\times E$
, see also [Reference OberdieckObe18b, Section 3.4]
$S\times E$
, see also [Reference OberdieckObe18b, Section 3.4]
Applying the same procedure as for
![]() $S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
, using Corollary 3.9 and Lemma 4.4, we obtain the following result.
$S\times \mathbb {P}^1$
, using Corollary 3.9 and Lemma 4.4, we obtain the following result.
Corollary 4.5. We have

By degenerating
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1$
to
$\mathbb {P}^1$
to
![]() $\mathbb {P}^1 \cup \mathbb {P}^1$
, sending the interior marking and the relative marking to the first component and applying the degeneration formula, we obtain
$\mathbb {P}^1 \cup \mathbb {P}^1$
, sending the interior marking and the relative marking to the first component and applying the degeneration formula, we obtain
where we used the fact that a reduced class restricts to reduced and nonreduced classes on irreducible components, which implies that it vanishes, unless
![]() $\check {\beta }=0$
on one of the components. We refer to [Reference Maulik, Nekrasov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMNOP06, Section 3.4] (see also [Reference Li and WuLW15]) for the standard degeneration formula and to [Reference OberdieckObe21b, Section 5.1] for the reduced one.
$\check {\beta }=0$
on one of the components. We refer to [Reference Maulik, Nekrasov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMNOP06, Section 3.4] (see also [Reference Li and WuLW15]) for the standard degeneration formula and to [Reference OberdieckObe21b, Section 5.1] for the reduced one.
Similarly, by degenerating E to
![]() $E \cup \mathbb {P}^1$
, sending the interior marking to the second component, and applying the degeneration formula, we obtain
$E \cup \mathbb {P}^1$
, sending the interior marking to the second component, and applying the degeneration formula, we obtain
The second term on the right is the wall-crossing term. Hence, we obtain the following equality of DT invariants on
![]() $S\times E$
.
$S\times E$
.
Corollary 4.6. We have
Using the Igusa cusp form conjecture, we can obtain an explicit expression for these higher-rank relative DT invariants. Moreover, by [Reference NesterovNes21, Lemma 4.14], the higher-rank invariants associated to the moduli space
![]() $M_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S\times E)$
can be related to invariants associated to moduli spaces of sheaves with a fixed determinant, denoted by
$M_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S\times E)$
can be related to invariants associated to moduli spaces of sheaves with a fixed determinant, denoted by
![]() $\widetilde {M}_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S\times E)$
,
$\widetilde {M}_{\mathbf {v},\check {\beta }}(S\times E)$
,
 $$\begin{align*}\int_{[\widetilde{M}_{\mathbf{v},\check{\beta}}(S\times E)/E]^{\mathrm{red}}}1={\mathrm{rk}}(\mathbf{v})^2 \langle \emptyset \rangle^{M(\mathbf{v}),0^+}_{E,\beta},\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}\int_{[\widetilde{M}_{\mathbf{v},\check{\beta}}(S\times E)/E]^{\mathrm{red}}}1={\mathrm{rk}}(\mathbf{v})^2 \langle \emptyset \rangle^{M(\mathbf{v}),0^+}_{E,\beta},\end{align*}$$
while the stability of fibers can be related to the slope stability on the threefold by [Reference NesterovNes21, Corollary A.6].
A Reduced obstruction theory
Consider the reduced obstruction-theory complex
![]() ${\mathbb {E}}_{\mathrm {red}}^{\bullet }$
from Equation (3.5). In this section, under certain assumptions, we will construct the obstruction-theory morphism,
${\mathbb {E}}_{\mathrm {red}}^{\bullet }$
from Equation (3.5). In this section, under certain assumptions, we will construct the obstruction-theory morphism,
The proof closely follows [Reference Kool and ThomasKT18].
Proposition A.1. Given
![]() $({\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf {v}),\check {\beta }) \in \Lambda \oplus \Lambda (-1)$
. Assume a first-order deformation
$({\mathrm {ch}}(\mathbf {v}),\check {\beta }) \in \Lambda \oplus \Lambda (-1)$
. Assume a first-order deformation
![]() $\kappa _S \in HT^2(S)\cong HH^2(S)$
from Proposition 2.3 is represented by a
$\kappa _S \in HT^2(S)\cong HH^2(S)$
from Proposition 2.3 is represented by a
![]() ${\mathbb {C}}[\epsilon ]/\epsilon ^2$
-linear admissible subcategory,
${\mathbb {C}}[\epsilon ]/\epsilon ^2$
-linear admissible subcategory,
where
![]() ${\mathcal Y} \rightarrow B=\operatorname {Spec}{{\mathbb {C}}[\epsilon ]/\epsilon ^2}$
is flat. Then there exists an obstruction theory morphism,
${\mathcal Y} \rightarrow B=\operatorname {Spec}{{\mathbb {C}}[\epsilon ]/\epsilon ^2}$
is flat. Then there exists an obstruction theory morphism,
Proof. Firstly, by taking the central fiber, we get that
is an admissible subcategory, where Y is the central fiber of
![]() ${\mathcal Y}$
. Therefore, there is an isomorphism of moduli stacks
${\mathcal Y}$
. Therefore, there is an isomorphism of moduli stacks
where
![]() $\mathfrak {D}_{\mathrm {Coh}(S)}(Y)$
is the moduli stack of objects on Y which are contained in the subcategory
$\mathfrak {D}_{\mathrm {Coh}(S)}(Y)$
is the moduli stack of objects on Y which are contained in the subcategory
![]() $\mathrm {Coh}(S)\subseteq \mathrm {D_{perf}}(Y)$
. This also implies that moduli stacks of quasimaps associated to pairs
$\mathrm {Coh}(S)\subseteq \mathrm {D_{perf}}(Y)$
. This also implies that moduli stacks of quasimaps associated to pairs
![]() $(M(\mathbf {v}),\mathfrak {Coh}(S))$
and
$(M(\mathbf {v}),\mathfrak {Coh}(S))$
and
![]() $(M(\mathbf {v}),\mathfrak {D}_{\mathrm {Coh}(S)}(Y))$
are isomorphic,
$(M(\mathbf {v}),\mathfrak {D}_{\mathrm {Coh}(S)}(Y))$
are isomorphic,
Let
be the relative moduli spaces of objects which are associated to moduli spaces
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M,\mathfrak {Coh}(S),\beta )$
and
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M,\mathfrak {Coh}(S),\beta )$
and
![]() $Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M,\mathfrak {D}_{\mathrm {Coh}(S)}(Y),\beta )$
, defined as in [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 3.5].
$Q^{\epsilon }_{g,N}(M,\mathfrak {D}_{\mathrm {Coh}(S)}(Y),\beta )$
, defined as in [Reference NesterovNes21, Section 3.5].
Secondly, the inclusion
induces a map between the Hochschild cohomologies,
given by restricting the natural transformation of functors,
This map sends
![]() $\kappa _Y$
to
$\kappa _Y$
to
![]() $\kappa _S$
(see, e.g., [Reference PerryPer, Lemma 4.6]), where
$\kappa _S$
(see, e.g., [Reference PerryPer, Lemma 4.6]), where
![]() $\kappa _Y$
is the class associated to the deformation
$\kappa _Y$
is the class associated to the deformation
![]() ${\mathcal Y} \rightarrow B$
. Moreover, for a complex
${\mathcal Y} \rightarrow B$
. Moreover, for a complex
![]() $F \in \mathrm {D^{\mathrm {b}}}(S\times C)$
, the class
$F \in \mathrm {D^{\mathrm {b}}}(S\times C)$
, the class
which is given by applying the natural transformation associated to
![]() $\kappa \in HH^2(S)$
to F, is the obstruction to deform F in the direction of
$\kappa \in HH^2(S)$
to F, is the obstruction to deform F in the direction of
![]() $\kappa $
. By [Reference TodaTod09, Proposition 5.2] and [Reference CăldăraruCăl05], it agrees with obstruction class given by composing the Kodaira–Spencer class with the Atiyah class,
$\kappa $
. By [Reference TodaTod09, Proposition 5.2] and [Reference CăldăraruCăl05], it agrees with obstruction class given by composing the Kodaira–Spencer class with the Atiyah class,
after applying the HKR isomorphism,
We now identify a sheaf
![]() $F\in \mathrm {Coh}(S\times C)$
with its image in
$F\in \mathrm {Coh}(S\times C)$
with its image in
![]() $\mathrm {D_{perf}}(Y\times C)$
, then the following triangle commutes
$\mathrm {D_{perf}}(Y\times C)$
, then the following triangle commutes

Hence, by the choice of
![]() $\kappa _S$
, the deformation of sheaves in the class
$\kappa _S$
, the deformation of sheaves in the class
![]() $(\mathbf {v},\check {\beta })$
viewed as complexes on
$(\mathbf {v},\check {\beta })$
viewed as complexes on
![]() $Y\times C$
is obstructed in the direction of
$Y\times C$
is obstructed in the direction of
![]() $\kappa _{Y}$
because the obstruction class is nonzero by the construction of
$\kappa _{Y}$
because the obstruction class is nonzero by the construction of
![]() $\kappa _S$
.
$\kappa _S$
.
Now, we will closely follow [Reference Kool and ThomasKT18, Section 3.2]. By the above discussion the inclusion of the central fiber over B,
is an isomorphism. The obstruction complexes of
![]() $M_{Y}$
and
$M_{Y}$
and
![]() $M_{S}$
are isomorphic under the natural identifications of the moduli spaces,
$M_{S}$
are isomorphic under the natural identifications of the moduli spaces,
because both complexes can be defined just in terms of
![]() $\mathrm {D^b}(S)$
, where
$\mathrm {D^b}(S)$
, where
![]() ${\mathbb {F}}_{S/Y}$
are universal families of
${\mathbb {F}}_{S/Y}$
are universal families of
![]() $M_{S/Y}$
, and
$M_{S/Y}$
, and
![]() $\pi _{S/Y}$
are natural projections. Recall that we are interested in the trace-zero part
$\pi _{S/Y}$
are natural projections. Recall that we are interested in the trace-zero part
![]() $R{\mathcal H} om_{\pi _S}({\mathbb {F}}_S,{\mathbb {F}}_S)_{0}$
of
$R{\mathcal H} om_{\pi _S}({\mathbb {F}}_S,{\mathbb {F}}_S)_{0}$
of
![]() $R{\mathcal H} om_{\pi _S}({\mathbb {F}}_S,{\mathbb {F}}_S)$
, cf. Section 3.1.
$R{\mathcal H} om_{\pi _S}({\mathbb {F}}_S,{\mathbb {F}}_S)$
, cf. Section 3.1.
Claim. The composition
where the first map is given by identification (A.3) and the second is given by the Atiyah class on
![]() ${\mathcal Y} \times M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
, is a perfect obstruction theory.
${\mathcal Y} \times M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
, is a perfect obstruction theory.
Proof of claim.
For the proof of the claim, we plan to use the criteria from [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF97, Theorem 4.5]. For any B-scheme
![]() $Z_{0}$
, a B-map
$Z_{0}$
, a B-map
![]() $Z_{0} \rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
factors though the central fiber. Hence, the B-structure map
$Z_{0} \rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
factors though the central fiber. Hence, the B-structure map
![]() $Z_{0}\rightarrow B$
factors through the closed point of B. Let
$Z_{0}\rightarrow B$
factors through the closed point of B. Let
![]() ${\mathcal F}_0$
be the sheaf associated to the map
${\mathcal F}_0$
be the sheaf associated to the map
![]() $Z_{0} \rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
. The morphism
$Z_{0} \rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
. The morphism
is an obstruction theory. By [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF97, Theorem 4.5], to prove that Equation (A.4) is an obstruction theory, it suffices to prove that the image of a nonzero obstruction class
![]() $\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0}) \in \operatorname {Ext}^2_{Y\times Z_{0}}({\mathcal F}_{0},{\mathcal F}_{0} \otimes p_Y^*I) $
with respect to the map
$\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0}) \in \operatorname {Ext}^2_{Y\times Z_{0}}({\mathcal F}_{0},{\mathcal F}_{0} \otimes p_Y^*I) $
with respect to the map
is nonzero for any square-zero B-extension Z of
![]() $Z_0$
given by an ideal I, where
$Z_0$
given by an ideal I, where
![]() $p_Y\colon Y\times _{B} Z_{0}=Y \times Z_0 \rightarrow Z_{0}$
and
$p_Y\colon Y\times _{B} Z_{0}=Y \times Z_0 \rightarrow Z_{0}$
and
![]() $p_S\colon S\times Z_0 \rightarrow Z_{0}$
are the natural projections. Given a square-zero B-extension Z of
$p_S\colon S\times Z_0 \rightarrow Z_{0}$
are the natural projections. Given a square-zero B-extension Z of
![]() $Z_{0}$
, there are two possibilities:
$Z_{0}$
, there are two possibilities:
-
1. the B-structure map
 $Z\rightarrow B$
factors through the closed point;
$Z\rightarrow B$
factors through the closed point; -
2. the B-structure map
 $Z\rightarrow B$
does not factor through the closed point.
$Z\rightarrow B$
does not factor through the closed point.
We will deal with them separately.
1. In this case, the obstruction of lifting the map to
![]() $Z\rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
coincides with the obstruction of lifting the map to
$Z\rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
coincides with the obstruction of lifting the map to
![]() $Z\rightarrow M_Y\cong M_S$
; hence, if
$Z\rightarrow M_Y\cong M_S$
; hence, if
![]() $\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0})$
is nonzero, its image with respect to Equation (A.5) is nonzero.
$\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0})$
is nonzero, its image with respect to Equation (A.5) is nonzero.
2. In this case, a lift to
![]() $Z \rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
is always obstructed, and the obstruction is already present at a single fiber of
$Z \rightarrow M_{{\mathcal Y}/B}$
is always obstructed, and the obstruction is already present at a single fiber of
![]() $p_{Y}$
in the following sense. By assumption, there exists a section
$p_{Y}$
in the following sense. By assumption, there exists a section
![]() $B \rightarrow Z$
which is an immersion (we can find an open affine subscheme
$B \rightarrow Z$
which is an immersion (we can find an open affine subscheme
![]() $U\subset Z$
such that
$U\subset Z$
such that
![]() $U \rightarrow B$
is flat, but then
$U \rightarrow B$
is flat, but then
![]() $U\cong U_{0} \times B$
because first-order deformations of affine schemes are trivial, thereby we get a section). Let
$U\cong U_{0} \times B$
because first-order deformations of affine schemes are trivial, thereby we get a section). Let
![]() $z\in Z$
be image of the closed point of B of the section, then the restriction
$z\in Z$
be image of the closed point of B of the section, then the restriction
applied to the obstruction class
![]() $ \varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0})$
is nonzero and is the obstruction to lift the sheaf
$ \varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0})$
is nonzero and is the obstruction to lift the sheaf
![]() ${\mathcal F}_{0,z}$
on Y to a sheaf on
${\mathcal F}_{0,z}$
on Y to a sheaf on
![]() ${\mathcal Y}$
; hence, due to the following commutative diagram,
${\mathcal Y}$
; hence, due to the following commutative diagram,

we conclude that the image of
![]() $\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0})$
in
$\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0})$
in
![]() $\operatorname {Ext}^2_{S\times Z_{0}}({\mathcal F}_{0},{\mathcal F}_{0} \otimes p^*I)_{0}$
is nonzero because the image of
$\operatorname {Ext}^2_{S\times Z_{0}}({\mathcal F}_{0},{\mathcal F}_{0} \otimes p^*I)_{0}$
is nonzero because the image of
![]() $\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0,z})$
is nonzero in
$\varpi ({\mathcal F}_{0,z})$
is nonzero in
![]() $\operatorname {Ext}^2_{S\times z}( {\mathcal F}_{0,z},{\mathcal F}_{0,z}\otimes p^*I_{z})_{0}$
. This establishes claim.
$\operatorname {Ext}^2_{S\times z}( {\mathcal F}_{0,z},{\mathcal F}_{0,z}\otimes p^*I_{z})_{0}$
. This establishes claim.
The absolute perfect obstruction theory
![]() $({\mathbb {H}}^{\bullet })^{\vee }$
is then defined by taking the cone of
$({\mathbb {H}}^{\bullet })^{\vee }$
is then defined by taking the cone of
![]() $ ({\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet })^{\vee } \rightarrow \Omega _{B}[1]$
. Hence, we have the following diagram:
$ ({\mathbb {E}}^{\bullet })^{\vee } \rightarrow \Omega _{B}[1]$
. Hence, we have the following diagram:

By the same argument as in [Reference Kool and ThomasKT18, Section 2.3], the composition
is an isomorphism. This finishes the proof of the proposition.
For example, if
![]() $M=S^{[n]}$
and
$M=S^{[n]}$
and
![]() $\check {\beta }_1 \neq 0$
, that is, the curve class is not exceptional, we can use a commutative deformation given by the infinitesimal twistor family
$\check {\beta }_1 \neq 0$
, that is, the curve class is not exceptional, we can use a commutative deformation given by the infinitesimal twistor family
![]() ${\mathcal S}={\mathcal Y} \rightarrow B$
with respect to the class
${\mathcal S}={\mathcal Y} \rightarrow B$
with respect to the class
![]() $\check {\beta }_1$
. The situation becomes more complicated already in the case of
$\check {\beta }_1$
. The situation becomes more complicated already in the case of
![]() $S^{[n]}$
and
$S^{[n]}$
and
![]() $\check {\beta }_1 =0$
(i.e., an exceptional curve class). in this case, a commutative first-order deformation can no longer satisfy the property stated in Proposition 2.3. If
$\check {\beta }_1 =0$
(i.e., an exceptional curve class). in this case, a commutative first-order deformation can no longer satisfy the property stated in Proposition 2.3. If
![]() $n=2$
and
$n=2$
and
![]() $S^{[2]}$
is isomorphic to a Fano variety of lines of some special cubic fourfold (e.g., see [Reference HassettHas00, Theorem 1.0.3]), then
$S^{[2]}$
is isomorphic to a Fano variety of lines of some special cubic fourfold (e.g., see [Reference HassettHas00, Theorem 1.0.3]), then
and the family
![]() ${\mathcal Y}\rightarrow B$
is given by deformation of Y away from the Hassett divisor.
${\mathcal Y}\rightarrow B$
is given by deformation of Y away from the Hassett divisor.
Remark A.2. In [Reference TodaTod09], Toda constructed geometric realisations of infinitesimal noncommutative deformations in
![]() $HH^2(X)$
for a smooth projective X. However, it is not clear, if they are of the type required by Proposition A.1. In principle, there should be no problem in proving Proposition A.1, dropping the assumption. For that, one has to show that Toda’s infinitesimal deformations behave well under base change.
$HH^2(X)$
for a smooth projective X. However, it is not clear, if they are of the type required by Proposition A.1. In principle, there should be no problem in proving Proposition A.1, dropping the assumption. For that, one has to show that Toda’s infinitesimal deformations behave well under base change.
Acknowledgements
First and foremost, I would like to thank my advisor Georg Oberdieck. Not a single result of this work would be possible without his inexhaustible support and guidance. I am grateful to Daniel Huybrechts and Thorsten Beckmann for multiple discussions on related topics and for reading preliminary versions of the present work. My understanding of quasimaps has benefited greatly from discussions with Luca Battistella, and a great intellectual debt is owed to Yang Zhou for his theory of calibrated tails, without which the wall-crossings would not be possible. I also thank Mathematical Institute of University of Bonn for stimulating academic environment and excellent working conditions. Finally, I want to express words of gratitude to an anonymous referee for providing numerous comments which improved the exposition of results.
Competing interest
The authors have no competing interest to declare.